What Are The Causes And Complications Of Charcot Foot?
Charcot foot is a complication that occurs in individuals with peripheral neuropathy that involves an inflammatory process affecting the soft tissues of the ankle or foot, bones, and joints. Peripheral neuropathy is a condition characterized by a loss of sensation in the feet from incurred nerve damage in the feet and lower legs. Charcot foot occurs in three stages. Fragmentation and destruction is the first stage and is characterized by small bone fractures, soft tissue swelling, and complete joint destruction. Coalescence, the second stage, is where the body attempts to heal the first stage damage where the bone and joint destruction slows down. Reconstruction is the third stage where the bones and joints of the foot heal themselves up, but not back to their original shape or condition. No further damage is incurred to the foot, but it is left in a weak and deformed state.
Several factors cause Charcot foot, and it can cause long-term complications. Learn about this now.
Rocker Bottom Deformity
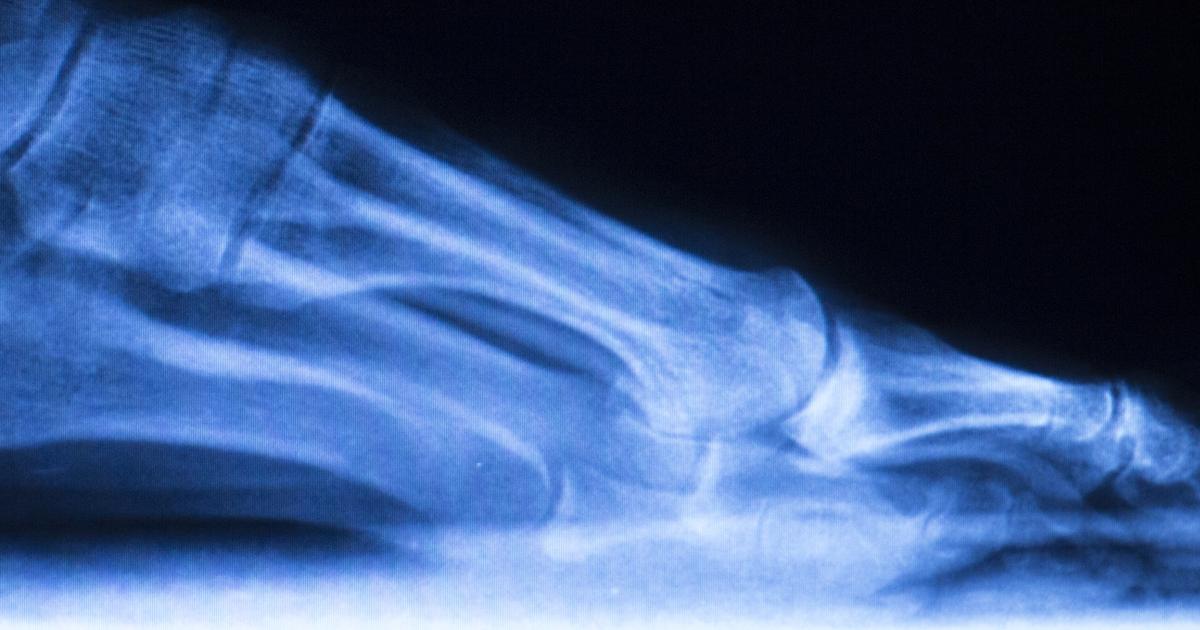
Rocker bottom deformity is a common complication that occurs in individuals affected by Charcot foot. This deformity is best characterized by a very pronounced heel bone, and a bulging rounded bottom of the patient's foot. As the joints in the ankle and foot of a Charcot foot patient start to weaken, the joints can become dislocated or collapse entirely. The bones can become fractured without the affected individual knowing about it since their peripheral neuropathy has caused them to have diminished sensation of trauma, pain, and temperature in their foot. The patient keeps walking on the foot and using it like normal, causing the deformity and disorder to progress. The arch of the affected individual's foot caves in, causing it to collapse down under the level of which it would be flattened. This process creates an appearance similar to the leg of a rocking chair. Most individuals who have rocker bottom deformity precipitated from Charcot foot will need surgery to correct the deformity.
Read more about the causes and complications of Charcot foot now.
Spinal Cord Injury Or Disease
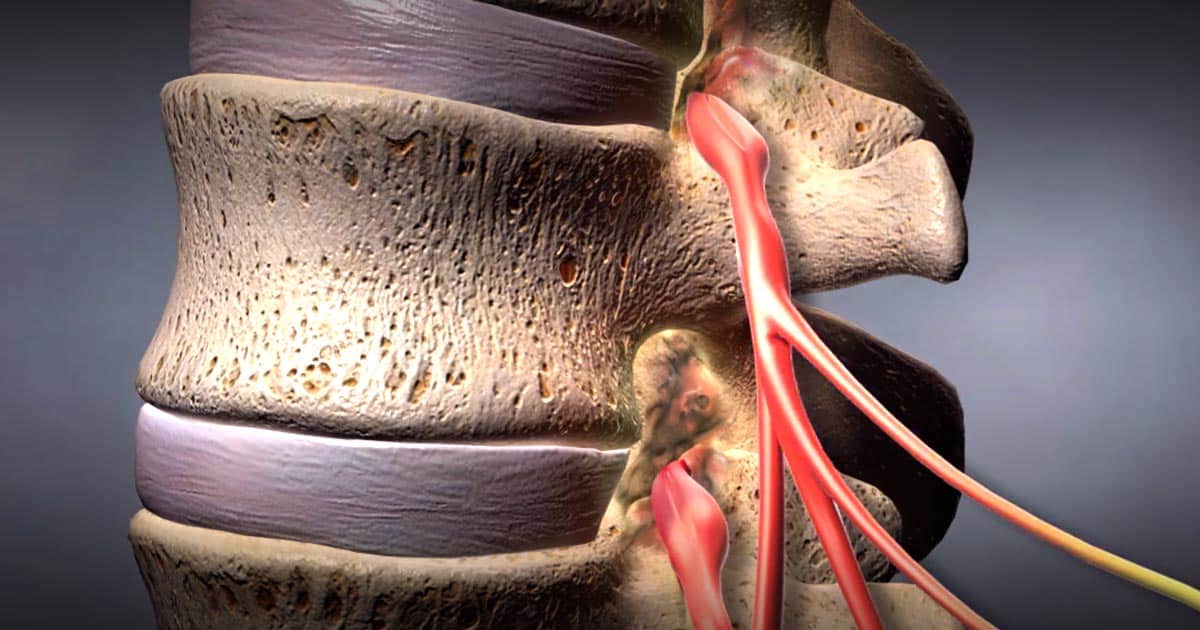
Charcot foot can occur when an individual is affected by a spinal cord injury or disease. The spinal cord is a cluster of nerves that runs from the brain all the way down the vertebral column past the pelvic bone. Most spinal cord injuries are caused by accidents involving motor vehicles, violence, falls, and sports. A sudden blow to the back that causes the vertebrae or discs to become dislocated can tear or bruise the spinal cord. This process causes many of the nerves to become crushed. When the nerves are compressed, they cannot function to send signals to their designated region of the body. When the nerves that supply sensation to the lower leg and foot are affected by a spinal cord injury, Charcot foot can develop. Multiple diseases that adversely affect the spinal cord can cause damage to the nerves, as well as spinal disc degeneration, chronic spinal cord inflammatory conditions, neurodegenerative diseases, arthritis, infections of the spinal cord, and cancerous tumors in and around the spine can all result in the development of Charcot foot.
Continue reading to learn more about Charcot foot causes and complications now.
Incorrectly Treated Broken Foot Or Ankle

An individual can develop Charcot foot when they have an incorrectly treated broken foot or ankle. When an individual injures their foot or ankle and suspects a bone could be broken or fractured, they typically go to a provider for medical diagnosis. Bone breaks and fractures can be detected by diagnostic imaging tests such as a bone scan, CT scan, MRI, and x-rays. Depending on the severity and location of the break or fracture, the patient may require surgery to realign the bone. With or without surgery, the affected individual will be placed in a cast for immobilization for at least six weeks to allow the bone to grow back together. However, some patients who become injured in the foot or ankle mistake a break for a minor sprain or strain, or they are not aware of the injury at all. This situation can happen in individuals who have nerve problems that compromise the pain sensation in their foot. Instead of getting proper treatment for the break or fracture, the patient continues walking and standing on the foot and ankle. Bone fractures and breaks are common in individuals who have sensation loss in the foot and ankle because their neuropathy causes balance issues and immobility that stimulate changes in the balance of bone production and breakdown. This imbalance causes bone loss and weakness, increasing the risk of suffering a fracture.
Uncover more details on Charcot foot complications and causes now.
Infections
Infections can be the cause of an individual's peripheral neuropathy that results in the development of Charcot foot. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that can spread to an individual's central nervous system when it is left untreated for several years. This infection results in an inflammatory response that causes the patient to develop numbness in some regions of the body. When this occurs in the individual's feet and ankle, Charcot foot can develop.
Another infection called poliomyelitis is caused by a virus that adversely affects the function of the central nervous system, resulting in peripheral paralyzation. When an individual is paralyzed in the ankle and foot due to polio, they can develop Charcot foot. HIV can also cause a patient to experience neuropathy in their extremities that can result in Charcot foot. Other infectious diseases that can cause Charcot foot include Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis C, rabies, herpes, brucellosis, leprosy, Lyme disease, hepatitis B, cytomegalovirus, and shingles. Patients affected by Charcot foot may also develop an unnoticed ulcer on the foot that can easily become infected as a complication of their disorder.
Discover additional complications of Charcot foot now.
Unsteady And Twisted Ankle
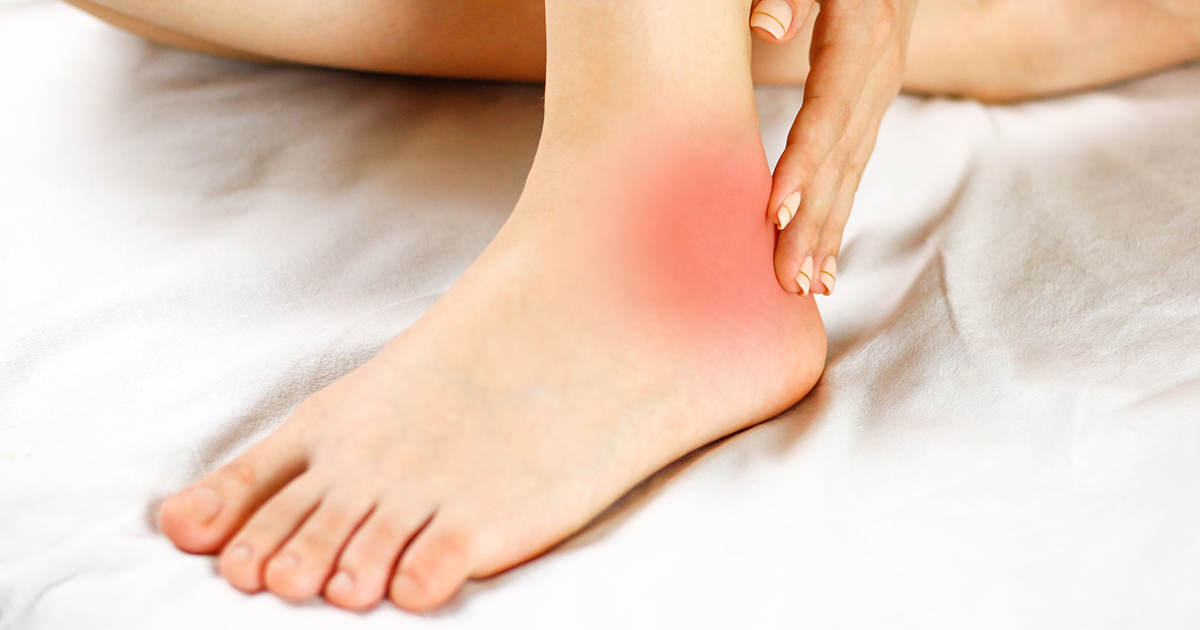
Individuals affected by Charcot foot often experience an unsteady and twisted ankle as a result of their disorder. A twisted ankle can also trigger the development of Charcot foot in some cases. In addition, the ankle joint can pop out of place or dislocate, allowing the foot to twist into an abnormal position without the patient noticing. Charcot foot is characterized by the weakness and breakdown of the joints in an individual's ankle and foot. As the joints become deformed, the foot will become weakened and cause problems with the patient's balance. The issues with balance cause the individual to place stress on bones and muscles that do not typically experience stress. This mechanism results in further weakness and instability of the foot and ankle as the disorder progresses. Instability can cause the foot to fit inappropriately in footwear that results in ulceration, making it difficult to fit a custom brace or footwear to the foot to help treat the disorder. Without any other effective option for treatment, patients with an unstable joint will require surgery to re-stabilize the foot or ankle.