Causes Of Metabolic Acidosis
When most individuals think of acid, they probably envision painful burning and discomfort. However, acid can do a lot of good for our bodies. Take amino acids, the 'building blocks' of protein, or stomach acid, which breaks down food and helps the body digest more easily. But when the body produces too much acid, a condition known as metabolic acidosis occurs. Metabolic acidosis refers to a build-up of acid in the body that disrupts the natural pH balance and causes painful symptoms. Here are details on the main causes of metabolic acidosis, including brief tips on treatment options available to patients.
Lactic Acidosis

The most common cause of lactic acidosis is intense exercise. When individuals perform a rigorous physical activity like running, their body produces an acid called lactate. Typically, the body breaks down glucose for oxygen during exercise, but when there isn't enough, lactic acid is produced. A build-up of lactic acid in the bloodstream will result in lactic acidosis.
There are other less-common but serious potential causes such as renal failure, liver problems, certain types of cancer, and heart disease. A fruity scent on the breath, jaundice, and rapid breathing may indicate a medical emergency. Individuals who suspect they might have a lactate build-up should seek help right away. Without treatment, this type of acidosis can be life-threatening.
Keep reading for more information on what can cause metabolic acidosis now.
Ketoacidosis
Individuals with diabetes must stay on top of their blood sugar levels. Failure to treat diabetes can result in many life-threatening conditions like ketoacidosis and metabolic acidosis. Blood acids called ketones accumulate in the bloodstream when the body can't make enough insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas, and its job is to help balance blood glucose.
Without enough insulin, the body begins to break down fats for fuel. This process produces ketones, and too many of them can lead to a life-threatening acidosis. Symptoms include excessive thirst and urination, nausea and vomiting, weakness, confusion, and a fruity smell on the breath.
Diabetes patients can check their ketone levels with a urine test at home to make sure they don't have a build-up. Frequently monitoring blood sugar is a strong preventative measure. Adjusting insulin levels as needed can help prevent ketoacidosis and metabolic acidosis, but if patients experience any acute symptoms, they should seek emergency care.
Reveal more on metabolic acidosis causes now.
Hyperchloremic Acidosis
Bicarbonate is a byproduct regulated by the kidneys. When individuals breathe, their blood brings bicarbonate to their lungs and exhaling releases the carbon dioxide. The kidneys also excrete and reabsorb bicarbonate, which influences the blood's acid levels.
When the bicarbonate concentration drops in an individual's bloodstream, there may also be an increase in plasma chloride. Blood chloride is called hyperchloremia, and it helps stabilize the body's acid-base balance. While there aren't always strong symptoms, some individuals will experience acute bouts of serious diarrhea and vomiting. This is caused by gastrointestinal loss of bicarbonate.
The imbalance between bicarbonate and chloride can result in acidosis. Typically, individuals with hyperchloremic acidosis suffer from kidney disease. Doctors will run tests to pinpoint the cause of a patient's hyperchloremic acidosis. This condition is usually treated with rehydration therapies.
Uncover more on the causes of metabolic acidosis.
Renal Tubular Acidosis

The body flushes acid out of its system through urination. When the kidneys malfunction or do not acidify urine enough, pH levels change. The acid increase caused by kidney dysfunction is called renal tubular acidosis.
Renal tubular acidosis is an ongoing problem for people with kidney disease. There are four types of renal tubular acidosis, and each one is diagnosed based on the location of the kidney malfunction. For example, type 1 is called classical distal renal tubular acidosis. The anatomical term 'distal' means distant, which means the defect in kidney function is far from the place where fluid enters the tube that collects waste to turn into urine.
Symptoms of renal tubular acidosis include fatigue, confusion, impaired growth in children and softening of the bones. Treatment is imperative, especially among younger patients, as it can lead to delayed growth and other developmental issues. Treatment involves restoring the body's pH balance through alkali therapy.
Get the details on the next cause of metabolic acidosis now.
Kidney Failure
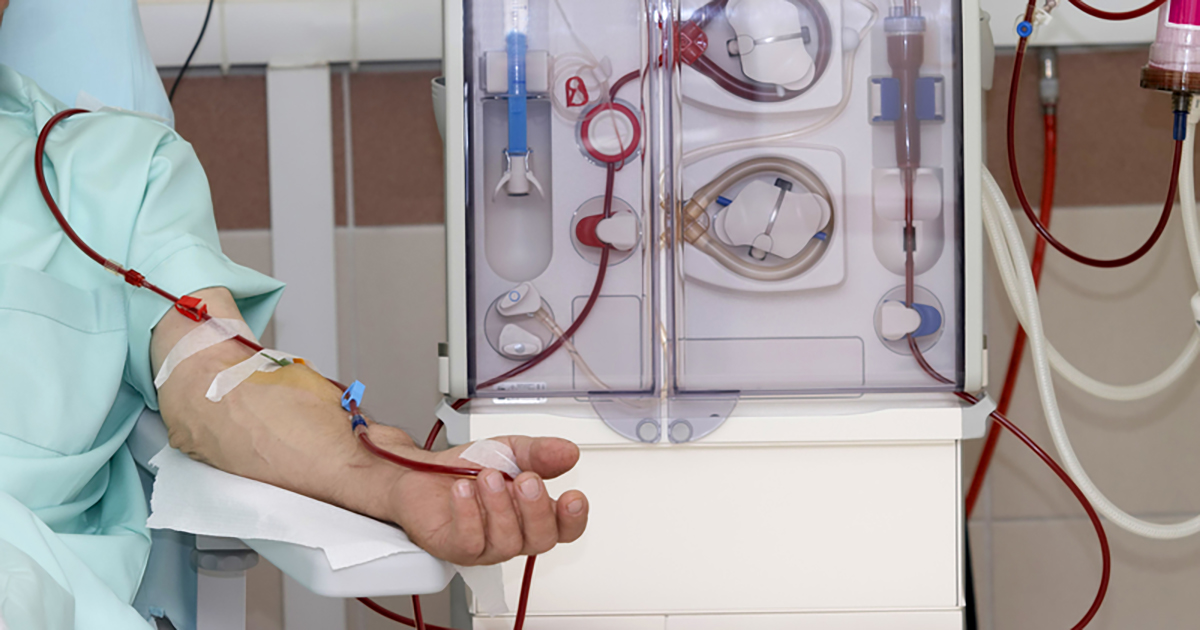
The kidneys play a large role in balancing the body's acid levels by removing waste from the blood. Individuals who are in kidney (renal) failure require dialysis, a treatment that performs the kidneys' tasks. Standard dialysis treatment is three times per week, but some patients need to go every day.
Without dialysis, individuals with kidney disease and renal failure will experience a build-up of acid in their bloodstream (metabolic acidosis). Doctors may also prescribe sodium bicarbonate or sodium citrate pills to treat metabolic acidosis brought on by renal failure. Not everyone experiences symptoms, but those who do might experience a rapid heartbeat, trouble breathing, vomiting, a loss of appetite, confusion, and extreme fatigue.