What Can Cause Respiratory Acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition resulting from the lungs being unable to properly remove as much carbon dioxide as they're supposed to. When too much of the carbon dioxide produced by the body remains inside of the lungs, certain bodily fluids, as well as the pH of blood, will reduce substantially, which causes the blood to become acidic. Patients will begin to suffer from respiratory acidosis when their blood's pH dips below 7.40. The lungs are supposed to bring in oxygen while at the same time removing the carbon dioxide produced by the body. If the lungs are unable to get rid of enough carbon dioxide, it's likely the individual's respiratory rate or the movement of air in the lungs has worsened. Before treatment can begin, it's important to identify the cause so the appropriate method can be selected. Learn about the various causes of respiratory acidosis now.
Acute Pulmonary Edema

Many of the causes on this list lead to the development of respiratory acidosis because they adversely affect the lungs' ability to properly remove carbon dioxide. Any condition or disease that affects an individual's breathing can also heighten their risk of respiratory acidosis. A common cause of this condition is acute pulmonary edema, which occurs when there's an excess amount of fluid in the lungs. This fluid develops within the various air sacs located around the lungs, which is what causes the breathing issues and makes it very difficult for the lungs to remove carbon dioxide, which is a problem that will eventually lead to respiratory acidosis. This can result from serious infections, heart problems, and trauma to the chest wall. Getting early treatment for acute pulmonary edema will substantially lessen an individual's risk of suffering from a severe health problem. The symptoms associated with acute pulmonary edema include irregular heartbeat, wheezing, anxiety, feelings of suffocation, and severe shortness of breath.
Uncover the next cause of respiratory acidosis now.
Scoliosis

Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine has a sideways curvature. The most common reason for this condition to develop is because of puberty and the growth spurt that occurs with it. However, it's also possible for such conditions as muscular dystrophy and cerebral palsy to bring about scoliosis. The vast majority of cases involving an odd curvature of the spine are considered mild, which means patients will have nothing to worry about and should be able to continue leading a normal life. It's when the issue becomes severe that it can lessen the amount of space available in the chest, which also causes problems with how the lungs function. If the effects are large enough, it's possible for respiratory acidosis to occur. The symptoms of scoliosis individuals should look out for include uneven shoulders, an uneven waist, imbalanced hips, and issues with the balance of their shoulder blades. If the curvature of their spine worsens because of this condition, one side of their ribs may stick out more than the other.
Learn more about the various causes of respiratory acidosis now.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that can adversely affect the optic nerves within the eyes, spinal cord, and brain. The effects on the spinal cord are the ones that will usually lead to the development of respiratory acidosis unless these effects are treated quickly. When an individual is diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, they may experience issues with balance, muscle control, vision, and a variety of additional body functions. This disease is brought about by the patient's immune system attacking a material in their body known as myelin. This material is meant to provide protection for the nerve fibers in the body. When it's attacked by the immune system, the nerves will invariably become damaged. Multiple sclerosis occurs in different stages, the most common of which is relapsing-remitting. If the patient's spinal cord becomes inflamed because of multiple sclerosis, respiratory acidosis can occur.
Get the details on the next potential cause of respiratory acidosis now.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
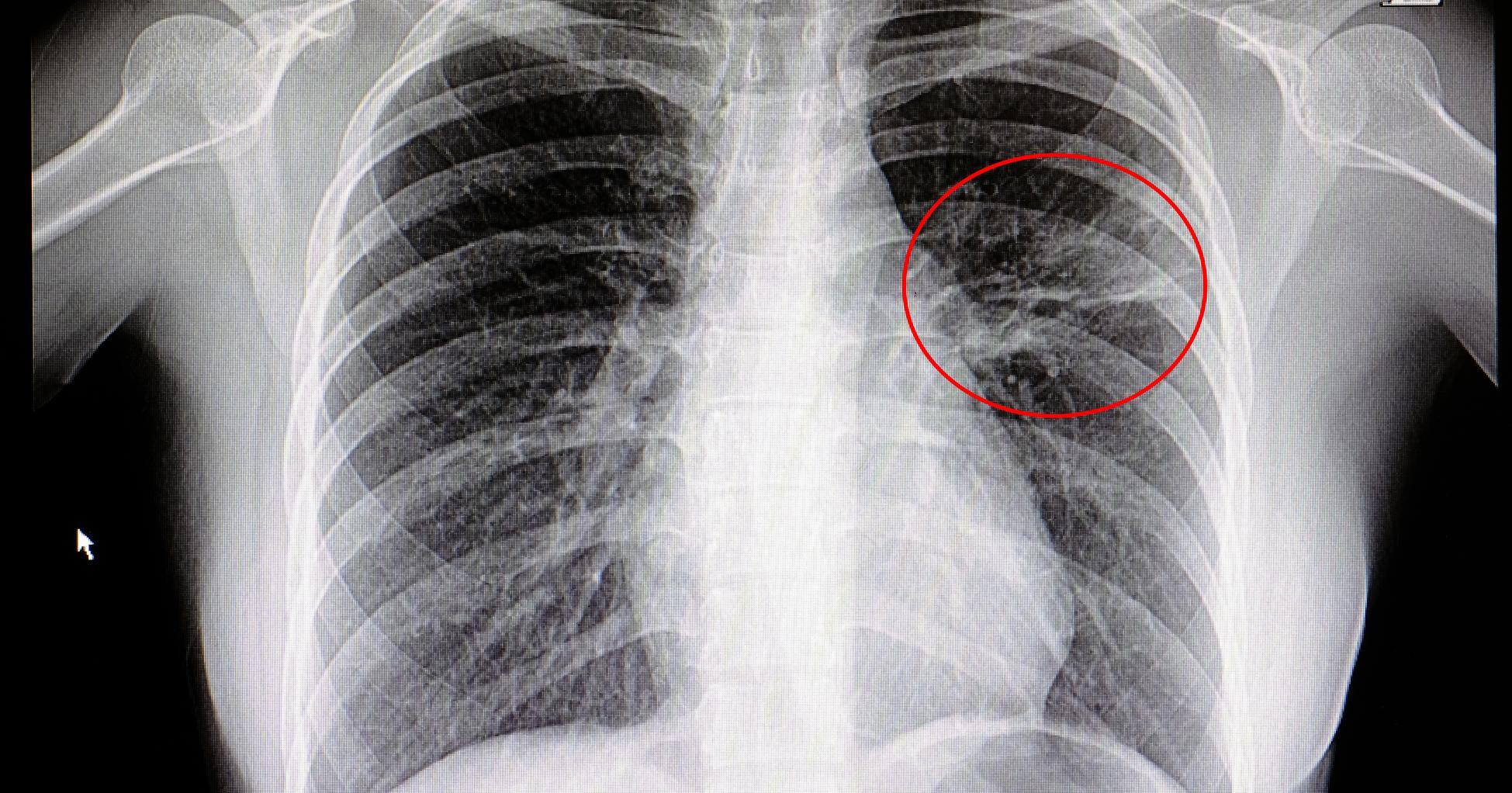
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a type of long-term lung disease. If it is not treated early, it can result in irreversible damage. Individuals suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can experience both emphysema and bronchitis, both of which block airflow in different ways and can make it difficult to breathe. The main symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are shortness of breath and an ongoing cough that produces mucus. The severity of this condition depends on which stage a patient has been diagnosed with. There are four stages in total, which are simply numbered one to four and worsen in severity. It's only when the condition hits stage two that patients will notice any symptoms. Their coughing will become constant and they will have trouble breathing and sleeping. Receiving treatment early on will lessen symptoms. Once this disease reaches stage two, it's possible for respiratory acidosis to occur.
Continue for more information on the causes of respiratory acidosis now.
Pneumonia

Pneumonia is a serious condition that causes inflammation in some of the air sacs throughout the lungs. When these air sacs are inflamed, they can become filled with liquid, and when this occurs, patients will have difficulty breathing and will likely cough regularly. Any combination of harmful fungi, bacteria, and viruses can cause pneumonia. While it's possible for the infection to be mild, there's a chance it can be life-threatening, which is especially common among infants and older adults. Aside from coughing and shortness of breath, symptoms of pneumonia include fever, chest pain when breathing, fatigue, and severe nausea. An individual's chances of developing respiratory acidosis when they also have pneumonia increase, as does the severity of respiratory acidosis should it occur. Most cases of pneumonia will dissipate with cough medicine, antibiotics, and pain relievers, along with sufficient rest.