Common Symptoms Of Mastocytosis
Mastocytosis is a condition where an affected individual has an accumulation of mast cells in their organs that may include the liver, skin, spleen, small intestine, and bone marrow. Mastocytosis that only affects the skin is called cutaneous mastocytosis, and mastocytosis that affects more than one organ is called systemic mastocytosis. Systemic mastocytosis is more common among adults, whereas cutaneous mastocytosis is more commonly found in children. This condition is caused by a spontaneous gene mutation in the KIT gene that has usually not been inherited from a family member. However, rare cases of mastocytosis may be the result of an inherited genetic mutation. Diagnosis is determined through the use of skin biopsy, bone marrow biopsy, blood test, urine tests, bone scan, genetic testing, and or gastrointestinal evaluations. Treatment for mastocytosis is highly dependent on which parts of the individual's body are having symptoms.
Get familiar with the major symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Itching

Individuals affected by mastocytosis may have excessive itching of the skin. Pruritis, itchy skin that stimulates the affected individual to itch, is caused by the production of a cytokine called Interleukin-31 or IL-31. Th2 cells, macrophages, dendric cells, and mast cells are all responsible for the production of IL-31. The overproduction and accumulation of mast cells cause the overproduction of IL-31. Increased numbers of IL-31 result in sensory nerve cell activation in the skin and surrounding tissues. The nerve cells become hyperactive when the IL-31 receptors on them become activated by signals precipitated from high levels of IL-31. Once activated, the sensory nerves send signals to the brain that cause the individual to feel an itchy sensation in their skin. Specific areas of mast cell concentration commonly appear in the form of lesions that can be very itchy. Skin contact with certain substances and ingestion of certain foods and drugs can cause an affected individual to experience a worse sensation of itchiness.
Keep reading to learn more about the symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Cramps In The Belly
An individual experiencing cramps in the belly along with other characteristic symptoms may be affected by mastocytosis. Gastrointestinal manifestations, like cramps in the belly, are the most common symptoms seen in cases of mastocytosis, second only to pruritis. The abdominal cramping that occurs in affected individuals can be caused by the infiltration of mast cells into the mucosal tissues of the digestive tract. This infiltration results in damage to the cells that make up these tissues, which results in malabsorption. Malabsorption causes diarrhea and provides a rich source of undigested food for the gut flora to consume and thrive on. Bacterial overgrowth in the intestine as a result of mast cell damage precipitated malabsorption may occur in some cases. Infiltration of mast cells into the affected individual's liver can cause them to be unable to digest fats, causing abdominal cramps associated with steatorrhea.
Uncover more information regarding the warning signs of mastocytosis now.
Facial Flushing
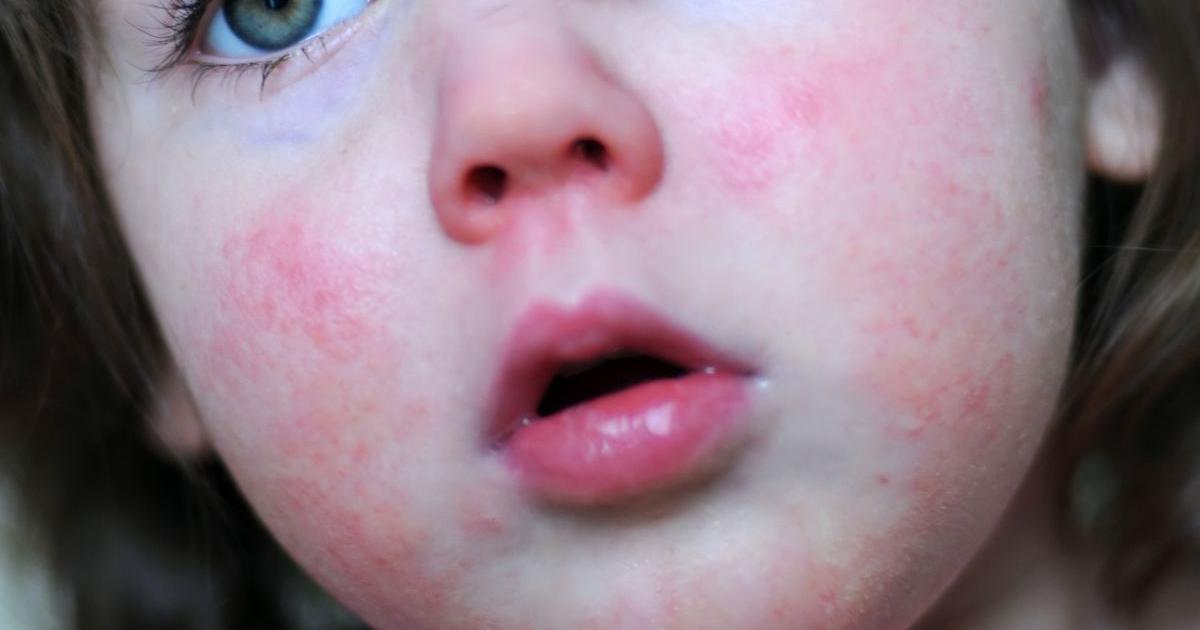
Facial flushing is a symptom of mastocytosis that occurs at some point in the majority of individuals affected by the condition. Facial flushing in systemic mastocytosis has been described as a bright red coloring of the face with sensations of itchiness and burning. This flushing often occurs alongside gastrointestinal symptoms that are also the result of systemic mastocytosis. Facial flushing in affected individuals tends to occur abruptly and quickly. Reddish-brown bumps have occurred as a feature of the facial flushing. Mastocytosis causes increased immune sensitivity to certain antigens and triggers that induce a release of histamine by excess mast cells in the affected individual's facial tissues. This produces a type of episode or allergic-like attack on the face, where histamine and other immune components cause a significant dilation of the blood vessels in the skin. The vessel dilation, histamine release, and congregation of other immune system components in the area are all implicated in giving the face a reddish appearance with burning and itching sensations.
Read more about common symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Lightheadedness

Mastocytosis is characterized by mast cell accumulation in different tissues around the body. Mast cells are certain migrant cells of an individual's immune system that feature granules of heparin and histamine. Mast cells are responsible for the regulation of blood vessel dilation, immune responses, vascular homeostasis, venom detoxification, and angiogenesis in the body. These cells have also been identified as playing a key role in the pathophysiology of asthma, gastrointestinal disorders, cardiovascular disease, allergies, anaphylaxis, and numerous types of malignancy. In a normal state, the lungs do not contain a large number of mast cell derivatives. When an antigen comes in contact with the respiratory tract lining, mast cell derivatives are summoned to the respiratory endothelium. Those affected by mastocytosis already have an excess amount of mast cells that may be concentrated in the lungs, exasperating the symptoms that occur upon their activation. Bronchial constriction and edema cause a decrease in lung capacity, which results in reduced blood oxygen concentration. Low oxygen concentrations in the blood cause deprivation of oxygen in the brain tissues that may result in lightheadedness. Hypotension from vasodilation has also been implicated as a cause of this symptom in mastocytosis.
Keep reading to learn more about the major symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Losing Consciousness
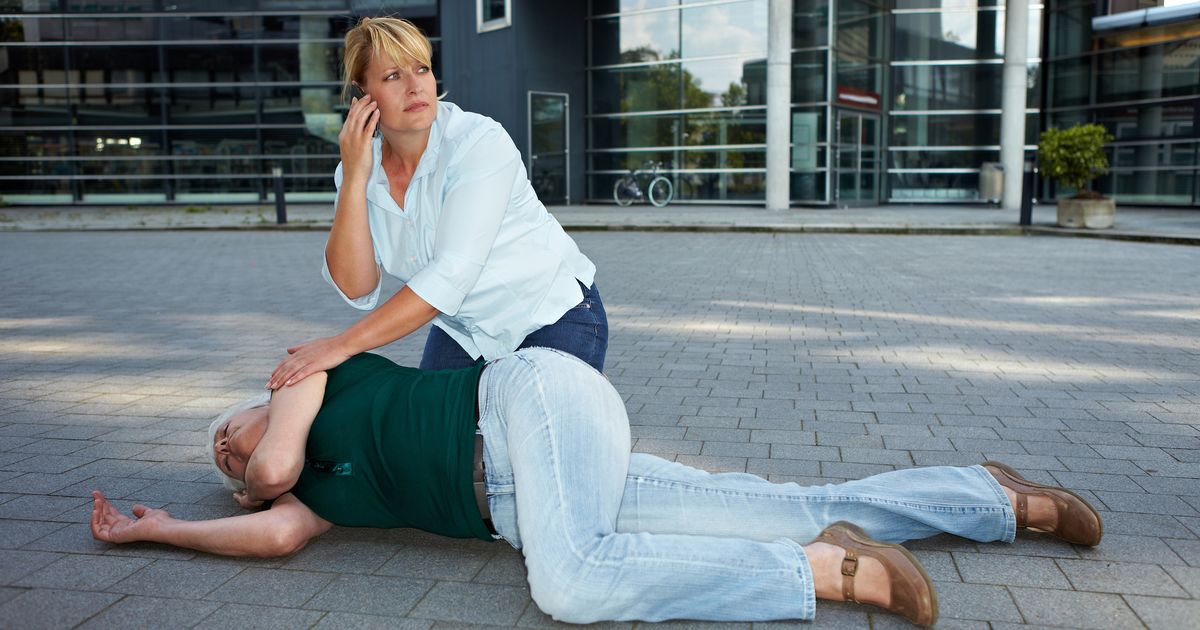

Fainting or loss of consciousness in affected individuals is the result of a sudden, dramatic decrease in their blood pressure. Low blood pressure causes a reduction in the amount of blood that reaches the tissues of the individual's brain. Poor blood flow to the brain causes a decrease in the amount of oxygen delivered to such tissues. Without oxygen, the brain tissues begin to shut down, causing the individual to faint or lose consciousness. The dramatic fall in blood pressure is attributed to the activation and degranulation of mast cells. The accumulated mast cells release histamine and activate other immune system components in the body that cause the blood vessels to become excessively dilated. This reaction occurs when the individual's tissues are triggered by some type of antigen, medication, or other endogenous factors like emotional anxiety, heat, or physical exertion. The reason the immune system induces vasodilation is to allow other immune cells and factors to diffuse through the vessel walls into the affected tissues faster and easier. The idea is for the body's natural pathogen fighting and damage mediating mechanisms to reach the site more efficiently. The most common triggers for fainting in individuals affected by mastocytosis are venom and certain medications.
Reveal more symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Anemia
Over ninety percent of adults affected by systemic mastocytosis develop lesions in their bone marrow. These lesions of mast cells cause the crowding out of other immature cells that are meant to grow into mature and functional red blood cells. Anemia is defined as a condition where an individual does not have enough functional red blood cells to meet the oxygen demands of their body. When some mechanism stops the bone marrow from producing an adequate amount of red blood cells, an individual will become anemic. Symptoms of anemia include pale skin color, loss of energy, pale skin, leg cramps, insomnia, problems with concentrating, breathlessness, headaches, rapid heartbeat, cold extremities, chest pain, and weakness. Other hematological abnormalities that can develop in mastocytosis patients can contribute to the loss of iron and other components in the blood due to excessive destruction and abnormal bleeding, which may also cause anemia to develop.
Continue for more details on the warning signs of mastocytosis now.
Nausea And Vomiting

Mast cells are responsible for causing symptoms in an individual's gastrointestinal system. These cells are critical immune system cells produced by the bone marrow that attack pathogens and release substances to eliminate any threat to the body. Mastocytosis patients experience higher levels of mast cells in their bodies than healthy individuals. Mast cells that detect an allergen release histamine, which causes swelling and redness of the affected area, producing inflammation. An individual who experiences inflammation of the nerves near the stomach and other digestive structures can experience nausea and vomiting as a result of the activation of the nausea center in the brain. Histamine is known to increase the production of gastric acid by the stomach, which can also cause nausea. Mast cell infiltration of the blood and digestive tract can result in hematological abnormalities. Some hematological abnormalities can make the patient prone to bleeding in their stomach and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Blood in the digestive tract serves as an irritant, and its presence can induce nausea and vomiting.
Discover additional symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Enlarged Spleen Or Liver
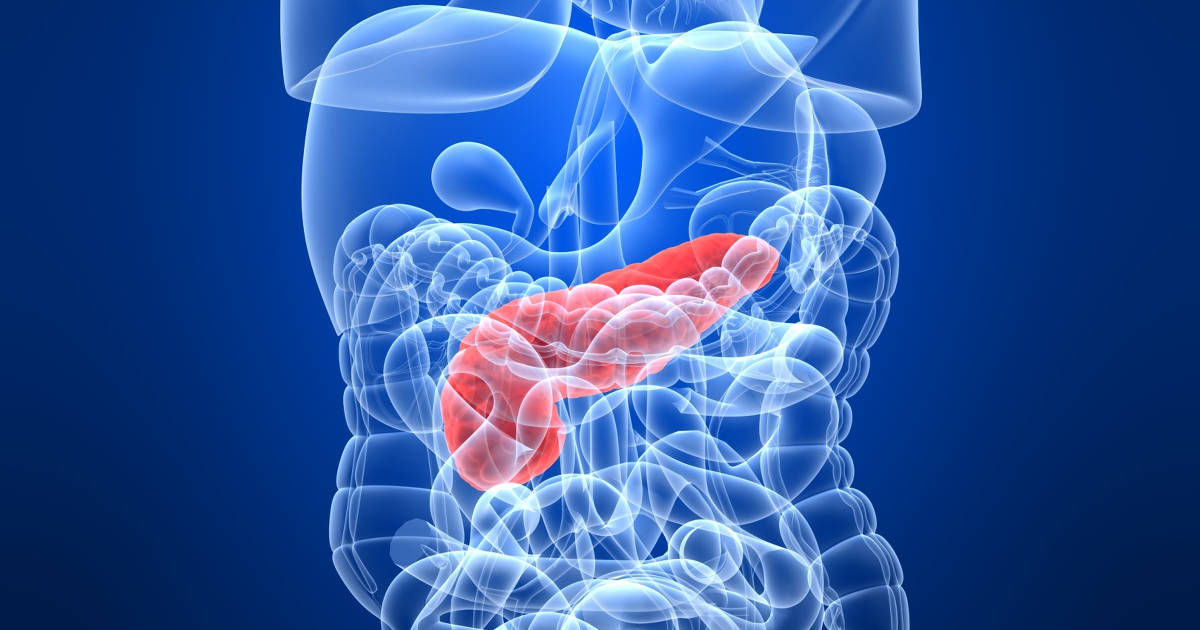
The liver is a large organ that helps clear toxins and waste products from the blood. The spleen is a lymphatic system organ that also serves to remove dead cell parts and wastes from the blood so they can be excreted in the stool and urine. Because mast cells are large cells, they can leave less room for components of the blood to circulate properly. This mechanism can produce portal hypertension, or an increased blood pressure level in the veins that make up the portal venous system. The portal venous system is the network of vessels that allow blood to flow throughout the liver. The accumulated mast cells in the blood can accumulate in the portal venous system as the liver tries to remove them from the blood. The spleen also becomes enlarged when it takes on a buildup of mast cells it is also trying to filter from the blood. Inflammation that occurs in the liver can cause the swelling of the spleen and vice versa because of their proximity to each other.
Uncover more details on mastocytosis symptoms now.
Diarrhea

Mastocytosis patients can experience an accumulation of mast cells in the mucosa of their digestive system. Individuals who have mastocytosis-precipitated diarrhea tend to have mast cell buildup in the small and large intestine where most of the nutrient and fluid absorption is meant to occur. The linings of the small and large intestines are specially formulated to provide a large amount of surface area to maximize the absorption of nutrients and fluids. When any mechanism interferes with the function of the intestinal linings physically and or chemically, these components of the consumed food are not absorbed. Mast cells that accumulate in the small intestine impair the ability to absorb nutrients, allowing the gut bacteria to digest and use the food for their benefit. This causes an overgrowth of the gut flora, which can produce inflammation and diarrhea. Mast cells that accumulate in the large intestine can interfere with its ability to absorb enough fluid from the digested food before it is eliminated from the body, which also causes diarrhea.
Learn more about the different symptoms indicative of mastocytosis now.
Anaphylaxis

Individuals affected by mastocytosis are more likely to have a severe allergic reaction because of the large number of mast cells in their bloodstream. When the mast cells are triggered by an allergen, they release large amounts of histamine in the patient's blood. This massive release of histamine is known to produce severe and life-threatening symptoms, including extremely itchy skin, abdominal pain, narrowing of the airways, wheezing, problems with breathing, dizziness, lightheadedness, swollen eyes, swollen lips, swollen feet, clammy skin, loss of consciousness, confusion, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, raised red rash, and swollen hands. Certain allergens are more common as triggers for anaphylactic episodes in mastocytosis patients. While food-related and drug-related reactions are less common, those caused by bee and wasp stings tend to be more prevalent.