What Are The Types Of Pneumoconiosis?
Pneumoconiosis is a disease of the lungs that results from exposure to certain dust particles. These particles typically consist of silica in rock and sand, asbestos fibers in roofing or insulation, cotton dust in textile manufacturing, beryllium, aluminum oxide, talc, cobalt, and coal dust from drilling into rock. Pneumoconiosis occurs when these dust particles enter an individual's airway and travel down into the lungs. Once the particles are in the sacs of the lungs, the individual's body attempts to fight them off. This process causes issues related to inflammation from the patient's immune system response. Pneumoconiosis is considered an occupational lung disease because in most cases the dust particles are typically found in the workplace. Although pneumoconiosis can be caused by a variety of substances, the symptoms are consistent throughout all types and they include breathlessness, phlegm-producing cough, and chest tightness.
Get familiar with the types of pneumoconiosis now.
Silicosis
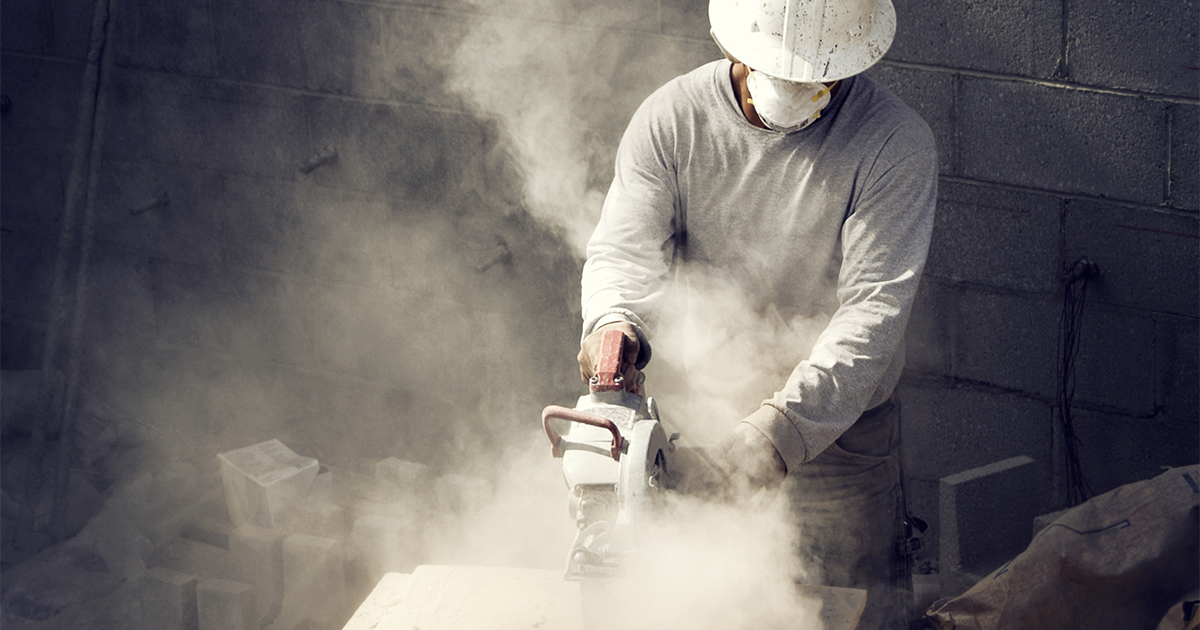

Silicosis is a type of pneumoconiosis that occurs when an individual inhales tiny silica particles or silicates. Silicosis most commonly occurs in individuals who have an occupation involving blasting or moving sand and rock or the use of sand and rock abrasives that contain silica. Generally, these occupations include quarry workers, sandblasters, foundry workers, ceramic workers, miners, stonecutters, glass makers, gemstone workers, and potters. Silicosis has also been found in individuals who install or manufacture countertops made of engineered silicates. Silicosis can develop after decades of exposure, or it can develop after severe exposure over several months. Both acute and chronic silicosis cannot be cured. The rate at which silicosis progresses can be predicted by how quickly a patient's symptoms worsen. Treatment of silicosis focuses on the management of debilitating symptoms and the effective prevention of dangerous complications such as mycobacterial diseases, lung cancer, and respiratory failure.
Uncover information on more types of pneumoconiosis now.
Asbestosis

Asbestosis is a form of pneumoconiosis caused by an individual's exposure to asbestos. A group of naturally occurring silicates, asbestos has shown to be useful in shipbuilding and construction materials, textiles, and automobile brakes because of its structural properties and resistance to heat. Three major types of asbestos are responsible for causing diseases such as asbestosis, and they include amosite, crocidolite, and a serpentine fiber called chrysotile. Individuals most commonly affected by asbestosis are those who have professions such as home remodelers, shipbuilders, construction workers, textile workers, asbestos abatement workers, and miners. Family members of workers who have been exposed to asbestos and who reside close to mines have also been commonly affected by asbestosis. One of the most concerning complications associated with asbestosis is the development of a type of lung cancer called non-small cell lung carcinoma. Treatment for asbestosis includes pulmonary rehabilitation, supplemental oxygen, early detection of lung cancer, and other forms of supportive care.
Read more about the various types of pneumoconiosis now.
Black Lung Disease
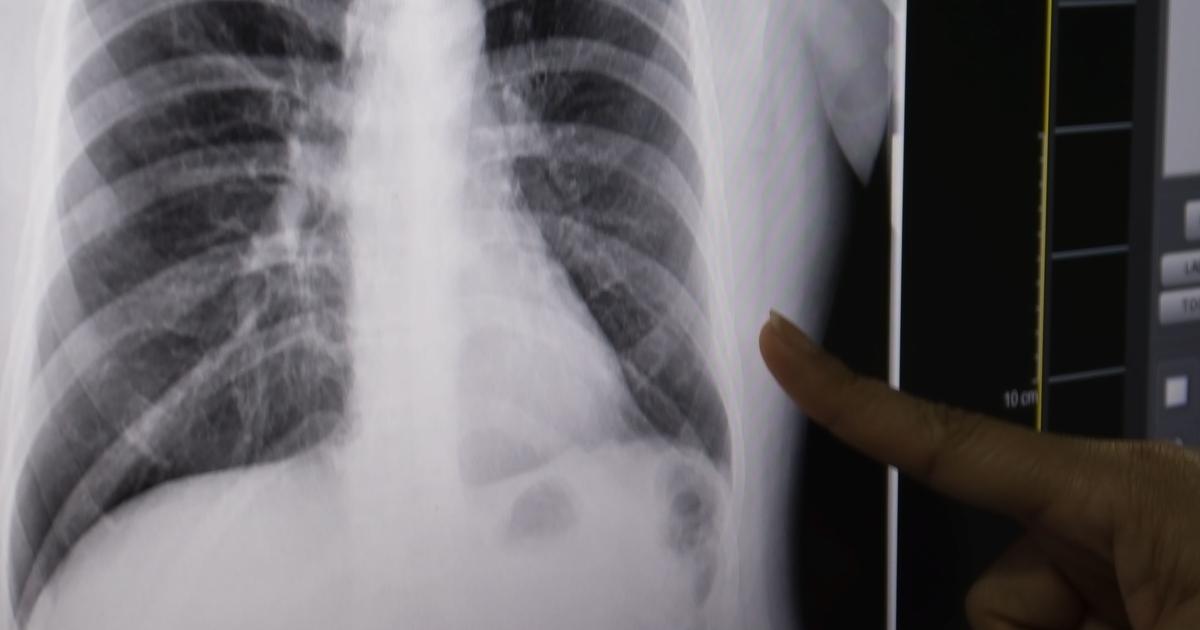
Black lung disease or CWP is a form of pneumoconiosis that occurs when an individual inhales graphite or coal dust for an extended period. Individuals who have occupations involving loading and stowing coal for storage, milling or mining graphite or coal, manufacturing of carbon black, and manufacturing of carbon electrodes are commonly affected by black lung disease. The lungs of these patients appear black rather than the pink coloring in healthy individuals. A coal macule or combination of macrophages and coal dust commonly develops in the lungs of those with black lung disease. These types of macules progress into coal nodules that are often large enough to stop or hinder the normal flow through the airways in the lungs. A common complication of black lung disease is cor pulmonale or right-sided heart failure. The right side of the heart is responsible for the pumping of blood into an individual's lungs. Because of the scarring and damage caused by black lung disease, the affected individual's heart has to work harder to pump blood through their impaired lungs. While no treatment has been effective for black lung disease, its complications can often be treated.
Learn more about what types of pneumoconiosis exist now.
Berylliosis

Berylliosis or beryllium disease is a type of pneumoconiosis that results from the inhalation of fumes or dust containing a substance called beryllium. Individuals who mine, extract, and transport beryllium for use in the manufacturing of fluorescent light bulbs, the electronics industry, and chemical industry are often affected by berylliosis. Individuals who have an occupation that includes the refining or casting of beryllium for use in the aerospace industry are also commonly affected. Berylliosis is one of the less common forms of pneumoconiosis because it only occurs in individuals who are sensitive to the substance. However, even the briefest exposure to beryllium dust can cause a beryllium-sensitive individual to develop berylliosis. Berylliosis can develop suddenly, or more commonly over an extended period. Berylliosis is a progressive disease that causes significant damage to a patient's lung structure and function. The heart of affected individuals often becomes overworked and strained, which results in right-sided heart failure or cor pulmonale. Treatment of berylliosis typically includes the use of corticosteroids, supplemental oxygen, pulmonary rehabilitation, heart failure medications, and lung transplantation in severe cases.
Uncover more details on the types of pneumoconiosis now.
Siderosis
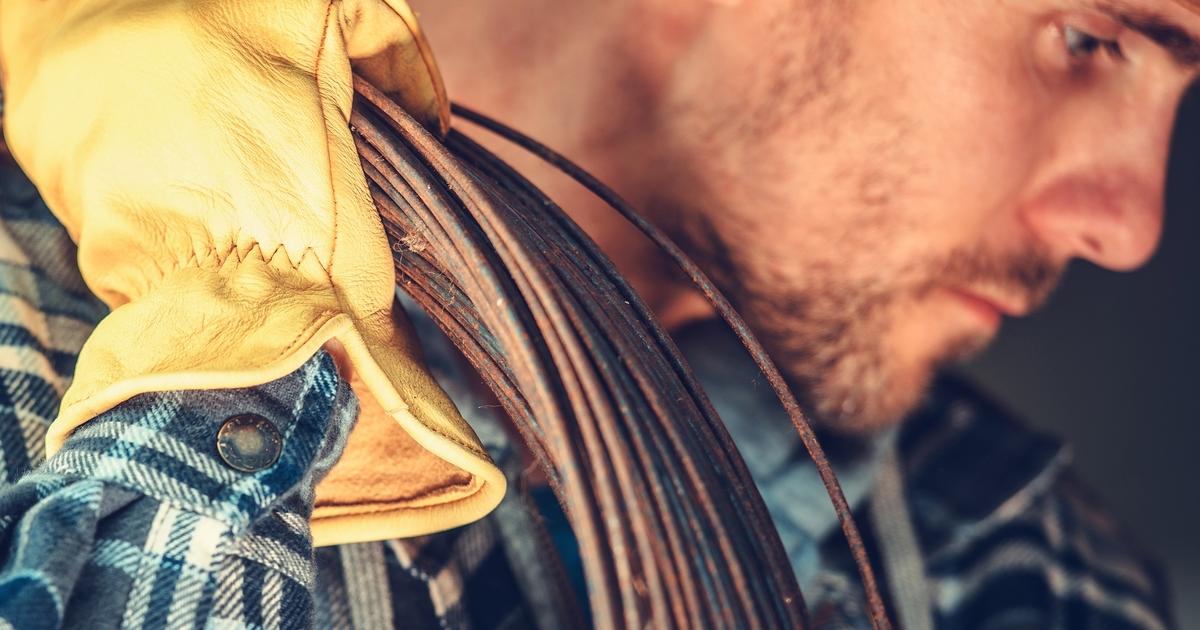

Siderosis is a variation of pneumoconiosis that occurs due to the prolonged inhalation of iron fumes or iron dust particles. Individuals who work in occupations involving iron rolling, metal sheet working, soldering, welding, steel rolling, mining, metal polishing, and steelmaking are commonly affected by this condition. Most individuals affected by siderosis do not develop symptoms for several years after the exposure to iron particles. Some patients develop severe scarring of the lung tissues. A concerning complication that occurs as a result of siderosis is lung cancer, particularly in individuals who work in welding. Because there is no cure for siderosis, any lung damage it has caused is permanent. While most cases of siderosis occur in individuals who are simultaneously exposed to other types of dust like silica, exposure to iron particles alone has caused siderosis to develop in some individuals. Treatment of siderosis is mild supportive care, unlike other types of pneumoconiosis because severe cases of siderosis are uncommon.