What Causes Myositis?
Myositis is a term referring to inflammation in the muscles that move the body. The condition can be caused by a number of different factors including infection, injury, or autoimmune disease. Though there are several different types of myositis, the condition tends to present with muscle weakness. Patients may also trip or fall unexpectedly, have trouble with breathing or swallowing, or experience fatigue after standing or walking. Diagnosis is done through a physical examination, lab testing, imaging, and finally a biopsy of the muscle. Myositis-related diseases have no cure, but the symptoms are treatable. Doctors typically recommend corticosteroids, medications, exercise, rest, assistive devices, and physical therapy. The exact treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause.
Reveal these causes now.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma, otherwise known as systemic sclerosis, is a disease of the connective tissue. It is chronic and falls under the autoimmune rheumatic category of diseases. The name of the illness comes from Greek words that translate to 'hard skin.' The most visible way the disease manifests is through physical hardening of a patient's skin. Systemic sclerosis varies widely in symptoms and progression from patient to patient. While it was previously believed to be a progressive disease, further research indicates not every case is progressive. As a chronic illness, scleroderma has the potential to be very serious. Some patients experience only mild effects, while others have life-threatening impairments. Mild cases have been known to progress to a greater severity when not treated. Myositis can be a symptom of this condition due to the ways the muscles and connective tissue interact.
Keep reading to learn more about the causes of myositis now.
Viral Infections

Any infection can cause myositis, but viral infections are significantly more likely to cause the disease. While fungal and bacterial infections have been the cause in past cases, these are rare experiences experts consider the exception to the rule. Viruses can sometimes invade the muscle tissue directly, damaging the muscles and leading to painful inflammation. Bacteria operates in much the same way. Even when a virus doesn't physically invade the muscles, it can still cause myositis. The virus releases substances that cause damage to muscle fibers, which in turn leads to inflammation. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can cause myositis as just one of many symptoms as it attacks the body. Untreated HIV patients are also more vulnerable to inflammation and infection because of a weakened immune system. The flu and common cold are also capable of causing myositis. The effects of myositis tend to be more unpleasant than the original flu and cold symptoms.
Uncover more potential causes of myositis now.
Rheumatoid Arthritis

There's strong evidence indicating rheumatoid arthritis can cause myositis. It's also likely that other autoimmune diseases could cause myositis. As the immune system floods the body with inflammation, both the joints and muscles are affected. The phenomenon has been dubbed 'rheumatoid myositis,' and though there isn't a lot of published research, the link between autoimmune inflammatory responses and myositis is too compelling to ignore.
Researchers have tried to ascertain the unique presentation and progression of rheumatoid myositis, as opposed to other forms of myositis. They've gathered information from rheumatoid arthritis patients who also have rheumatoid myositis. In one study, every patient with these conditions also had inflammatory deposits present. This implies the same autoimmune cause of rheumatoid arthritis is also behind rheumatoid myositis. It's not yet clear whether every rheumatoid arthritis patient with inflammatory deposits will develop rheumatoid myositis, but the connection makes a lot of sense. Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by an autoimmune inflammation of the joints and other tissues, while rheumatoid myositis is caused by an autoimmune inflammation of the muscles. The only difference is the type of tissue targeted.
Get the details on more myositis causes now.
Rhabdomyolysis

Rhabdomyolysis is a serious condition that stems from an indirect or direct muscle injury. When the muscle is injured, the muscle fibers die. Instead of healing like an injury is meant to, the dead fibers release their contents into a patient's bloodstream. In serious cases, the sudden flood of toxicity can lead to kidney failure. From there, if a patient doesn't receive emergency medical treatment, they could die. With that said, the outcome tends to be positive for patients who receive timely medical care. The syndrome is difficult to categorize in terms of symptoms, because there's no telling what parts of the body will be affected. It's most common for patients to experience muscle pain in their lower back, thighs, or shoulders, since the dead muscle fibers are causing inflammation. They may also experience impaired mobility and muscle weakness, along with brown or dark red urine.
Learn more about the causes of myositis now.
Dermatomyositis
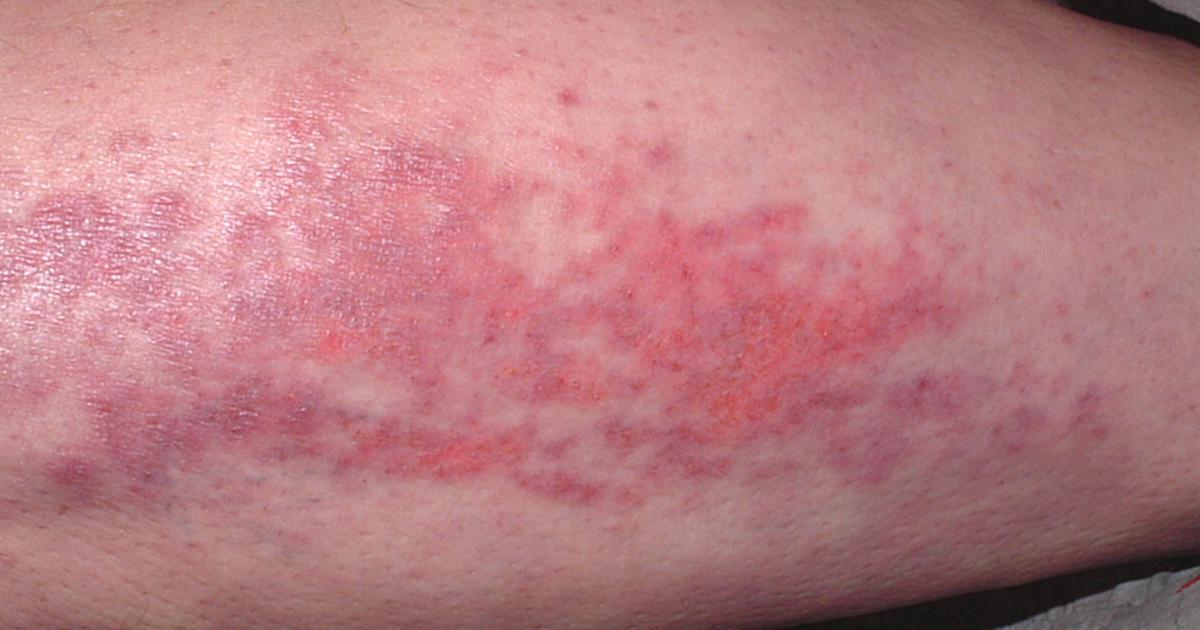
Dermatomyositis is one of the two best-known kinds of myositis. It's categorized as an inflammatory myopathy, meaning it causes inflammation of the muscles. The disease includes chronic muscle inflammation, hence why 'myositis' is present in the name. In addition, patients experience muscle weakness. The condition is best known for the skin rash that comes directly before or during periods of muscle weakness. The condition can occur in any gender or age, but most commonly presents in adults between forty-five and sixty-five years old. It also commonly occurs in children between five and fifteen years old. Dermatomyositis is chronic and does not have a cure, but there are multiple treatment options available for symptoms.