What Causes Swollen Lymph Nodes?
The lymphatic system is the part of the body that circulates lymphatic fluid. The lymph nodes are glands that act as the filtration system for this part of the body. They also store white blood cells, which are an important portion of the immune system that kill invading pathogens. When individuals have a tumor or an infection, the lymph nodes become swollen. When abnormal or diseased cells, bacteria, and viruses pass through the lymphatic system, the lymph nodes stop them from being circulated to other parts of the body. If the body is fighting an illness or infection, the lymph nodes catch debris. There are lymph nodes above the collarbone, on either side of the neck, on either side of the groin, under the jaw, and in the armpits.
Get familiar with the conditions and other issues that can cause swollen lymph nodes now.
Measles
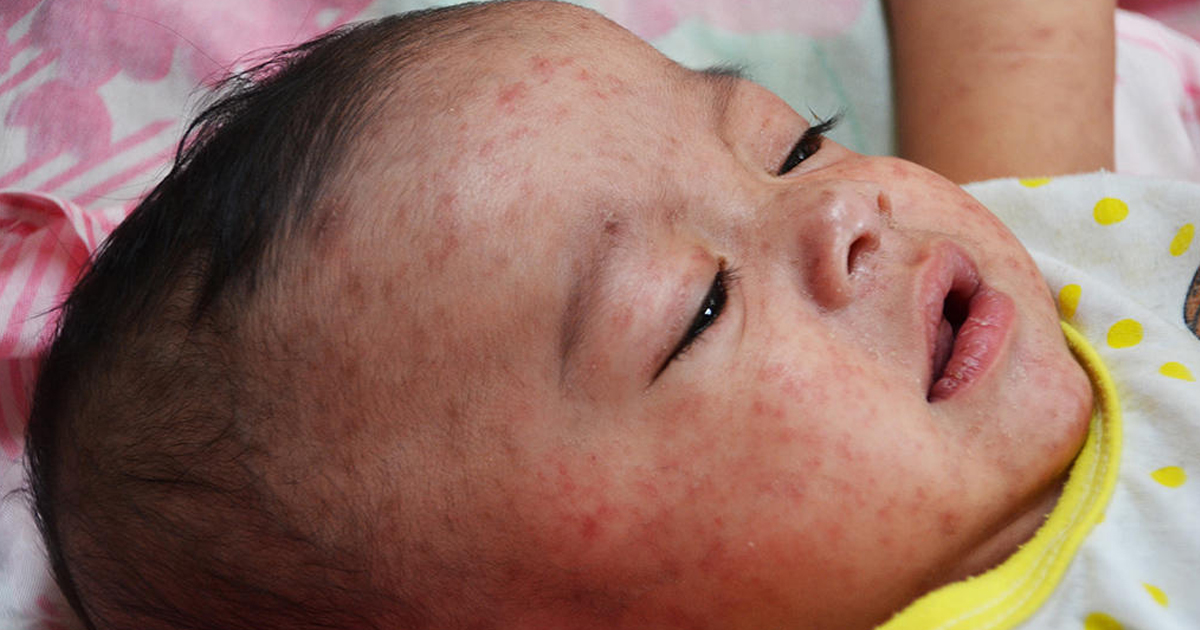
Measles, otherwise known as rubeola, is a highly contagious disease. It can be prevented with vaccines, and keeping up-to-date on vaccinations is vital. Because of parents choosing not to vaccinate their children, there have been some measles outbreaks recently despite the disease previously being virtually eradicated in the United States. Measles occurs in children and can be serious enough to be fatal. Throughout the world, more than 100,000 individuals are killed by measles every year, the majority of whom are under age five. The signs and symptoms of measles tend to appear around ten to fourteen days after someone is exposed to the virus. The most common symptoms are a fever, sore throat, runny nose, dry cough, and inflamed eyes. There's also often a skin rash that consists of large and flat blotches flowing into one another. One characteristic sign of measles is tiny white spots on a red background with bluish-white centers, which are located on the cheek's inner lining or inside of the mouth.
Learn more about what can cause swollen lymph nodes now.
Strep Throat
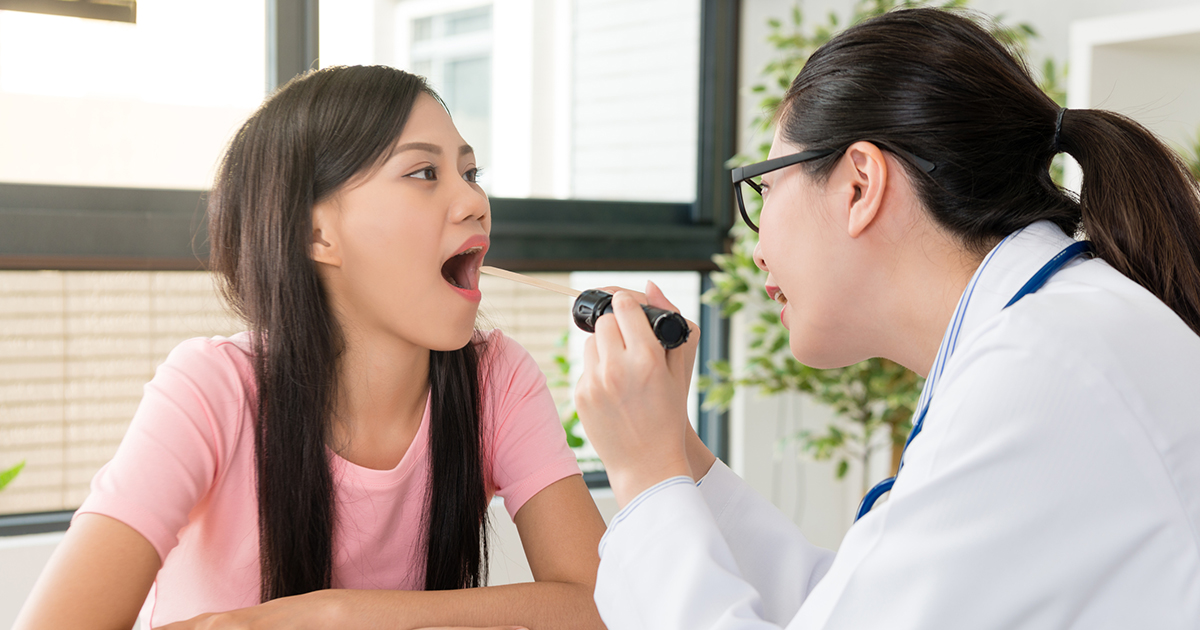

Strep throat is a bacteria-related infection that leads to pain and inflammation in the throat. The bacteria responsible for the condition is group A Streptococcus. The condition can affect adults and children of any age, and it tends to be highly contagious. It's most common in children between five and fifteen years old. Coughing and sneezing can cause bacteria to spread between individuals. The severity of the condition varies depending on the person. The mildest cases tend to present with just a sore throat, but some patients have trouble swallowing and develop a fever. Swollen lymph nodes often accompany the fever. Fevers associated with strep throat often come on suddenly and reach temperatures of 101 degrees Fahrenheit or higher. Patients might also have a reddened throat with white patches, a headache, chills, and loss of appetite. The lymph nodes in the neck are typically the ones that become swollen due to strep throat. Patients typically experience symptoms five days or less after they are initially exposed to the bacteria.
Continue reading to learn more about the different conditions that can result in swollen lymph nodes now.
Mononucleosis

Mononucleosis is an infectious disease that is most commonly caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Some other common terms for the illness are 'mono' and 'the kissing disease.' In addition to getting the virus through kissing, individuals can get it by sharing silverware or drinks with others. Though mononucleosis is contagious, individuals are less likely to catch it than they are to catch the common cold. This condition doesn't tend to be serious, but it can cause potentially serious complications. Some patients only experience mild symptoms, while others experience more severe problems. It might be impossible to partake in normal daily activity for multiple weeks. The symptoms are diffuse and tend to vary from patient to patient. Symptoms tend to show up four to seven weeks after exposure to the Epstein-Barr virus. The most common symptoms are sore muscles, a sore throat, a loss of appetite, swollen lymph nodes, a fever, and fatigue. The majority of patients recover within two to four weeks, but it's possible to feel fatigued for multiple weeks after the other symptoms abate.
Get more details on the causes of swollen lymph nodes now.
Ear Infections
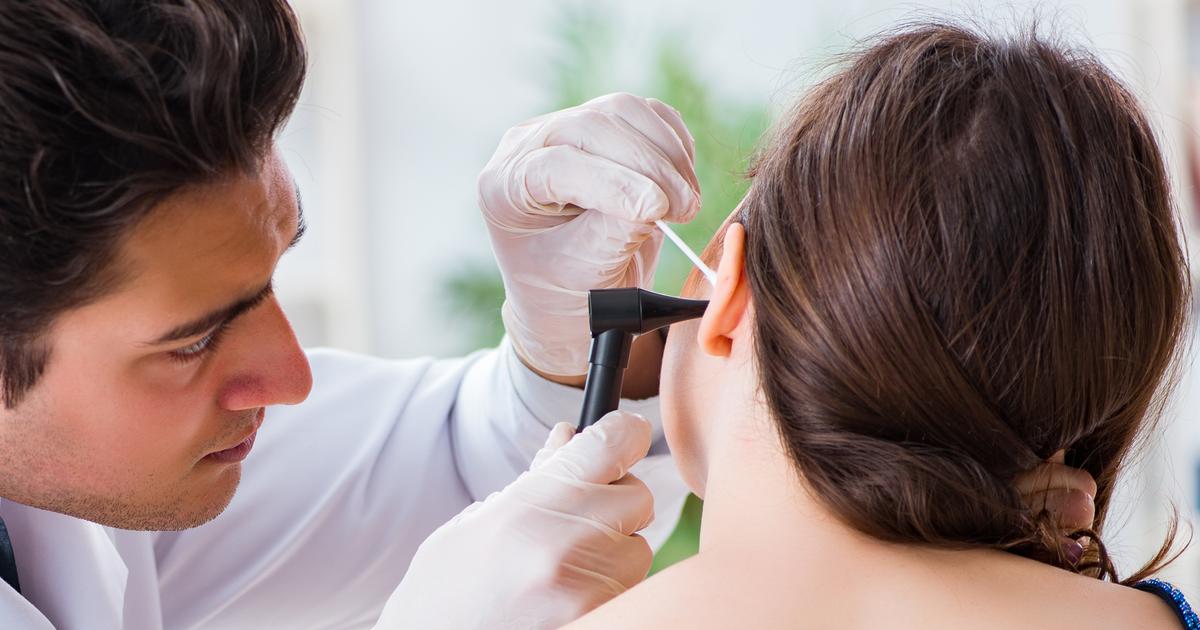
Ear infections most often occur in the middle ear. Infections can also occur in the inner ear, but these are less common. The middle ear is the air-filled area behind the eardrum. It contains the small bones in the ear that vibrate. These vibrations are picked up by the nerves and sent to the brain, which interprets them as sound. Ear infections are more common in children than adults, but anyone can get one. It's common for ear infections to clear up by themselves. However, there are some situations where antibiotics are necessary to help clear the infection. Doctors might choose to monitor the problem and manage pain rather than prescribing antibiotics right away. Some individuals are prone to getting multiple ear infections, either simultaneously or very close to each other. This can lead to potentially serious complications including hearing loss. Symptoms of an ear infection tend to come on rapidly. Patients might have swollen lymph nodes, and they might experience fluid drainage from their affected ear.
Discover additional conditions that cause swollen lymph nodes now.
Cellulitis
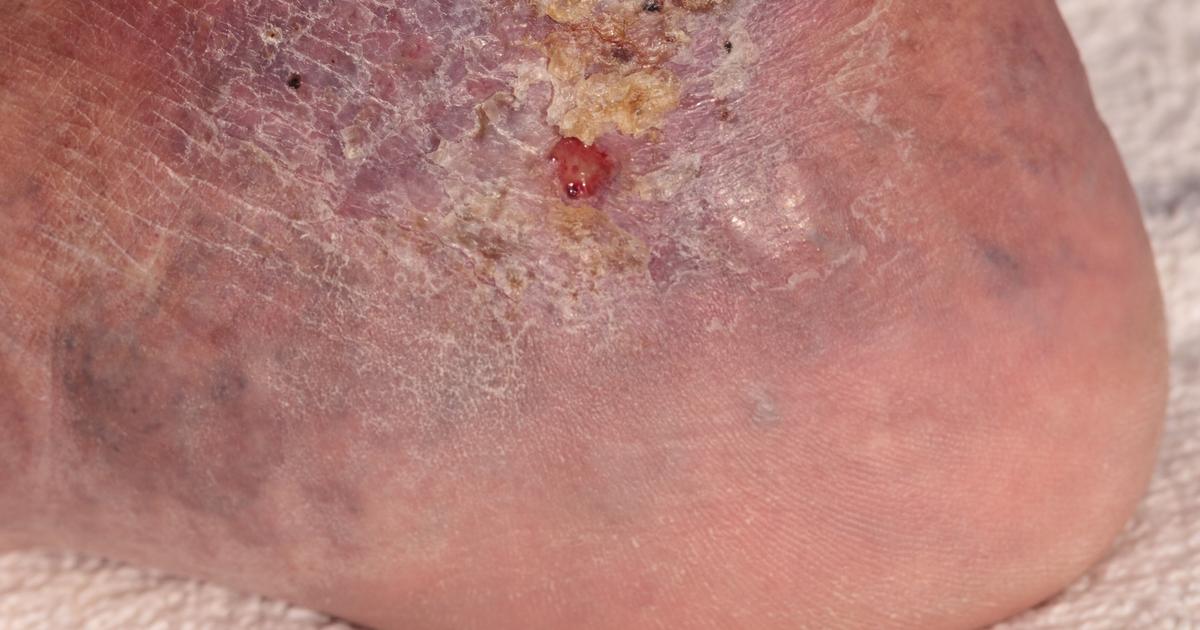
Cellulitis occurs when bacteria infect the skin and the tissues directly below the skin. Many types of bacteria can cause cellulitis, though some being more common than others. Individuals are more likely to develop cellulitis if they have open wounds like scratches, surgical wounds, ulcers, sores, or punctures. The lymph nodes that become enlarged will vary depending on where the infection is. Other common symptoms include swelling, tenderness, pain, redness, and the affected area being warm to the touch. The infection often occurs in the legs, but it can develop anywhere in the body. This is not a contagious infection. If cellulitis spreads to other organs of the body, it can cause life-threatening complications. Cellulitis that has spread becomes an emergency medical condition that requires immediate treatment. The main treatment for cellulitis is a course of oral antibiotics, or intravenous antibiotics in severe cases.