Causes Of Cerebral Edema
Cerebral edema, also known as swelling in the brain, is a life-threatening condition. When the brain swells, it can set off a chain of events, and the side effects are seen throughout the body. The stress of the injury can magnify the body's response or negate it entirely and make the issue harder to treat. Early management and treatment are crucial to improving the patient's prognosis. Learning more about the underlying conditions can help medical staff recognize the signs and symptoms sooner. Once those are treated, the edema should hopefully resolve, giving the patient a better chance at making a full recovery.
Traumatic Brain Injury
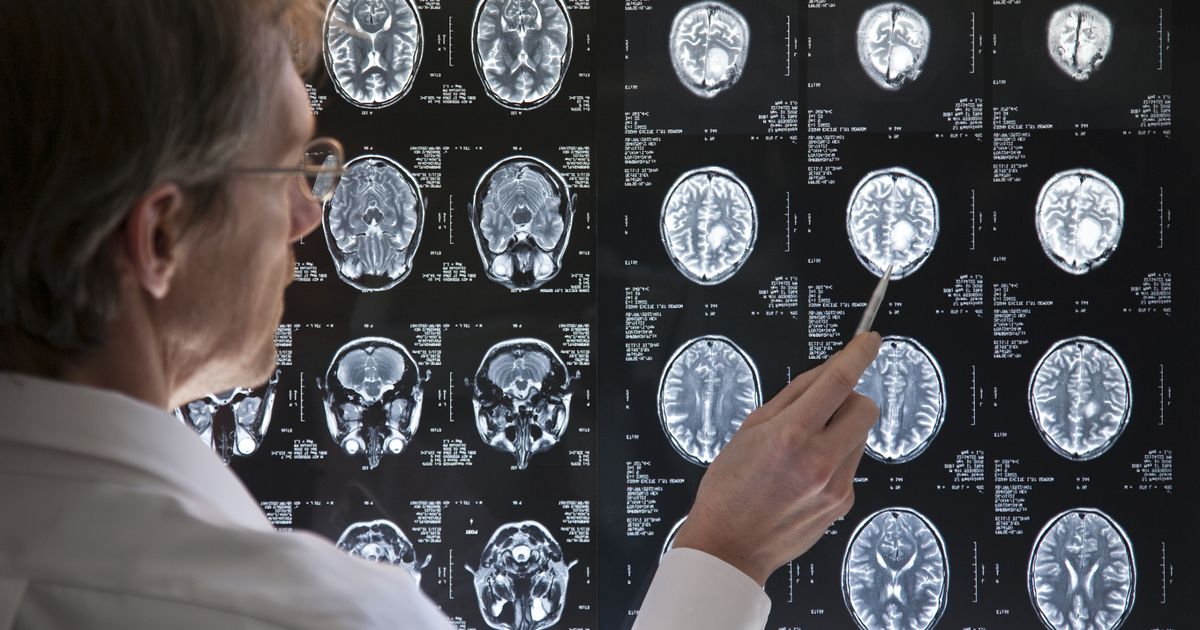
When your brain receives an injury, a few things occur. Concerning cerebral edema, the part to focus on is what's called a vasogenic response. There is something called the blood-brain barrier, which acts as a protective membrane to keep anything deemed toxic out of the brain. During a traumatic brain injury, this membrane can be disrupted, which would allow it to let more fluid and substances through, rather than filtering them out, leading to cerebral edema.
The other thing that could occur is something called cytotoxic edema. This happens when the blood-brain barrier is unaffected, but the pump that pushes sodium and potassium around the cells is disrupted instead. This can lead to prolonged fluid retention or cerebral edema.
Continue reading to learn about a connection to strokes.
Ischemic Stroke

An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot prevents adequate blood flow to the brain, which prevents oxygen and other nutrients from reaching the cells and starts to cause cell and tissue death. This results in increased fluids and swelling of the remaining tissues, which sets off a chain of events. The increased swelling causes the brain to shift, and other areas are compressed from lack of room for expansion. The compressed areas don't receive enough of a blood supply, and they can eventually suffer cell death as well. This is a good example of why early treatment is essential.
Continue reading to learn about the type of bleeding linked to cerebral edema.
Brain Hemorrhage
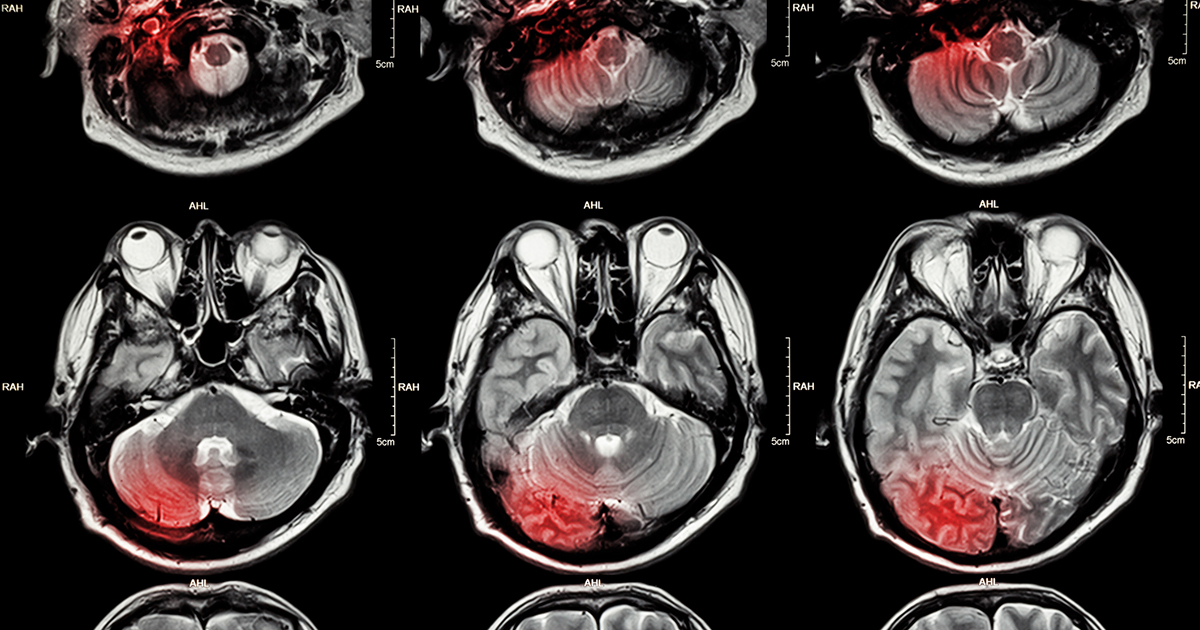
A brain hemorrhage is where there is bleeding in an area of the brain. This type of bleeding can be caused by things like trauma or injury, or even uncontrolled high blood pressure. As the blood collects within in the brain, the body recognizes it as a type of foreign substance. The body then initiates an inflammatory response to help protect the brain. Tons of histamines and prostaglandins are released, and the capillaries are dilated to allow the increased flow to the area, which causes more fluids to pool, thus resulting in cerebral edema.
Continue reading to learn the connection between cerebral edema and infections.
Infections
Infections starting anywhere in your body will end up producing an inflammatory response, which is the body's way of directing white blood cells and other types of cells into the infected area to fight off the offending pathogen. The cells damaged by the infection causing pathogen will release things like histamine and prostaglandins. In turn, this causes the local tissues to leak fluids into the surrounding areas, which is where the cerebral edema comes from. The swelling then essentially walls off the damaged or infected tissues from the healthy tissues as a way to help control the infection and prevent it from spreading.
Continue reading to learn about a type of growth that can result in cerebral edema.
Tumors

Tumors occur mainly due to an unmoderated amount of growth. Normal cells have mechanisms in place to sense the cell wall of another cell, and they stop growing. This function is impaired with tumor cells, and they continue to grow as long as there is a nutrient source. They can even create their own source if needed. This unchecked growth causes the breakdown of various capillary junctures between cells. Fluids and plasma start to leak from these impaired junctions and enter the brain. Cerebral edema occurs, and the pressure within the skull increases.