Treatments For An Epidural Hematoma
An epidural hematoma is a medical condition that occurs after head trauma. Upon impact, the brain bounces inside the skull, causing tears and damage to its lining and blood vessels, resulting in bleeding inside the skull. A mass of blood may form between the brain and the skull. This mass is called an epidural hematoma. The mass of blood increases pressure on the brain, which leads to swelling, which in turn leads to more pressure. The initial head trauma already caused a brain injury, and the epidural hematoma might make the brain damage worse. Untreated hematomas can be life-threatening, or at the very least, permanently debilitating. Fortunately, there are some successful treatment methods. Get familiar with them now.
Surgery
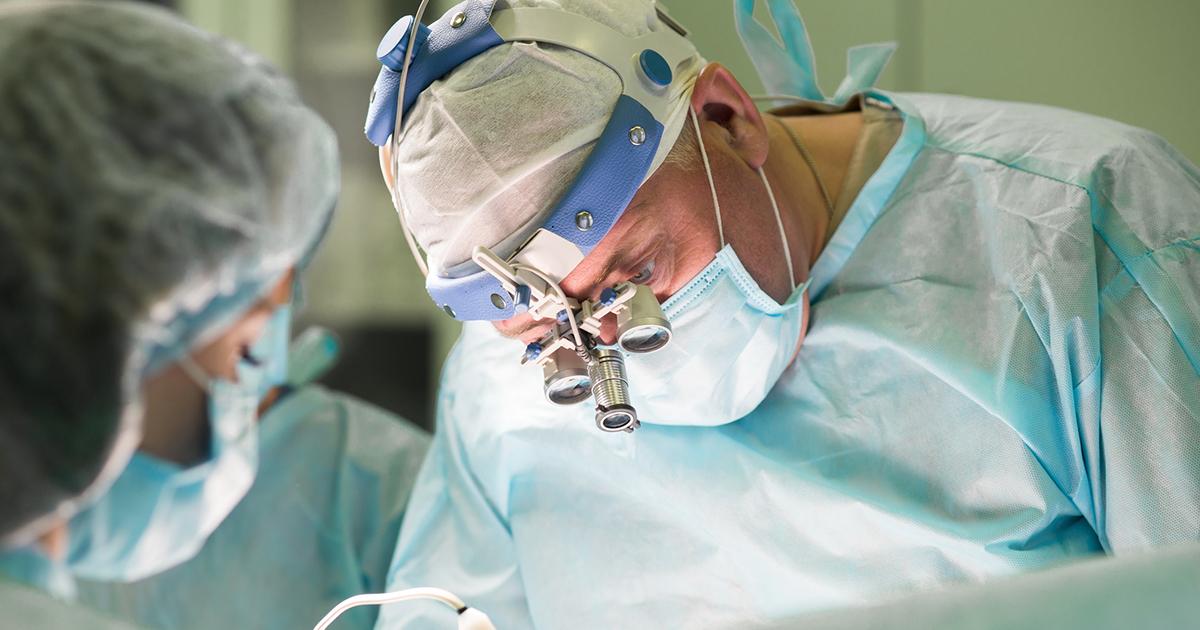
In the majority of cases, the main course of action doctors will suggest is surgery to remove the hematoma. The procedure tends to involve a craniotomy, where a surgeon opens up a small portion of the patient's skull to remove the epidural hematoma. This helps reduce the pressure inside the skull.
Another common surgical procedure is aspiration. This type of operation is recommended less often, as it tends to work in cases where the hematoma is particularly small. If the epidural hematoma is already increasing the pressure on a person's brain, it's too big to be removed through aspiration.
When performing an aspiration operation, the surgeon cuts a small hole into the patient's skull and removes the hematoma through suction. This is a far less invasive operation, and as such, it has a much faster recovery time. But it should only be used when the hematoma is small enough. If a surgeon uses the wrong procedure, they might fail to remove the entire hematoma, which would require a second operation at best, and cause critical complications at worst.
Continue to learn more about treating epidural hematomas.
Medication
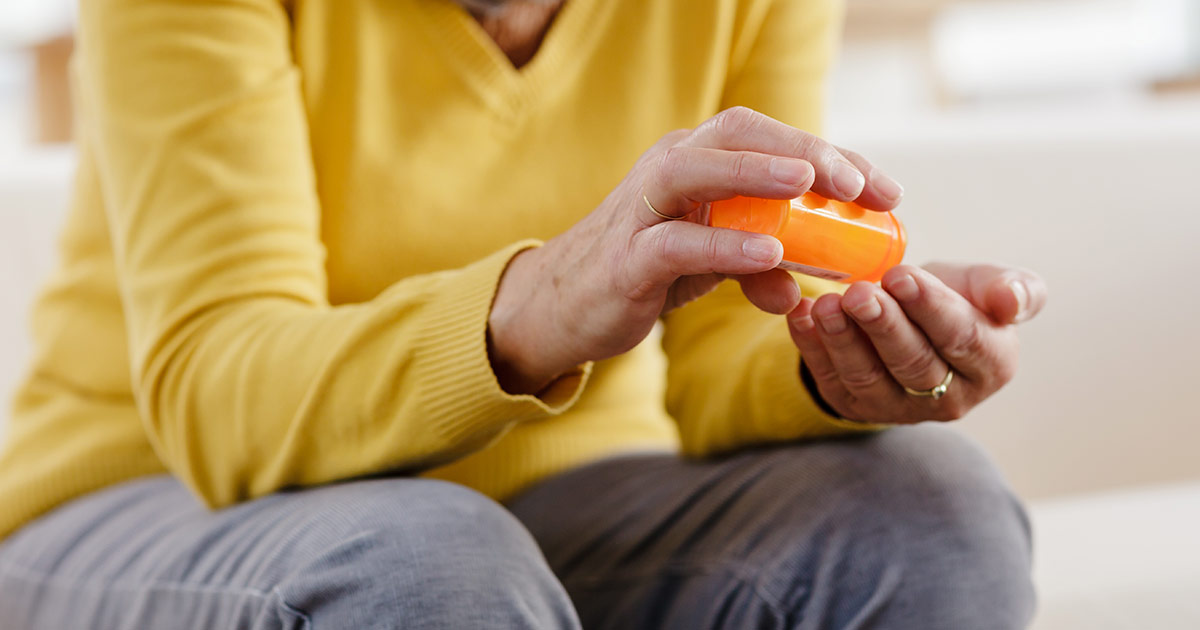

Unless the epidural hematoma is causing critical pressure on the brain, an operation generally won't be performed without the patient taking medication beforehand. Doctors will generally prescribe drugs that help reduce intracranial pressure and overall inflammation. One group of medication is called hyperosmotic agents, including hypertonic saline, glycerol, and mannitol, which are designed to reduce the swelling in a person's brain. One of the most common complications of a head injury is the potential for seizures, which is why doctors might prescribe anti-epileptics and anti-seizure drugs. Depending on the severity of trauma, patients might need to take these medications for a long time. Some patients use them for years, although this is usually only the case if they have already experienced seizure-related complications.
Continue for the next way to treat an epidural hematoma.
Rehabilitative Therapy
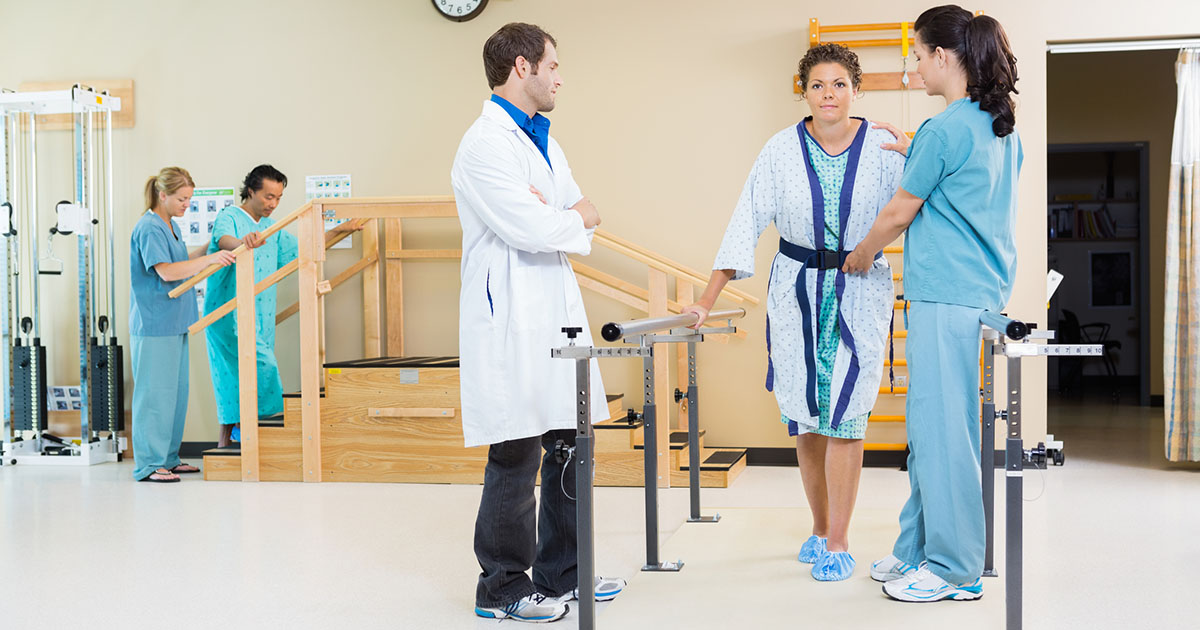

After patients have undergone surgery and been prescribed maintenance medication, doctors might refer them to specialized therapists. The therapists doctors will recommend vary depending on patient circumstances. However, rehabilitative therapy, particularly physical, occupational, and speech therapy, is a common one.
Physical therapists will help with the physical complications from the injury. This might include difficulty with walking, general muscle weakness, and difficulty using hands. A physical therapist will also be recommended when a patient has become paralyzed or lost sensation in parts of their body. An occupational therapist will help patients familiarize themselves with everyday tasks again. Here, patients relearn how to live in their home environment and perform whatever daily tasks are now difficult.
A speech therapist will help with any issues regarding speech. If you have problems with slurring words or talking slowly, speech therapy can help overcome this. Aphasia, which is the phenomenon of forgetting words or being unable to process them, is also covered in the realm of speech therapy.
Continue to discover the next method of treatment for an epidural hematoma.
Rest And Relaxation

The most important part of recovery is letting yourself take time to heal, as your brain has just suffered a huge amount of trauma. You've had your initial head injury, which caused damage. Then, your blood caused the pressure on your brain to swell, which could severely increase the damages. After that, you needed to undergo an operation to relieve the pressure. Now, you're dealing with the aftermath of brain damage, and everything that entails for your unique case.
You need to take time off to engage in rest and relaxation. It's one of the hardest things for a patient to do, especially one committed to their career and other obligations. But if you try to return to normal too quickly, you could cause even more complications. It's imperative to follow the recommended treatment plan laid out by your doctor. Rest whenever you get tired and avoid contact sports and alcohol.
Continue reading to learn about the next element of treating an epidural hematoma.
Slow Return To Activity

The recovery process for a brain injury is slow. No matter how severe the damage, individuals with epidural hematomas have one thing in common: their brain has been put through a great deal. You'll need to work with the therapists mentioned earlier regarding the damage to your body and speech capabilities. These therapists will help you recover as much of your previous capacity as possible. They'll also teach you how to adjust to new challenges presented by any permanent disabilities.
Your activity level should be increased gradually. The majority of improvements in your condition will happen in the six month period following your treatment. However, you might see further improvements for a full two years, so be committed to the recovery process. A slow return to activity will help you safely become accustomed to the life you want.