Diagnostic Methods And Treatments For Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic primary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive condition, considered a type of interstitial lung disease, characterized by lung tissue scarring. In the United States, approximately fifty thousand individuals have this condition. As the lung tissue scarring gets worse, the lungs lose their ability to function normally. The scarring typically begins at the lung edges and works its way in toward the center of the lungs. Initially, the scarring is usually mild, but over the years, the heavily scarred tissue can make it hard to breathe and oxygenate the body. There is no cure for this disabling disease, but there are some treatment options patients can explore with their doctors.
Learn about the treatment options as well as how idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is diagnosed now.
Lung Function Tests
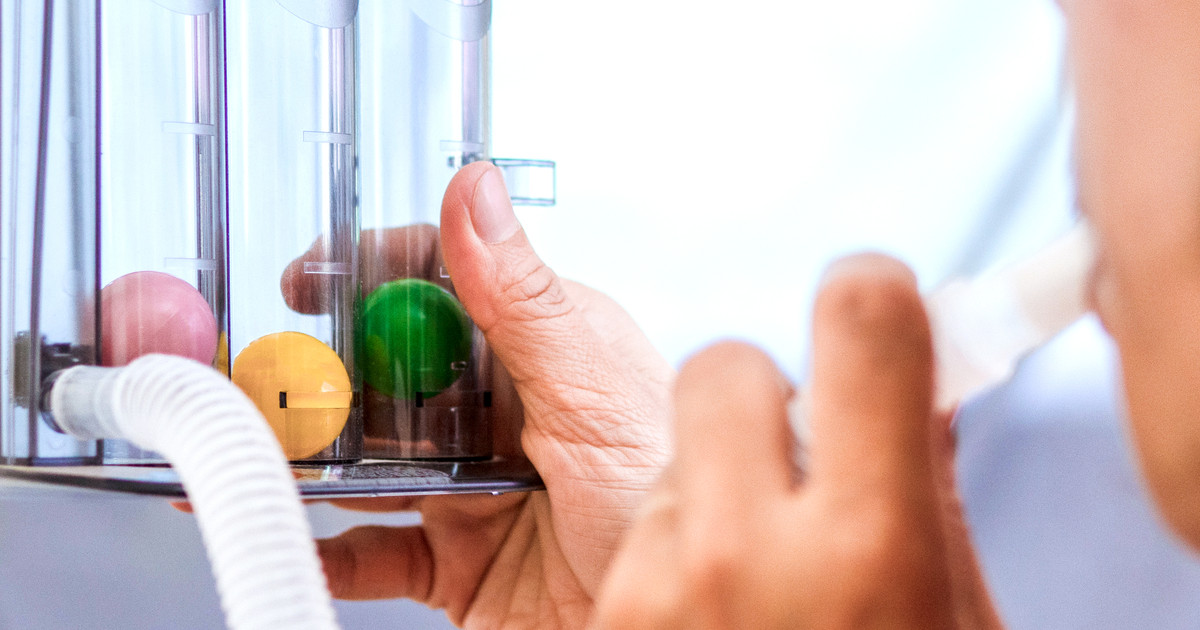

An individual who is suspected to have idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis may need to have lung function tests as part of their diagnosis process and to gauge the severity of their disease. Lung function tests are a series of evaluations that measure how well an individual's lungs are working. Spirometry is a basic test that measures the quantity of air that an individual's lungs can hold and how forcefully they can expel air from their lungs. A more precise form of spirometry that is used in the diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis is lung volume testing. Exercise testing is a lung function test used in the diagnosis of many lung conditions and diseases where a patient exercises on a treadmill while numerous vital signs are monitored, including heart rate and oxygen levels. Lung function tests may be used during the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis to evaluate how and at what rate the disease is progressing. The efficacy of different treatments can also be analyzed with the use of lung function tests in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients.
Keep reading for information on treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Oxygen Therapy
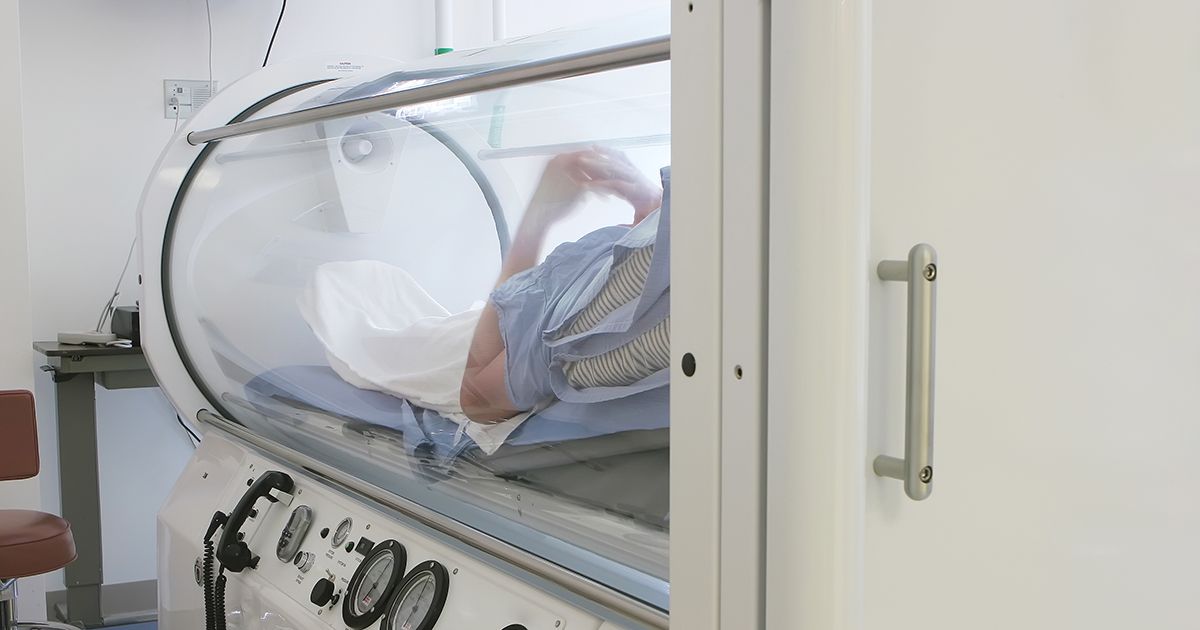

Oxygen therapy is a common treatment since this condition makes it difficult for the body to absorb oxygen. The reduced oxygen levels can cause fatigue and shortness of breath. Supplemental oxygen makes up for the oxygen the lungs are not producing. Depending on the severity of the patient's idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, some patients might require oxygen constantly, while others will only need it during sleep or exercise. The oxygen is typically delivered through a nasal cannula. Patients will be prescribed a specific amount and will set their oxygen tank to deliver oxygen at this level. A pulmonologist will evaluate a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis to determine if supplemental oxygen will be beneficial. Patients are typically re-evaluated every three to twelve months to determine if the supplemental oxygen level needs to be increased.
Keep reading for information on treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with a form of rehabilitation now.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
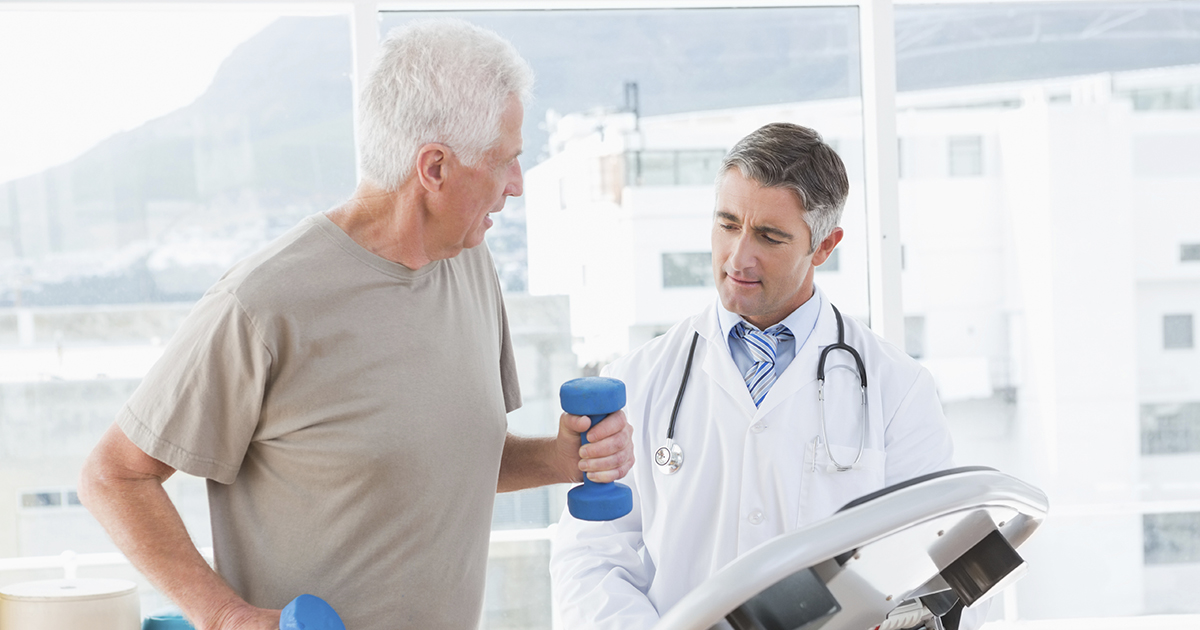

Pulmonary rehabilitation is a combined education and exercise program focused on patients with lung disease. Patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis will learn how to breathe more efficiently so they can reduce the fatigue and shortness of breath that occurs with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. This rehabilitation also helps patients adjust how they do their activities of daily living so they can conserve oxygen and experience less breathlessness. This rehabilitation is comprehensive and often includes a variety of the following: exercise training that targets the lungs, learning more about idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and different management techniques, breathing strategies, nutritional counseling, energy-conserving techniques, and psychological counseling. A team of specialists is typically involved in this process. The methods used are usually adjusted based on the progression of the patient's disease.
Learn about how medication comes into play when treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Medications
While no medications can cure or slow the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, there are medicines that may help improve a patient's quality of life. Prednisone is a steroid that reduces inflammation in the lungs. It may be administered orally, via injection, or into a vein. Due to the potential for serious side effects, this medicine is usually only given short-term during periods of significant symptoms. When taking prednisone, doctors often recommend vitamin D and calcium supplements since this medication can cause bone loss. Azathioprine, an oral daily medication, suppresses the patient's immune system and is usually only given for up to six months at a time due to the potential for serious side effects. N-acetylcysteine, an antioxidant patients take orally several times a day, may help prevent lung damage. It is usually combined with azathioprine and prednisone.
Uncover more on how to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Symptom Management

Some of the symptoms of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis can be addressed individually to improve a patient's quality of life. Symptom management treatments are sometimes considered for weight loss, fatigue, dry cough, and leg swelling. For weight loss, patients may meet with a nutritionist to improve their diet. Diets are usually focused on increased calories and ensuring a proper macronutrient ratio with emphasis on protein. Sleep hygiene can be beneficial for fatigue, as it helps patients develop a regular sleep routine so they are getting adequate rest every day. For a dry cough, tea with honey, throat lozenges, ginger, staying hydrated, and a saltwater gargle can help soothe the cough and associated throat soreness. Leg swelling can benefit from elevating the legs above heart level and balancing fluid and salt intake.
Continue reading to learn more about treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis effectively now.
Lung Transplant

If the patient's condition is very severe or progressing rapidly, doctors might discuss a lung transplant with them. Getting new lungs can help to prolong a patient's life and ensure a higher quality of life. This is a major surgery that requires a lifelong commitment to preventing the body from rejecting the transplanted lungs. Following the surgery, patients should expect to spend up to three weeks in the hospital. During this time, patients will heal from surgery, have their pulmonary function monitored, and receive respiratory therapy. Once the new lungs are in place, patients will take anti-rejection medication for the rest of their lives. It is also recommended that, for the rest of the patient's life, they make healthy lifestyle choices, do not smoke, receive all routine vaccines, and practice good hygiene.
Get more information on treatments for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Immunizations For Pneumonia And Influenza
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients often need to ensure they receive immunizations for pneumonia and influenza as part of their treatment. An individual affected by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis has lungs that cannot function normally due to a buildup of scar tissue. Scar tissue is a type of dense and fibrous tissue the body utilizes to replace the damaged tissues in the organs. However, scar tissue rarely works the same as the original tissues it has replaced. Because scar tissue makes the inner tissues of the lungs less capable of oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange, the overall function of the lung is compromised. Pneumonia is a life-threatening lung infection caused by viruses or bacteria and is known to have a high mortality rate in individuals with pre-existing lung conditions like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by a virus that is also more deadly in those who have pre-existing lung conditions. The risk of morbidity from these infections can be reduced if patients receive these immunizations.
Uncover more ways to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Quit Smoking

An individual who has been diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis will need to quit smoking if they are a regular smoker in order for their disease to respond to treatment. Those who smoke regularly are more likely to develop idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An individual who smokes tobacco products regularly will experience damage to the tissues in their lungs due to the repeated exposure to thousands of toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke. This damage to the lungs makes them less capable of oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange before any condition or disease is introduced into the mix. Therefore, the combination of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and accumulated damage from repeated exposure to cigarette smoke can cause an individual's lungs to fail entirely. Smoking cigarettes or other tobacco products is known to cause a more rapid progression of all forms of pulmonary fibrosis than in individuals who do not smoke. Smoking cessation must occur for an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patient to have the chance to slow the progression of their disease.
Read more about treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Stay Active

An individual diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis may be advised to stay active as part of their treatment plan. There are several benefits of an active lifestyle for these patients. Many individuals affected by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis who are physically active on a daily basis report an overall reduction in stress. Less stress can help slow the progression of their lung disease because the hormones released in the body when an individual is stressed cause their heart and lungs to work harder than they typically would. Regular exercise is known to improve the strength and health of an individual's heart, which can prevent the development of certain cardiovascular complications associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An active lifestyle also plays a huge role in ensuring an individual has a healthy body mass index, as excess weight can place unnecessary pressure on the heart and compromised lungs.
Discover additional ways to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis now.
Follow A Healthy Diet

Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients may need to change their diet to include more healthy foods for their treatment efforts to be effective. Consuming a healthy diet can help patients obtain and keep a healthy body mass index. Body mass is important in lung disease because excess weight puts unnecessary pressure on the heart and lungs that can cause a faster disease progression. A low sodium diet is also recommended because it reduces excess fluid retention, making it easier for the lungs to fill with air. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients are also advised to consume several smaller meals throughout the day instead of three large meals. This practice helps reduce the restriction of the lungs from filling with air due to an expanded stomach. An individual who uses supplemental oxygen as part of their treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is also advised to use their oxygen while they are eating and digesting their meals.