Proven Facts You Should Know About Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is a term used to describe an eye disorder that causes vision loss. It is the leading cause of vision loss in adults over the age of sixty. It occurs due to the deterioration of the eye’s macula, which is a small area of the retina responsible for central vision and the ability to see fine details. It is caused by the formation of deposits or abnormal blood vessels under the retina. Symptoms may include blurriness, distortion of central vision, and eventually loss of central vision. Keep reading to learn these fast facts about this disease now.
It Does Not Cause Blindness
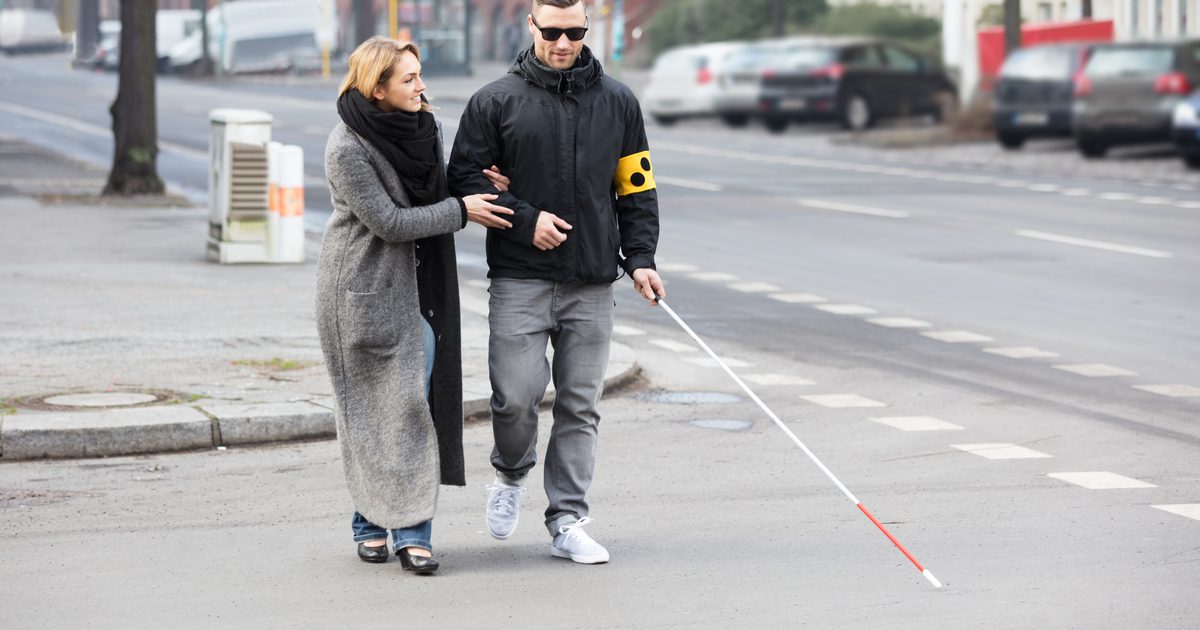

Although patients with more advanced stages of macular degeneration may ultimately lose their central vision, rarely does the disease cause total blindness even without treatment. In most cases, people with macular degeneration will still be able to utilize their peripheral vision or the vision that allows a person to see to the side. Some cases of macular degeneration may even cause a minimal impact on vision. Seeking treatment at the first sign of the disease is the best way to preserve central vision.
Next, learn about the risk factors associated with this condition.
Risk Factors
Age plays a significant role in determining when and if a person will develop macular degeneration. Research shows most cases develop over the age of sixty, but it may occur earlier. Smoking has been shown to double the risk of developing macular degeneration. The disease is more common among those of European ancestry than individuals of African or Latin descent. Individuals who have a family history of macular degeneration are also more likely to develop the condition.
Discover how lifestyle choices play a role in this disease now.
Lifestyle Factors
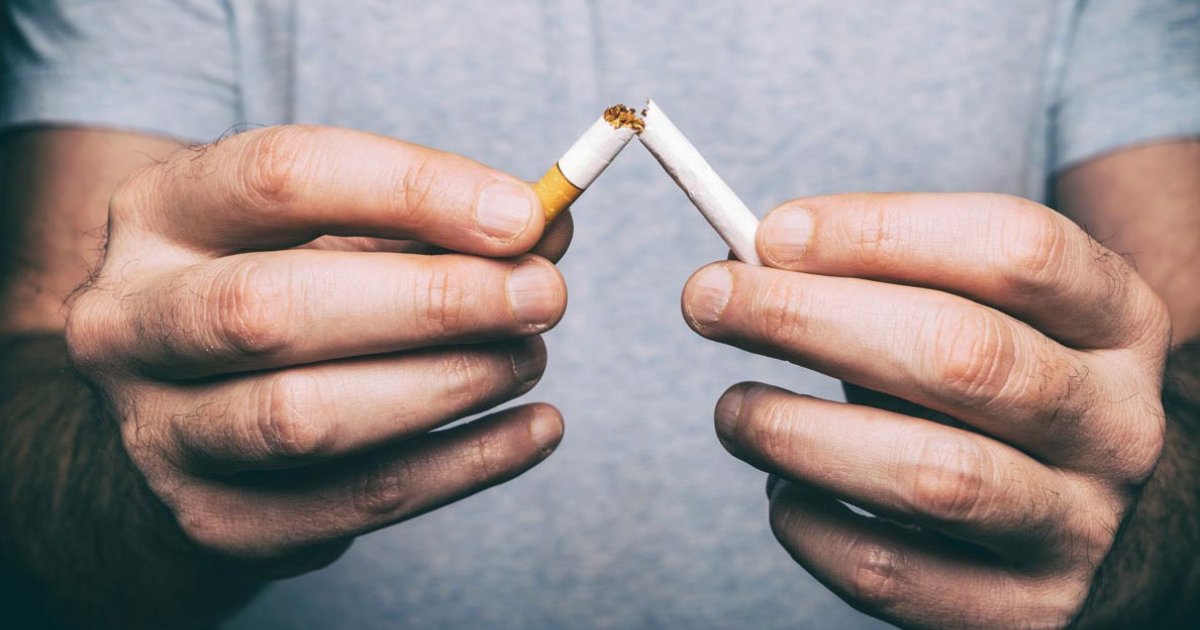

Smoking is the only environmental factor proven to be linked to macular degeneration by researchers. But other unhealthy habits may "turn on" or activate one of the twenty different genes that have been associated with the condition. For that reason, it is best to avoid smoking. Be sure to exercise daily, eat a healthy diet including lots of fruits, vegetables, and fish. Maintain healthy cholesterol and blood pressure levels as these factors, if problematic, may elevate the risk of developing the disease.
Explore the various signs and symptoms of this disease now.
Signs Of Macular Degeneration
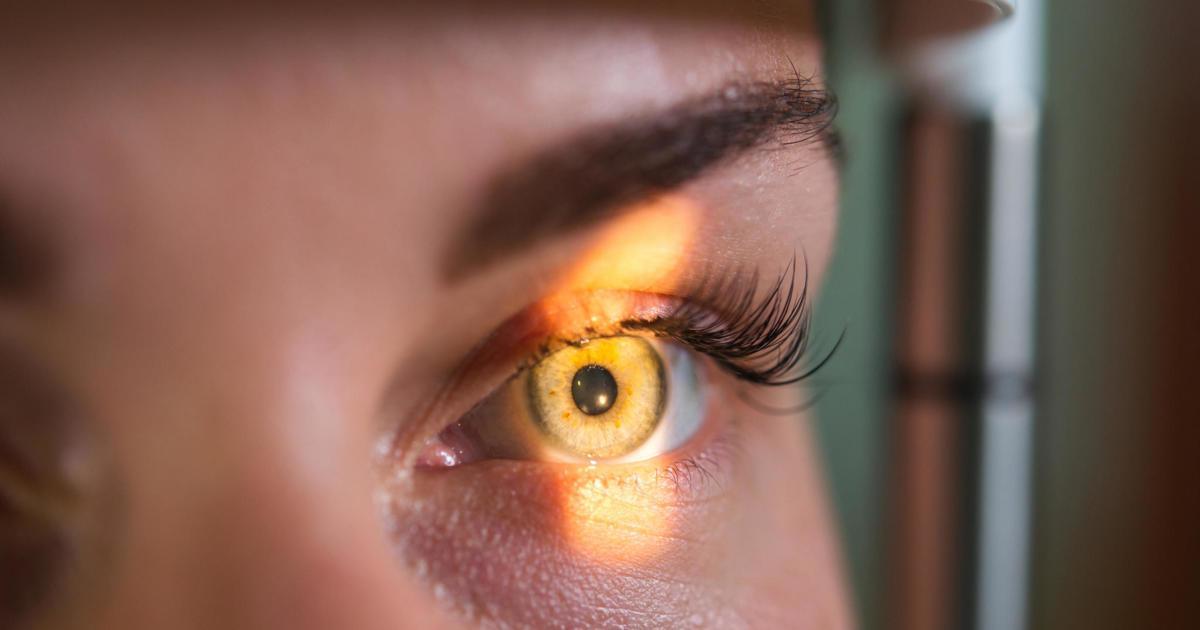

One sign of macular degeneration is the presence of color changes under the retina. Pigment changes may occur in the iris or the colored part of the eye. This is because there are pigmented cells located underneath the retina and when they break down, they release pigment that can be seen in the form of dark clumps in the eye. These changes are generally painless and will not affect eye color, but can be a sign of macular degeneration.
Continue reading to understand the significance of eye exams in detecting macular degeneration.
Eye Exams Can Detect Macular Degeneration

Although early symptoms of macular degeneration may be hard to detect or they may not exist at all, only a comprehensive dilated eye exam can detect the disease. A dilated eye exam occurs when the eyes are dilated by using eye drops so the doctor can view the back of the eye and check the optic nerve for signs of disease. The exam may also include a visual acuity test, which checks how well a person sees long distance.
Next, learn how other eye exams can help detect macular degeneration.
Other Eye Exams May Be Conducted
Eye doctors look for yellow deposits located beneath the retina known as drusen when performing a dilated eye exam. In addition to a dilated eye exam, an eye doctor may perform an optical coherence tomography, which is an ultrasound that uses light waves to take pictures of the tissues in the eye to search for abnormalities. Amsler grid is a test that can be used to verify a person’s central vision accuracy. Fluorescein angiograms occur when a dye is injected into the patient’s arm, and pictures are taken as the dye passes through the blood vessels in the eyes.
Find out the different stages of macular degeneration now.
Stages Of Macular Degeneration

There are three stages of macular degeneration, which are defined by the size and number of drusen located underneath the retina. Early macular degeneration occurs when medium-sized drusen about the width of human hair are present. This stage does not include vision loss. Intermediate macular degeneration occurs in people with large drusen and pigment changes in the eye, which can only be detected through an eye exam. Gradual vision loss may be present. Late macular degeneration occurs when vision loss from damage to the macula has occurred.
Keep reading to better understand two stages that occur later on with this disease.
Two Stages Of Late Macular Degeneration
There are two additional stages of late macular degeneration. Geographic atrophy occurs when there is a gradual breakdown of macula cells that are responsible for detecting light. These changes make it hard for the eye to send visual information to the brain. Neovascular macular degeneration occurs when abnormal blood vessels develop underneath the retina and leak fluid such as blood, which may cause swelling and damage to the eye. Having both conditions in one eye is possible.
Unveil treatment options that can help manage macular degeneration today.
Treatment

There are no current treatment options available for early macular degeneration, so instead, most health care professionals focus on early preventative procedures. These may include quitting smoking, eating more fruits, vegetables, and fish, exercising regularly, and getting proper sleep at night. Research shows that taking a supplement with a combination of zinc, copper, vitamins C and E, lutein and zeaxanthin can reduce the risk of late macular degeneration by twenty-five percent.