A Comprehensive Guide To Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a disease that develops over time when the arteries become damaged or diseased. As the arteries become damaged, the injured areas are filled with cholesterol-containing deposits of plaque and become inflamed. As the plaque continues to build up in the coronary arteries, the arteries begin to narrow which causes a decrease in blood flow to the heart. As the blood flow progressively decreases, it can lead to many symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and eventually a heart attack or heart failure.
It is estimated that 370,000 people die from coronary artery disease in the U.S. each year, which is why it is so important to know the signs and symptoms of the disease and how it progresses.
Signs And Symptoms Of Coronary Artery Disease
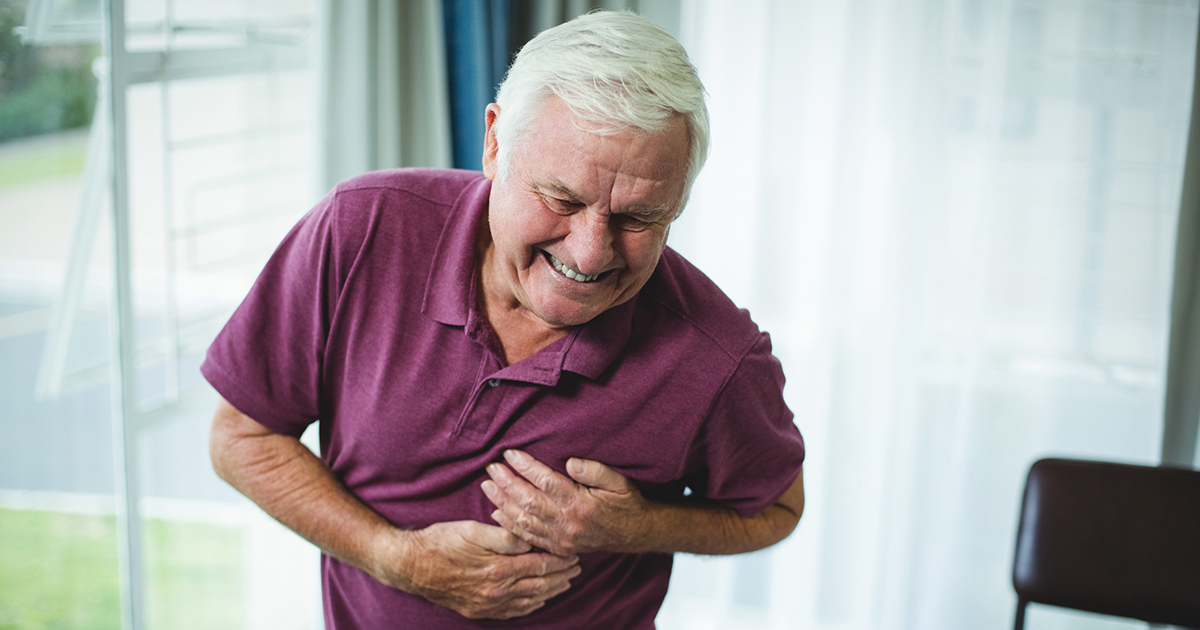

When coronary arteries begin to narrow, they can no longer supply enough oxygen-rich blood to the heart. There may not be any signs or symptoms when the blood flow begins to decrease, but as plaque continues to build up in the arteries, symptoms may start to arise.
Some of the symptoms of coronary artery disease include chest pain (angina), which can be pressure or tightness in the chest that is triggered by physical or emotional stress, shortness of breath, and a completely blocked coronary artery that can result in a heart attack. The symptoms of a heart attack include pressure in the chest, pain in the shoulder or arm, shortness of breath, and sweating.
Now that you know the signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease continue reading to discover what can cause it.
Causes And Risk Factors For Coronary Artery Disease
The causes of coronary artery disease are the same factors that damage the inner layers of the arteries, which can begin as early as childhood. Causes include smoking, high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, high levels of bad fats and low-density (LDL) cholesterol, and blood vessel inflammation. When the inner walls of the arteries become damaged, the site of the injury can be filled with fatty deposits of plaque.
Some of the significant risk factors of coronary artery disease patients should be aware of includes a family history of the disease, smoking, a lack of physical activity, an unhealthy diet, obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, high levels of LDL cholesterol, an insulin resistance, and reaching an older age. For men, the risk of coronary artery disease increases at forty-five years old, whereas for women, the risk increases at fifty-five.
Many causes contribute to developing coronary artery disease. Keep reading to learn what methods are used to diagnose it.
Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease
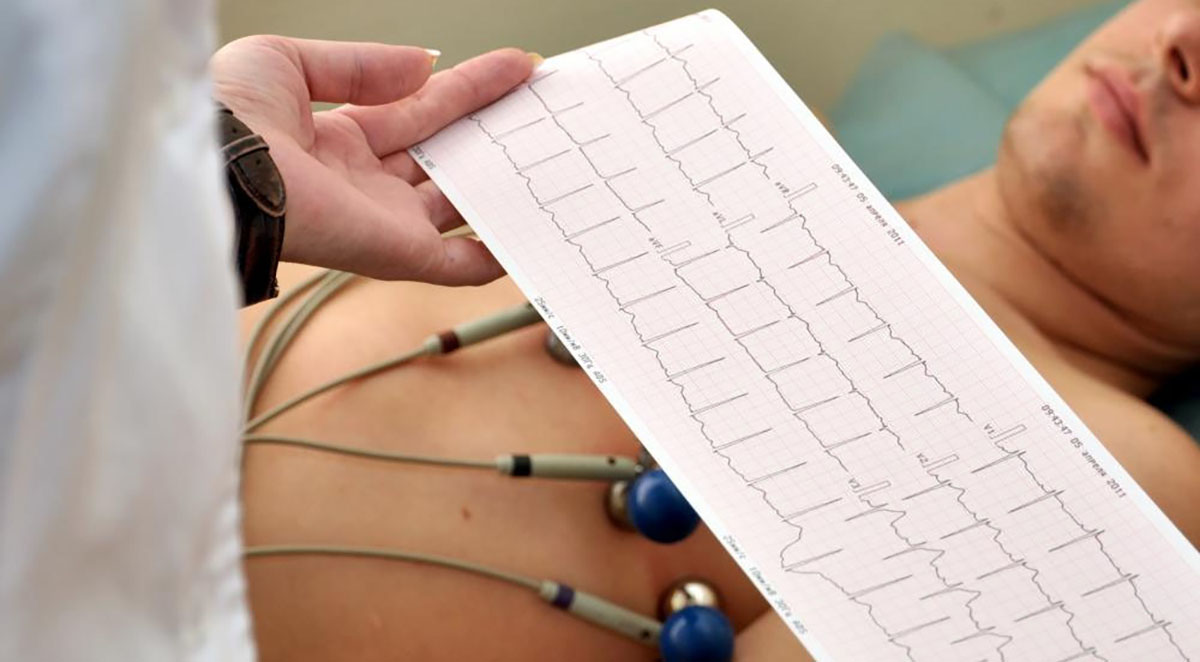
To begin diagnosing coronary artery disease, a doctor must ask their patient about their medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order some blood tests. However, many other tests can be performedto diagnose the condition accurately.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) may be utilized to record the electrical signals as they travel through the heart. The ECG can reveal previous heart attacks and discover one that is in progress. A computerized tomography (CT) scan can determine whether there are calcium deposits in the arteries that contribute to the narrowing of them. Some other tests may include a cardiac catheterization or angiogram, an echocardiogram, and a stress test.
Now that you know how coronary artery disease is diagnosedcontinue reading to learn how it can be treated.
Treatments For Coronary Artery Disease

Treating coronary artery disease begins with making healthy lifestyle changes, taking medications, and possible medical procedures. The lifestyle changes to promote healthier arteries include quitting smoking, eating healthy foods, getting regular exercises such as jogging or brisk walks for thirty minutes to an hour each week, reducing stress, and ultimately achieving a healthy weight.
The medications that may be in addition to lifestyle changes could be any - or a combination - of the following: aspirin, blood thinners, beta blockers, cholesterol-modifying medications, nitroglycerin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).
There are many methods of treatment regarding coronary artery disease, starting with a change in the lifestyle. Read further to find out some home remedies and alternative medicines that may help.
Home Remedies And Alternative Medicines For Coronary Artery Disease

Some at-home remedies that coincide with lifestyle changes include monitoring and controlling blood pressure, which should be below 120 systolic and 80 diastolic and measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), as well as checking cholesterol regularly. LDL cholesterol levels should be below 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
Some alternative medicines alongside lifestyle changes and medications prescribed by a doctor may contribute to reducing the symptoms and the risk of developing coronary heart disease. Alternative medications that may reduce inflammation, blood pressure and cholesterol include omega-3 fatty acids, garlic, artichoke, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), barley, cocoa, and oat bran.
Now that you know some home remedies and alternative medicines that may ease coronary artery diseasecontinue reading to learn how to prevent and reduce the risk before it is diagnosed.
Preventing And Reducing The Risk Of Heart Disease

All of the lifestyle changes that are implemented to treat coronary artery disease can also be used beforehand to help prevent and reduce the risk of developing coronary artery disease and other heart diseases.
To improve heart health, the first steps are to quit smoking and to stay or become physically fit by getting a minimum of thirty minutes to an hour of exercise per week. When that activity no longer feels strenuous, add fifteen minutes of exerciseto theroutine. Other methods to improve heart health include reducing or better managing stress, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in fat and sodium.
Making healthy lifestyle changes is one of the best ways to prevent and treat heart disease. Keep reading to learn what can happen if coronary artery disease is left untreated.
What Happens If Coronary Artery Disease Goes Untreated?
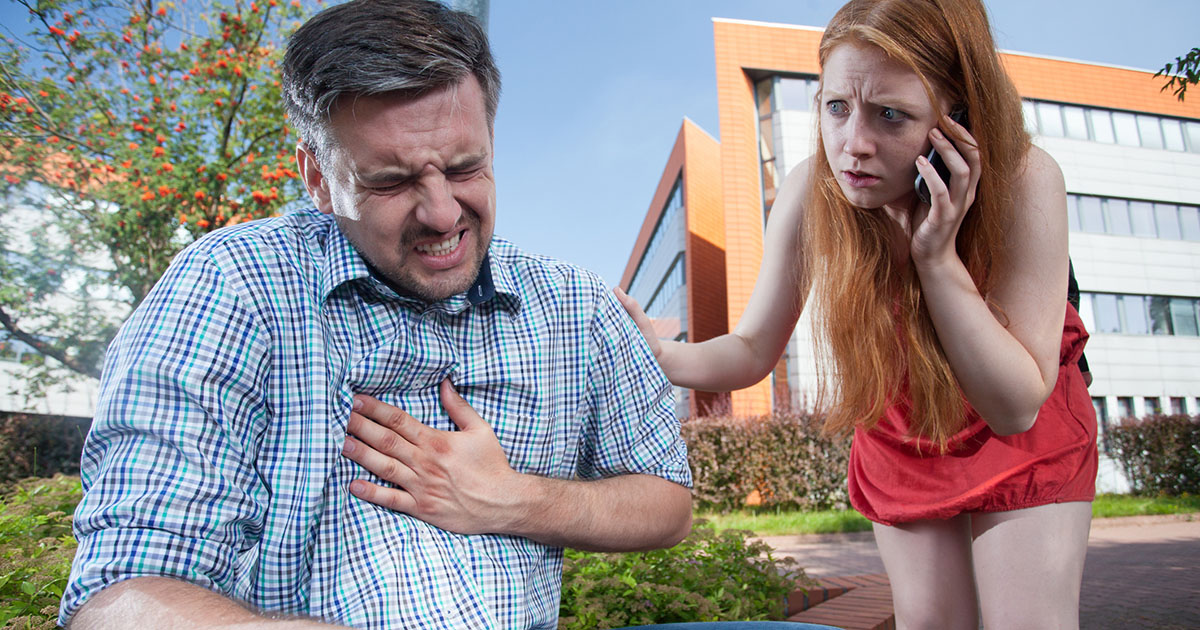

If coronary artery disease is untreated, or not appropriately treated, it can lead to many other complications. As the coronary arteries narrow, the heart may no longer receive enough blood when it is needed, which can result in chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath. An insufficient supply of blood to the heart or damage done to the tissue can impede the electrical impulses of the heart, which can cause abnormal heart rhythms.
Some of the more severe complications that can arise due to untreated coronary artery disease include a heart attack, or if the heart becomes too weak to continue pumping enough blood necessary for survival, it may cause heart failure.
Maintaining a healthy diet and a healthy lifestyle is the best defense against heart disease. Without it, coronary heart disease will continue to progress.