Signs & Symptoms Of Fanconi Syndrome
Fanconi syndrome is a rare disorder affecting the functioning of the kidneys. Specifically, the disorder negative impacts the kidney tubules and causes excessive amounts of glucose, phosphate, uric acid, bicarbonate, potassium, and some amino acids to be excreted in the urine. There are a variety of factors that can cause or influence the development of Fanconi syndrome. It can be inherited or caused by exposure to chemotherapy and antiretroviral drugs, for example. Having a vitamin D deficiency, being exposed to heavy metals or chemicals, or undergoing a kidney transplant are also potential risk factors. In patients with Fanconi syndrome, the thyroid gland can cause an underactive thyroid gland, which prevents the renal tubules in the kidneys from adequately reabsorb necessary fluids and materials. While the causes are varied, several major symptoms can identify the onset of Fanconi syndrome.
Muscle Weakness

The physical manifestation of Fanconi syndrome will depend on the underlying causes of that particular case. Because bodies affected by this syndrome excrete increased and excessive amounts of certain vital substances, the bones and muscles can be heavily impacted. Adult patients, in particular, may develop severe osteomalacia, which is a softening of the bones due to insufficient levels of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate. This impairment affects bone metabolism and can manifest through bone pain and extreme muscle weakness. Hypokalemia, or low levels of potassium in the blood, may also develop, which also presents with muscle weakness.
Get to know more symptoms of Fanconi syndrome to watch out for now.
Excessive Thirst

Properly functioning kidneys are in charge of cleansing the blood while keeping the acidity, salt, and water contents in balance. They achieve this by keeping what is necessary and filtering the excesses out of the body through the urine. After filtering the blood, the kidneys are meant to reabsorb the crucial vitamins and minerals, returning them to the bloodstream. It is this reabsorption step that malfunctions in Fanconi's syndrome. As a result, those crucial substances that are normally reabsorbed are lost.
Because of the overactive nature of Fanconi syndrome, the body ends up excreting vital vitamins and minerals through increased urination. When these vitamins and minerals, mainly potassium, sodium, magnesium, and calcium, in addition to fluids like water are not replaced, it can cause the patient to experience dehydration and excessive thirst.
Continue reading to learn about more signs of Fanconi syndrome.
Hyperaminoaciduria

Hyperaminoaciduria occurs when excessive amounts of amino acids are faultily excreted and lost through the urine, a major problem associated with Fanconi syndrome. As described previously, this syndrome works by causing the body's filtration system to be overactive and faulty, neglecting to reabsorb the materials necessary for proper functioning. Losing amino acids is just as harmful, if not more so, than having vitamin and mineral deficiencies. The role of amino acids in the body is a crucial one, as they are the ultimate building blocks of cell functioning and are essential for nearly every function that takes place in the body, such as metabolism, hormone/protein/enzyme synthesis, and neurotransmission.
Keep going to reveal more symptoms of Fanconi syndrome now.
Hypokalemia

As mentioned above, hypokalemia is a dangerous condition that can develop in conjunction with Fanconi syndrome. Proper potassium levels are critical for nerve and muscle functioning, especially for the muscle cells of the heart. The kidneys are the organ responsible for controlling the body's levels of potassium, removing excesses through increased sweat production or via the urine. When the kidneys are not working properly, as is the case with Fanconi syndrome, potassium regulation suffers and can eventually lead to full-on renal failure. Sodium and potassium replacement therapy is one of the first and most important treatment strategies utilized to correct or prevent this.
Continue for more on the warning signs of Fanconi syndrome.
Rickets
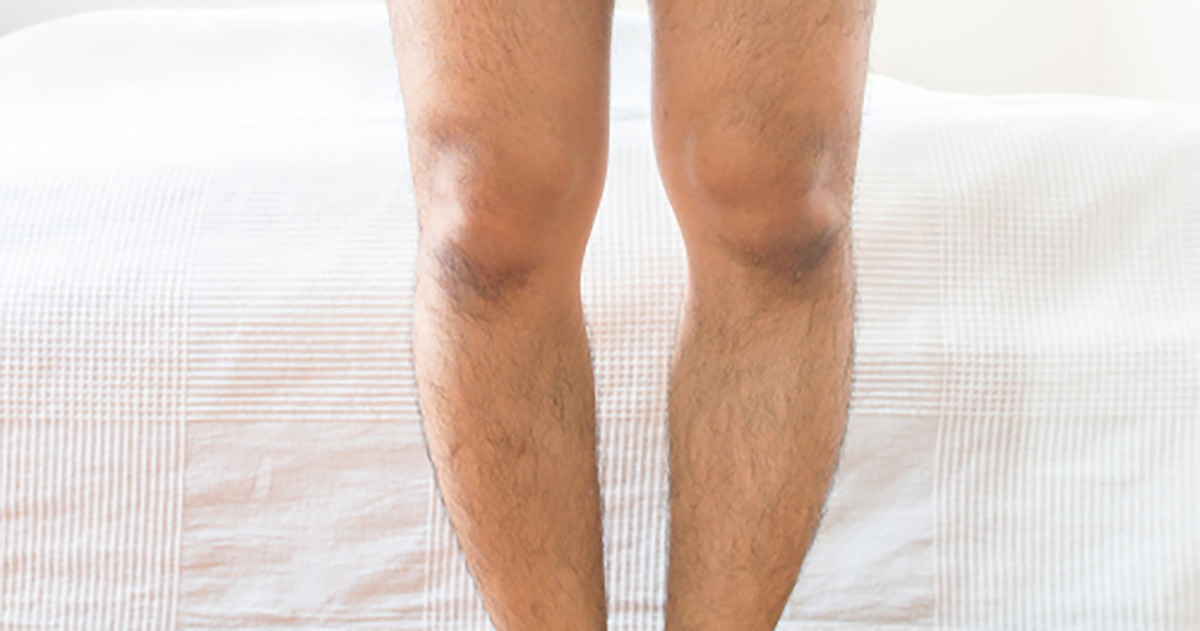
Rickets is a disorder that affects the skeleton caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, phosphate, or calcium, which are some of the vitamins and minerals lost through excessive filtration in Fanconi syndrome. These nutrients are essential for strong and healthy bones. Individuals who develop rickets often suffer from soft and weakened bones, stunted bone growth and development, and, in more severe cases, skeletal deformities. The condition typically comes with pain and tenderness in the rapidly growing bones. Rickets as a symptom of Fanconi syndrome is more commonly present in children, typically between six months old and three years old, whereas osteomalacia is more commonly present in adults with the syndrome.