What Are The Types Of Kidney Disease?
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs roughly the size of a fist. Most healthy individuals have two kidneys, one on either side of the lower spine. These organs are the blood's filtration system, and they manufacture urine to remove waste products and excess water from the body. Together with the bladder and ureters, the kidneys form part of the urinary tract. Kidney diseases can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, autoimmune conditions, and overuse of certain medicines.
Patients with kidney disease often feel fatigued, and they tend to feel cold in warm environments. Some individuals with kidney problems could experience dizziness or weakness, and shortness of breath is common. Patients might notice swelling of the face, hands, or feet, and the skin may become very itchy. The urine might change to pink or red, and patients could experience more frequent nighttime urination or a sensation of pain or pressure during urination. Certain types of kidney diseases can cause changes in taste; for example, some patients have reported food having a metallic taste. Kidney disease can be diagnosed using blood and urine tests, and imaging studies or kidney biopsies may be needed. Depending on the specific kidney issue, treatment options could include medication, dialysis, or a kidney transplant.
Some of the most common forms of kidney disease are discussed below.
Chronic Kidney Disease

Chronic kidney disease is a gradual loss of normal kidney function. Individuals with diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease are at an increased risk of this condition, and the presence of other kidney conditions such as glomerulonephritis or polycystic kidney disease can also increase the risk of chronic kidney disease. Patients in the earliest stages of this condition may not have any symptoms at all. As the condition progresses, patients might notice a loss of appetite, skin itching, muscle twitches, sleep disturbances, and declines in mental sharpness. Nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, and fatigue may be present, and patients who have hypertension could find it becomes more difficult to control.
Patients with diabetes and other conditions that increase the likelihood of developing chronic kidney disease will typically have their kidney function monitored with urine and blood tests at their regular checkups. If chronic kidney disease is suspected, doctors may perform an ultrasound of the kidneys to check their size and structure. Many cases of chronic kidney disease are not curable, and treatment focuses on slowing the progression of the condition. Doctors usually prescribe medication to control blood pressure, reduce cholesterol, and protect the bones. Some patients may be advised to restrict their dietary protein intake to minimize the amount of waste that must be filtered by the kidneys. In the most advanced stages of chronic kidney disease, patients will need to begin dialysis, and a kidney transplant may be recommended.
Uncover more types of kidney disease now.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic condition that causes clusters of cysts to form on the kidneys. As the cysts grow, they can reduce kidney function, and this may eventually result in kidney failure. Patients could have polycystic kidney disease for many years without realizing it. When symptoms do appear, they could include headaches, pain in the back or side, hypertension, blood in the urine, and an increase in abdominal size. Patients might also have kidney infections or kidney stones, and urinary tract infections may occur.
Ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRI scans are the primary methods used in the diagnosis of this condition. Patients are normally treated with medication to reduce blood pressure, and prescription pain relievers may be prescribed for those in severe pain. Surgery can sometimes be used to remove very large cysts that are causing pain, and patients who have blood in their urine as a result of this disease will be advised to drink plenty of water to dilute their urine.
Get more details on the various types of kidney disease now.
Diabetic Nephropathy

Diabetic nephropathy is a gradual loss of kidney function that can develop as a complication of type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Roughly twenty-five percent of diabetes patients will eventually develop this condition. Risk factors for diabetic nephropathy include poor control of blood glucose or cholesterol, hypertension, and tobacco use. To diagnose diabetic nephropathy, doctors will perform urine tests to check for high levels of protein, and blood tests will also be needed to provide more information about kidney function. CT and MRI scans help doctors assess blood flow within the kidneys, and patients might also need to have ultrasounds, renal analysis testing, or a kidney biopsy.
The most important steps in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy are to control blood glucose and hypertension. Prescription medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors may be necessary to reduce blood pressure, and patients may be asked to take statins to reduce cholesterol; these medications also reduce protein in the urine. In the advanced stages of diabetic nephropathy, patients will normally need to begin dialysis, and kidney transplants or kidney-pancreas transplants may be considered in certain cases.
Continue reading to reveal more types of kidney disease now.
Glomerulonephritis

Glomerulonephritis is a condition that causes inflammation in the glomeruli, small structures made of blood vessels. These structures are responsible for the proper filtration of the blood and the removal of excess fluids. Patients with acute glomerulonephritis could experience coughing due to an accumulation of fluid in the lungs, and they may also notice they are urinating less than usual. Urinary output may appear rusty due to the presence of blood. Individuals with chronic glomerulonephritis typically urinate more frequently than usual during the overnight hours, and their urine may appear foamy or bubbly as a result of excess protein. Abdominal pain, swelling of the face and ankles, and frequent nosebleeds could develop as well.
To diagnose glomerulonephritis, doctors generally rely on blood and urine tests, ultrasounds, and CT scans. Some patients may need to have immunology testing, chest x-rays, or an intravenous pyelogram, and a kidney biopsy could be necessary to confirm the presence of this condition. If a patient's glomerulonephritis is caused by an autoimmune condition, corticosteroids or plasmapheresis may be used as treatment options. Individuals with chronic glomerulonephritis are often prescribed diuretics to reduce swelling, and dietary changes to reduce protein, salt, and potassium will be recommended. These patients need to carefully monitor their fluid intake too.
Read more about the various types of kidney disease now.
Kidney Stones
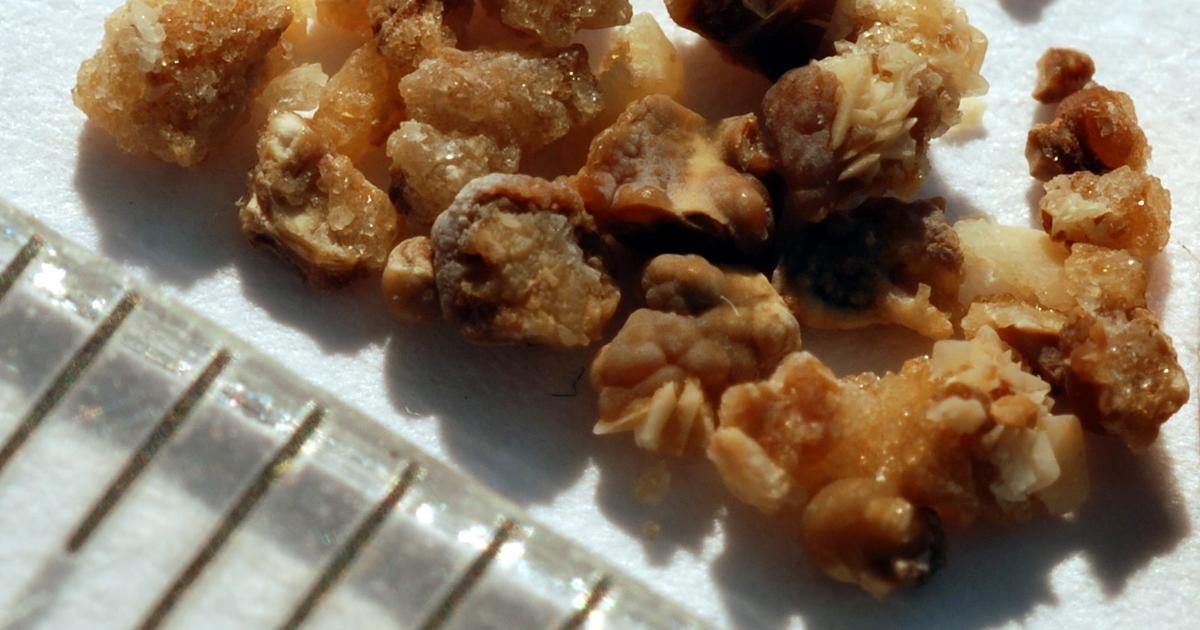

Kidney stones are hard deposits made up of minerals and salts. The stones can form inside the kidneys as a result of dehydration, kidney infections, and changes in diet or hormone levels. Patients with kidney stones often experience severe pain in the back and side of the abdomen, and they may also have blood or pus in the urine. Some individuals could develop a fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting, and urinary output may be reduced. Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, and hyperparathyroid conditions are associated with an increased risk of kidney stones, and patients who have had a gastric bypass operation also have an elevated risk.
Kidney stones can be detected with ultrasounds, and doctors may also perform CT scans, blood and urine tests, and an intravenous or retrograde pyelogram. If kidney stones are discovered, they may need to be treated in the hospital. A lithotripsy procedure can be performed to break up large stones, and doctors may choose to surgically remove them using percutaneous nephrolithotomy. This operation is used if a kidney stone is causing an obstruction, and it is also appropriate in cases where kidney stones are causing unmanageable pain.