Guide To The Prevention And Treatment Of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Plasma Exchange
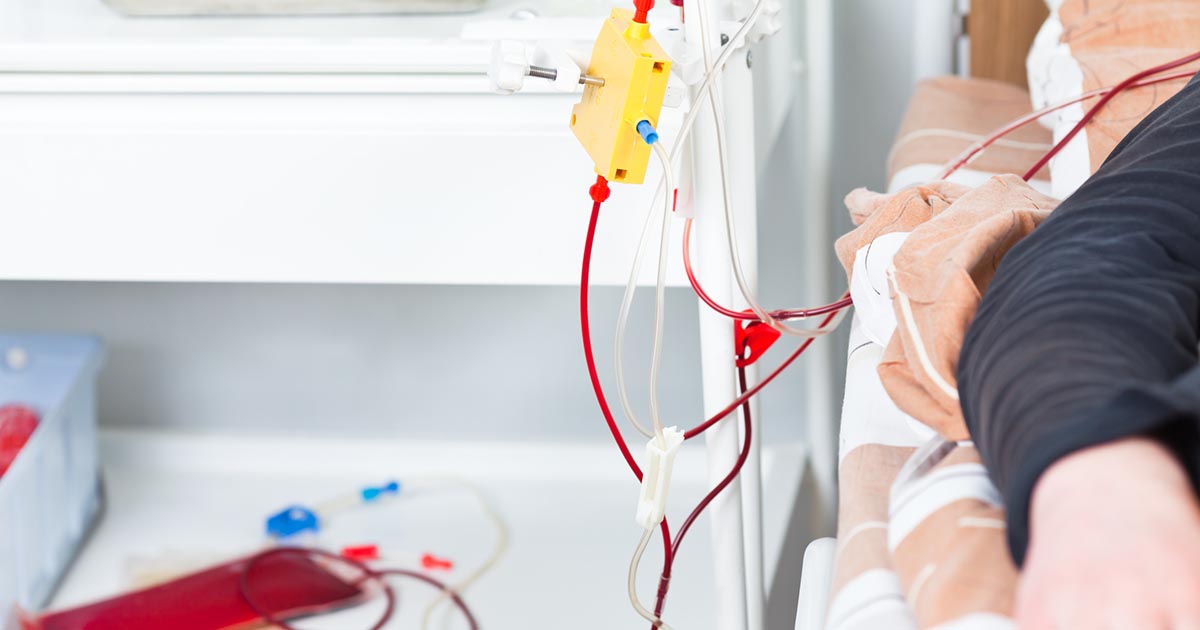
Plasma exchange is a method of cleaning the blood similar to dialysis. Also called plasmapheresis, this procedure involves replacing the patient's plasma with plasma from a donor. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood, and it contains proteins and nutrients that are crucial for overall health. To perform a plasma exchange, a nurse will insert two intravenous lines, one in each arm. The patient's blood will flow out of one of the lines and into a machine. The machine separates the patient's plasma from the rest of the blood cells, and the separated plasma is mixed with donor plasma. This mixture is then sent back into the patient's body through the second intravenous line. The treatment can take between two to four hours, and patients may need treatment two or three times each week for several weeks. While receiving treatment, the patient may have a lower than normal blood pressure, and nurses will carefully monitor this.