Breast Cancer Causes And Health Effects
Ionizing Radiation Exposure
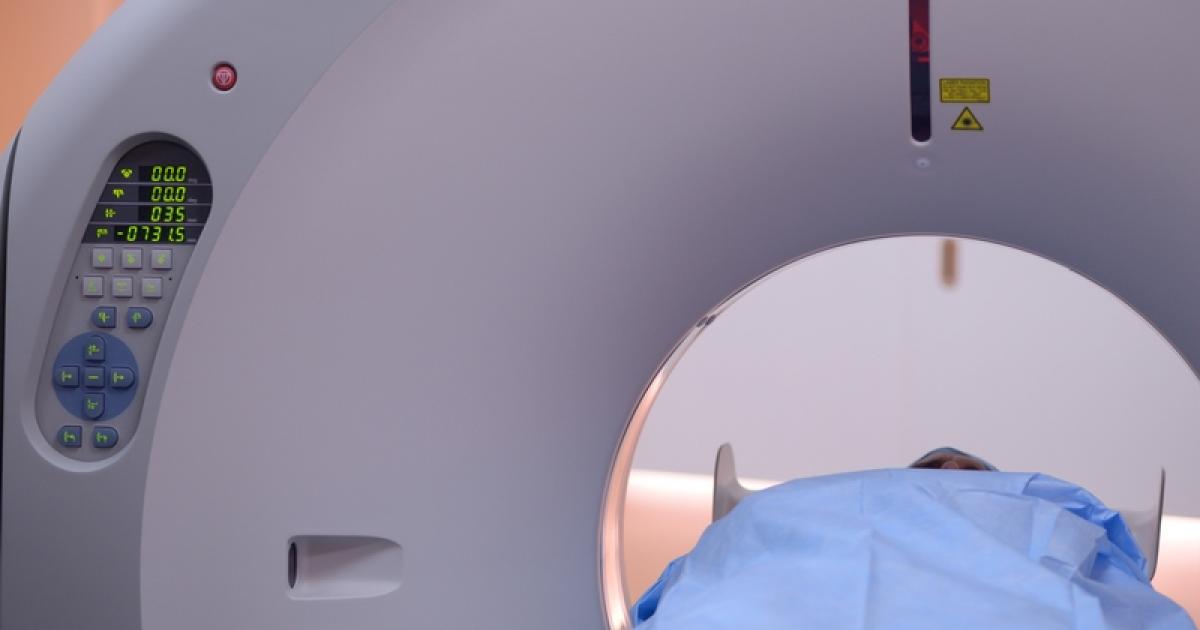
Breast cancer development in some individuals can be caused by ionizing radiation exposure. Ionizing radiation is a form of radiation with energy levels that have the ability to extract an electron from a molecule or atom. This electron extraction results in an ionized form of the atom or molecule. Ionizing radiation exists in the forms of x-rays, radon, neutrons, gamma rays, alpha particles, and beta particles. Nuclear power plant accidents and the testing or use of atomic weapons are sources of exposure to this type of high-energy radiation. Exposure to ionizing radiation may also come from specific medical imaging and treatment therapy procedures when they are administered frequently. These procedures include computed tomography (CT) scans, chest x-rays, positron emission tomography (PET) scans, and radiation therapy treatment. While breast cancer derived from ionizing radiation exposure from these factors is relatively rare, enough exposure to this type of radiation can cause significant cell damage that may result in widespread mutations of cellular DNA. If these mutations occur in the right section of a breast cell's DNA, breast cancer can develop.
Next, discover how genetics and breast cancer are closely related.