Guide To Chemotherapy Side Effects
Increased Ease Of Bruising And Bleeding
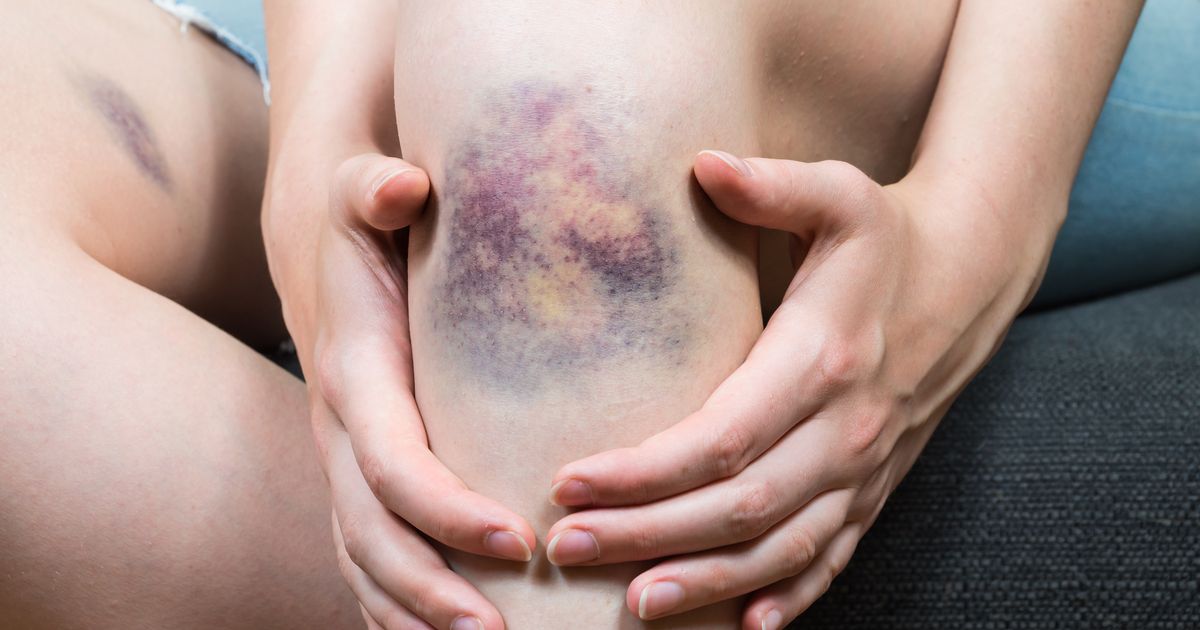
Drugs used in chemotherapy can cause a patient to experience increased ease of bruising and bleeding. The extent of a healthy individual's bruising and or bleeding with an injury is dictated by the components in their blood referred to as platelets. Platelets are responsible for sticking together and forming the blood clots in the body that stop an individual from losing too much blood, both internally and externally. Platelets are formed in bone marrow, a spongy substance that fills the hollow core of the bones and produces all blood components. Chemotherapy destroys a large number of platelets and platelet forming cells, which can cause a patient's total platelet count to decrease. Decreased platelets mean the body is not able to stop internal or external bleeding as effectively as it should. A patient with low platelets due to chemotherapy treatment may bleed and bruise easily with a small insignificant bump or injury due to this mechanism. Chemotherapy can also cause these side effects through poor nutrition in an affected individual because vitamin K is required for the blood to clot properly.
Learn about more potential side effects of chemotherapy now.