The Main Differences Between Angina Attacks & Heart Attacks
What Causes A Heart Attack?
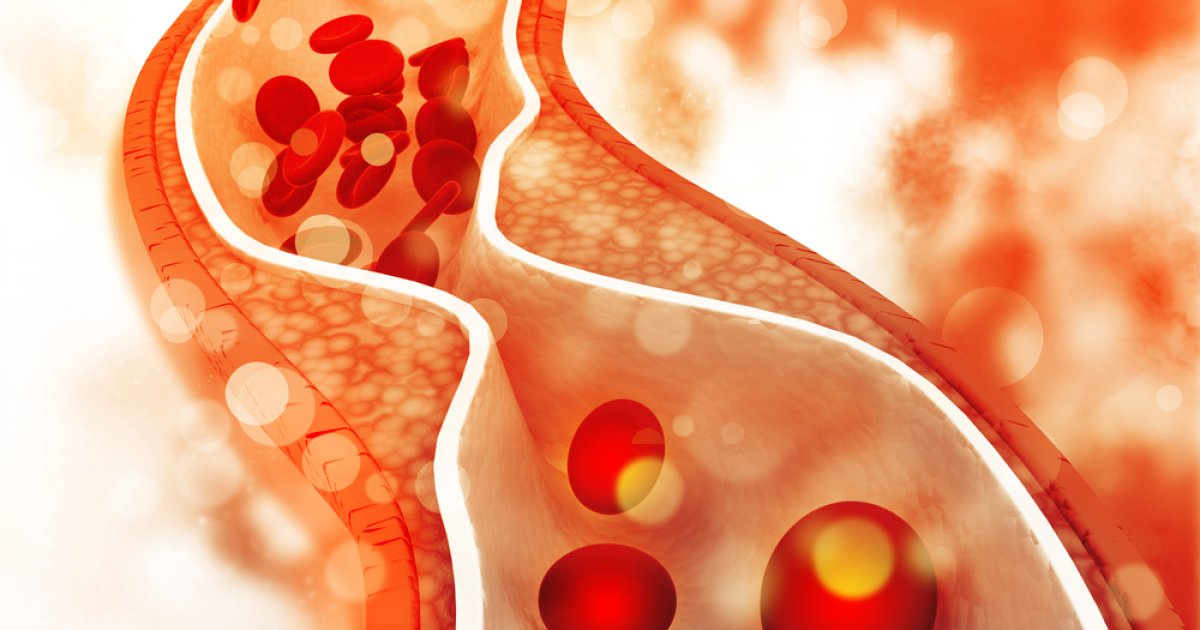
A heart attack, also called a myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of blood to one or more of the coronary arteries becomes blocked due to fat, cholesterol, and other substances that form plaque and thus clog the arteries. The plaque eventually breaks away from the buildup and forms a clot, which interrupts blood flow through the arteries and leads to damage to parts of the heart muscle. A coronary artery can narrow from the buildup of multiple substances, such as cholesterol, which results in coronary artery disease, the most common cause of a heart attack.
During a heart attack, one of these plaques may rupture and spill cholesterol into the bloodstream, where a blood clot forms at the site of the rupture. If the blood clot is big enough, it can block the flow of blood through the coronary artery, resulting in the heart starving for oxygen and nutrients. Another cause of a heart attack is a spasm of the coronary artery that stops the flow of blood to a part of the heart.
Next, learn about one of the most common differences between angina pain and heart attacks.