Causes Of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Ependymomas
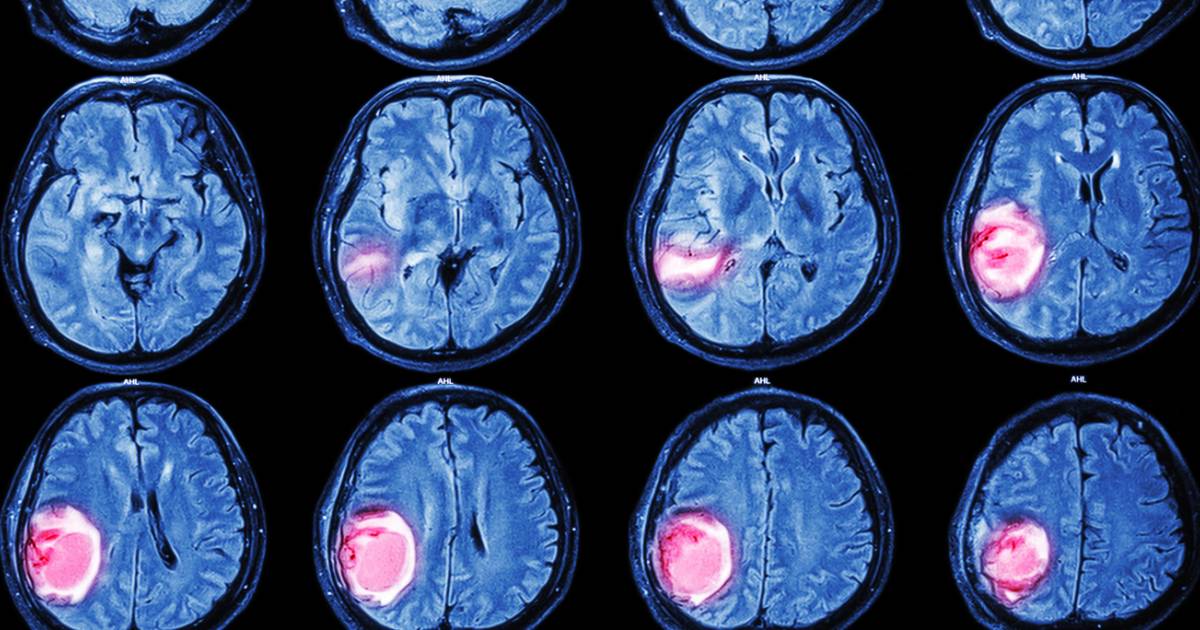
Ependymomas are tumors that develop in the ependymal cells of the brain and spinal cord. Although children and babies count for most cases of ependymomas, these tumors can affect adults as well. With childhood ependymoma, the tumor is usually found in the brain and can cause the skull size to become enlarged. Adults, conversely, are more likely to have the tumor developed in the spinal cord. Furthermore, victims can experience headaches, vomiting, nausea, weakness in the legs, seizures, irritation, and vision loss with the tumors. As of now, it isn't known what causes the tumors to form. Males have a higher possibility of developing them than females.
Ependymomas, classified as Grade II ependymal tumors, happen the most frequently of all types which also include subependymomas and myxopapillary (Grade I) with analestic versions (Grade III). In overall terms, they are rather uncommon with two hundred cases reported annually in the United States.