Common Causes And Risk Factors Of A Pneumothorax
Mechanical Ventilation
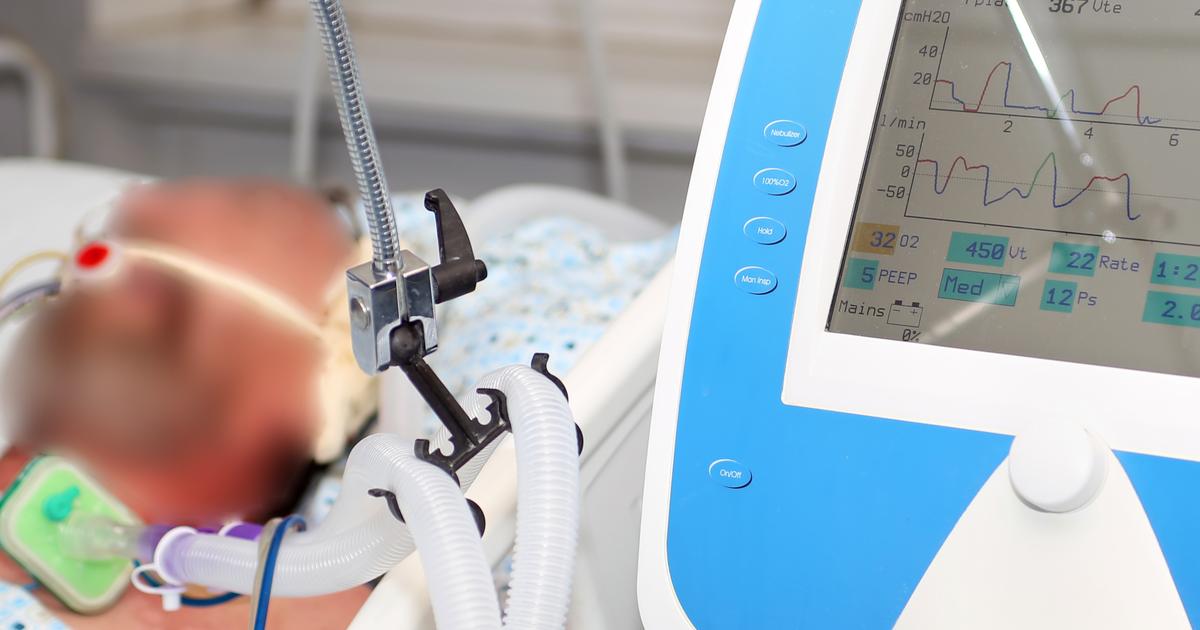
Mechanical ventilation, also known as assisted breathing, is a type of life support treatment. This form of ventilation breathes for the patient when they cannot breathe unaided. Mechanical ventilation is typically provided in intensive care units, and it helps transport oxygen into the lungs and the rest of the body. Before being placed on a ventilator, a doctor must place a tube into the patient's windpipe, a process known as intubation. Ventilation does not cause pain, and patients are carefully monitored while they undergo assisted breathing. Nurses and other medical staff will frequently check the patient's blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen saturation. Sometimes, however, the use of mechanical ventilation may create an imbalance in the air pressure inside the chest. This could trigger a severe type of pneumothorax that results in the complete collapse of the lung. To reduce the risk of this issue, most patients on ventilators are given periodic chest x-rays, which enable doctors to detect this complication and provide appropriate treatment.
Get more details on what can result in a pneumothorax now.