Histoplasmosis: Complications And Prevention
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
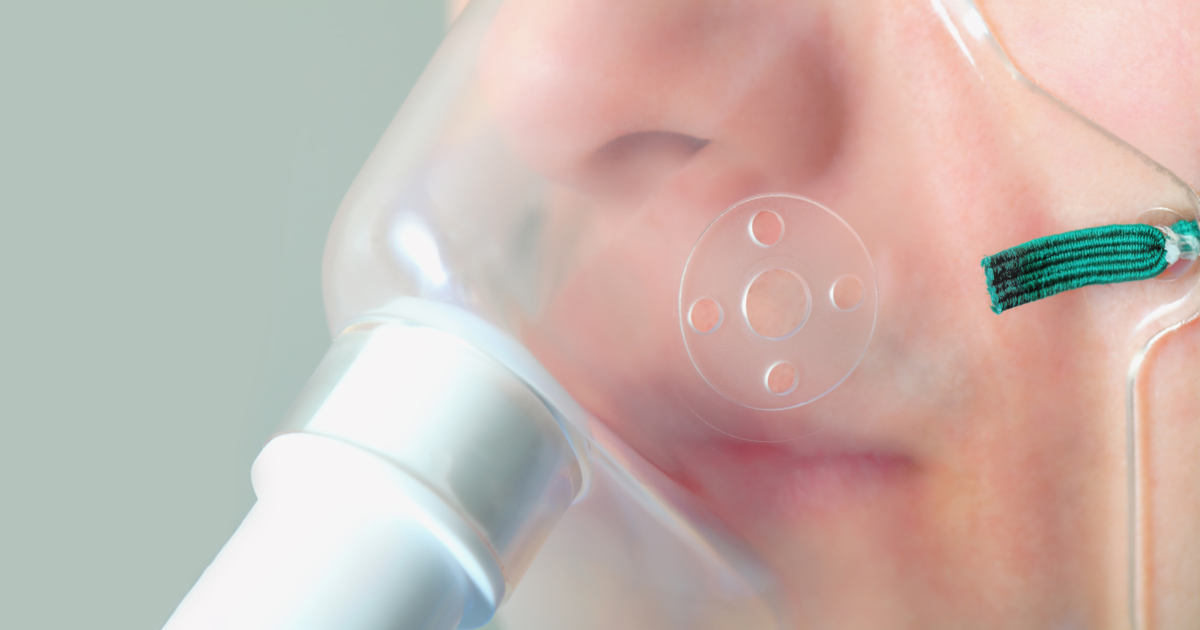
Acute respiratory distress syndrome may occur if histoplasmosis causes significant lung damage. Considered a form of respiratory failure, symptoms of acute respiratory distress syndrome often include shortness of breath, a blue tinge to the skin, and rapid breathing. These symptoms are produced when the lungs fill with fluid, resulting in low oxygen levels and making breathing nearly impossible. Doctors can diagnose acute respiratory distress syndrome with a physical examination, blood tests, and a chest x-ray. The syndrome requires emergency treatment in the hospital, where patients are provided with oxygen, and staff may also try to get the patient to lie face down on the hospital bed. Known as prone positioning, this is believed to improve the body's oxygen levels. If necessary, patients can be placed on a ventilator to help them breathe. The ventilator delivers oxygen into the patient's trachea, and patients may need to be sedated while on the ventilator. Some patients will also be given diuretics to reduce the amount of fluid accumulation in the lungs. In severe cases, doctors may try to use extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) as a treatment option. This complex procedure involves removing blood from the body and pumping it through a device that adds oxygen and takes out carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood is then returned to the patient.
Uncover more potential complications of histoplasmosis now.