Signs Of Hypophosphatasia
Hypophosphatasia is a rare, inherited disease most commonly found in Caucasian populations. It affects the development of teeth and bones by interrupting the mineralization process. This process involves calcium and phosphorous absorbing into newly growing bones and is essential for proper development. There are different degrees of hypophosphatasia, ranging in severity from premature loss of baby teeth to death. The most devastating cases happen in infancy. Children with the disease may have bowed legs, an irregular skull shape, and are typically shorter. Reveal more of the warning signs of hypophosphatasia now.
Skeletal Abnormalities Similar To Rickets
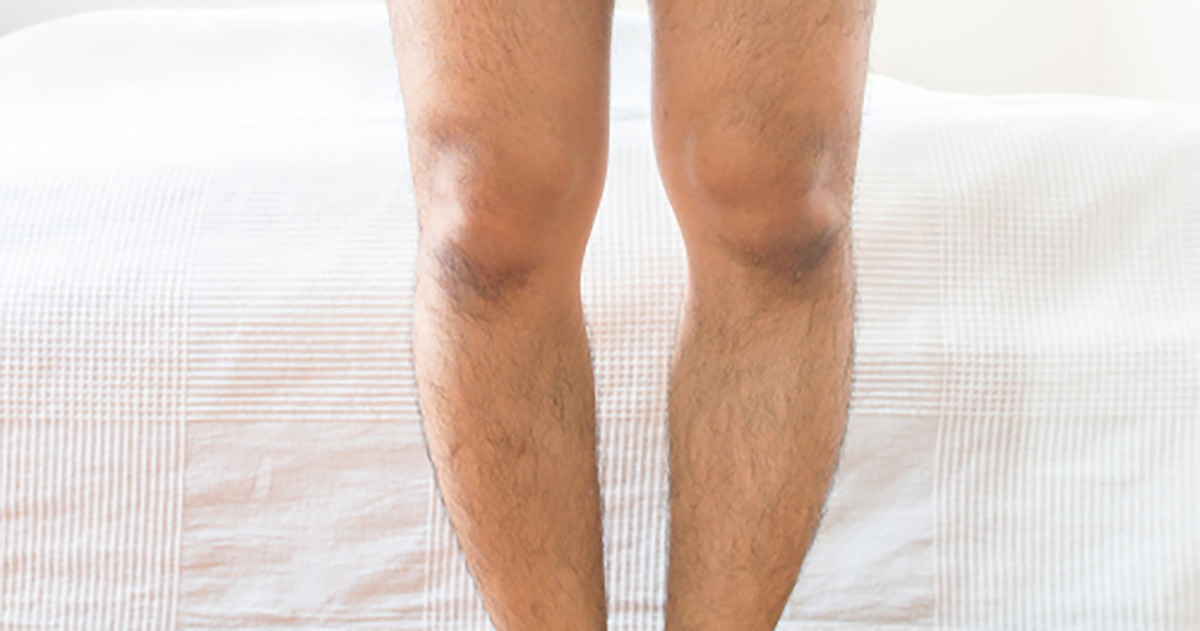
Hypophosphatasia causes similar skeletal deformities as seen with rickets, which is a disease caused by a lack of vitamin D, and affects developing bones in infants and small children. These skeletal deformities include lumps in the ribcage, a protrusion of the sternum, and pelvic deformities. A common deformity is an irregularly shaped skull; resulting in pressure on the brain. Spine deformities include scoliosis, an irregular curve to the spine, and kyphosis, a hunched back. Pain and tenderness can be felt in the spine, legs, arms, and pelvis. Muscles are usually not as well developed and are prone to cramping. Individuals suffering from this disease tend to be shorter and grow to less than five feet tall.
Keep reading for more symptoms of hypophosphatasia now.