Guide To The Locations And Types Of Spinal Cord Injuries
Thoracic Spinal Cord Injuries
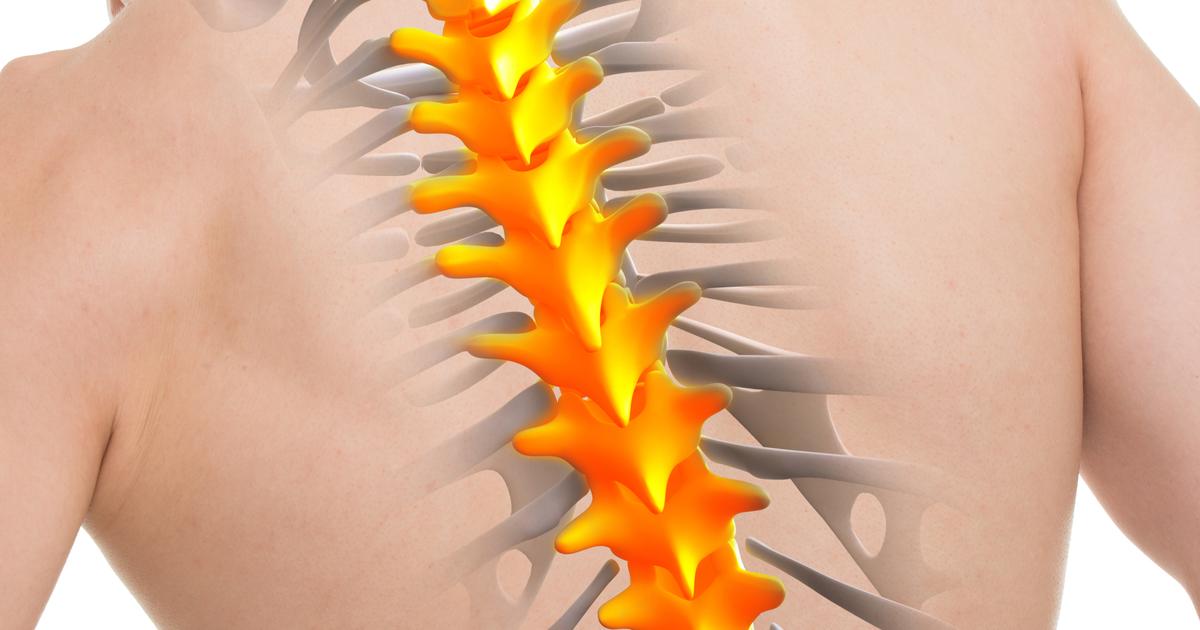
When an individual incurs damage to the region of their spinal cord that runs through and controls their abdominal muscles, mid-back, and upper chest, it is referred to as a thoracic spinal cord injury. The thoracic spine contains twelve levels of vertebrae that house the thoracic spinal cord. Injuries that occur in an individual between the T1 and T5 levels affect the nerves controlling the muscles that help them breathe, the abdominal muscles, and the muscles that move the diaphragm, lungs, and ribcage. Individuals who have a thoracic spinal cord injury at the levels between T6 and T12 experience effects in the muscles responsible for posture, balance, and coughing. Injuries at the T1 to T5 levels typically result in paraplegia but leave the arms and hands with functionality. Injuries that occur between the T6 and T12 levels also result in paraplegia but impair the patient's control of their bladder and bowel. Most individuals affected by a thoracic spinal cord injury will keep normal movement ability in their upper body, arms, and hands. These individuals do require the use of a manual wheelchair but may be able to stand with special assistive equipment.