Symptoms Of Meningioma
A meningioma is a relatively common type of tumor that occurs in the meninges, or the membrane surrounding the spinal cord and brain. About twenty-seven percent of all primary brain tumors are meningiomas. While frightening, the vast majority of meningiomas are benign and grow very slowly. Meningiomas rarely spread to other parts of the body, though depending on the location, a meningioma can grow quite large before causing noticeable symptoms. Meningiomas are most common among women and individuals between forty and seventy. The symptoms of meningioma will depend largely on the size and location of the tumor. Some patients have no signs at all while others develop classic symptoms of a brain tumor. Because of this, some meningioma diagnoses are only made when an MRI or CT scan is ordered for something else.
Get to know some of the symptoms now.
Vision Changes
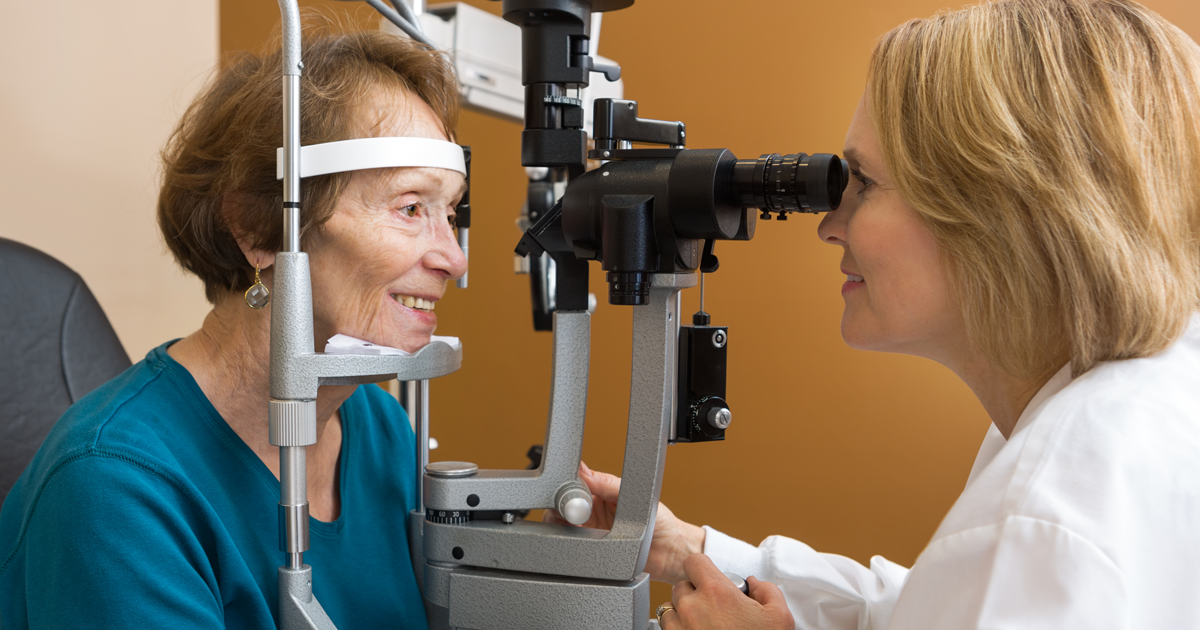
Vision problems are most common with certain forms of meningioma, including sphenoid wing meningioma, located on the base of the skull behind the eyes (twenty percent of all meningiomas), and suprasellar meningioma, positioned at the base of the skull near the optic nerve and pituitary gland. Vision symptoms are prevalent with intraorbital meningioma in which the meningioma develops on the optic nerve sheath. These three forms of meningioma can compress the optic nerve and cause high pressure in the eyes.
Vision changes associated with a tumor that compresses the optic nerve can include loss of peripheral vision, an increasingly large blind spot, double vision, and blurred vision. Some patients even develop blindness as the meningioma grows.
Continue reading to get to know the next primary symptom of meningioma.