Guide To Serious Nervous System Disorders
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
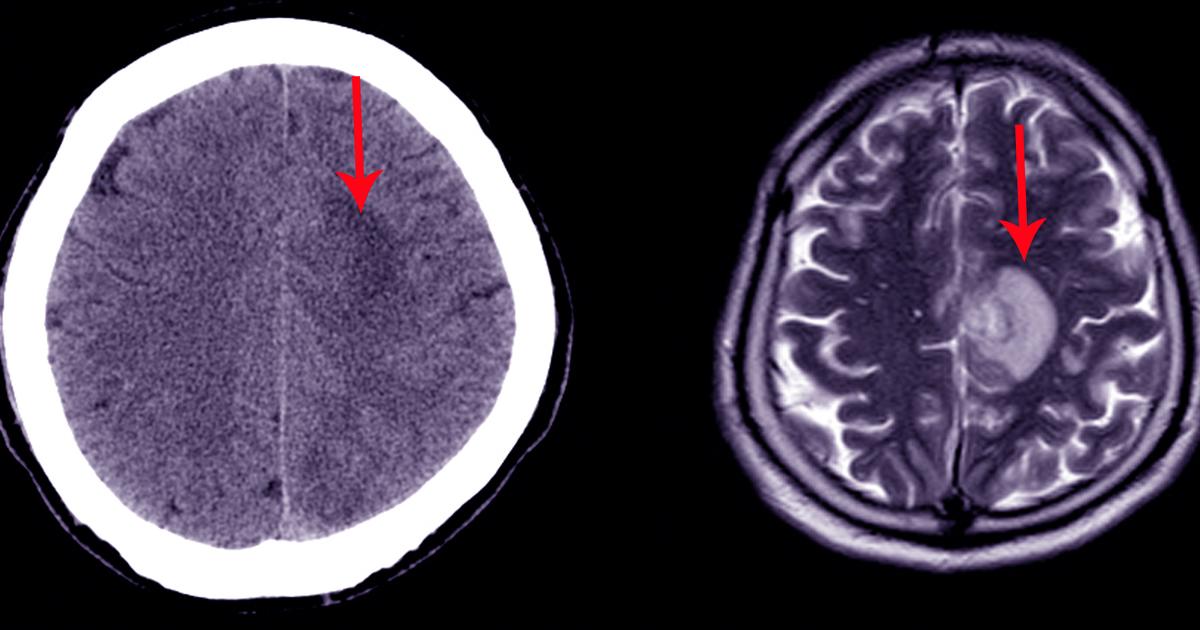
A subarachnoid hemorrhage develops when there is bleeding in the subarachnoid space, the area between the brain and the membrane surrounding it. The hemorrhage has a sudden onset, and the first symptom is usually a severe headache that may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Patients experiencing a hemorrhage might briefly lose consciousness. In some cases, a popping sensation in the head may be felt just before the hemorrhage begins, and seizures, confusion, and numbness throughout the entire body could occur. Serious head injuries such as falls and injuries from car accidents could lead to a subarachnoid hemorrhage, and they can be caused by blood thinners or an underlying medical condition such as an arteriovenous malformation. This condition is considered a medical emergency, and emergency medical services should be called immediately. At the hospital, doctors will perform a physical examination, and CT scans, MRI scans, and a cerebral angiography test may be performed as well. Surgical procedures will be carried out to reduce the buildup of pressure in the brain and to stop the bleeding.