What Increases The Risk Of Calciphylaxis?
Blood-Clotting Abnormalities
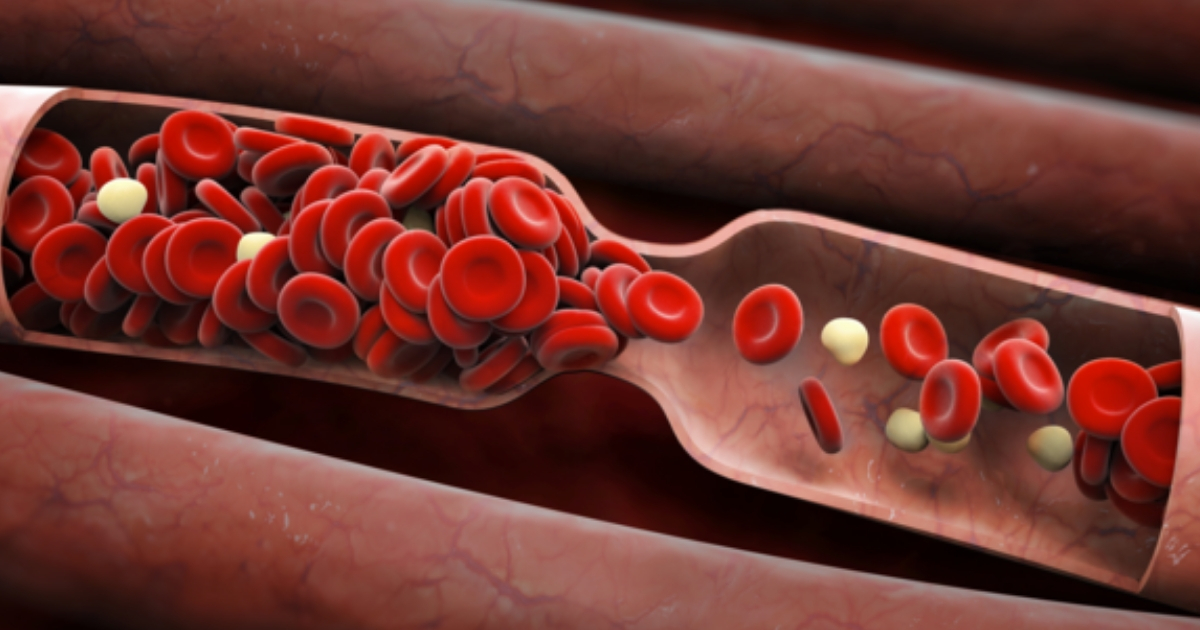
Blood-clotting abnormalities are disorders where the platelets or cell fragments within the blood responsible for clotting do not work properly. The platelets can either clot too much, or they can be scarce enough to where they are unable to form clots properly. Disorders that involve excessive clotting are the type of clotting abnormalities that can increase an individual's risk for developing calciphylaxis. This category of clotting disorders is generally referred to as hypercoagulation disorders. These disorders can be a result of several factors, including the presence of protein C deficiency, combined thrombophilia, and lupus anticoagulant. All three of these factors cause platelets to stick to each other and other tissues when they should not be. The prevalent presence of thrombophilia and lupus anticoagulant in the blood of individuals who have calciphylaxis suggests patients with hypercoagulation problems are more likely to develop the disease. The exact chemical mechanism that occurs in individuals with hypercoagulation that results in the development of calciphylaxis is not clear.