What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Compartment Syndrome?
Swelling And Tightness
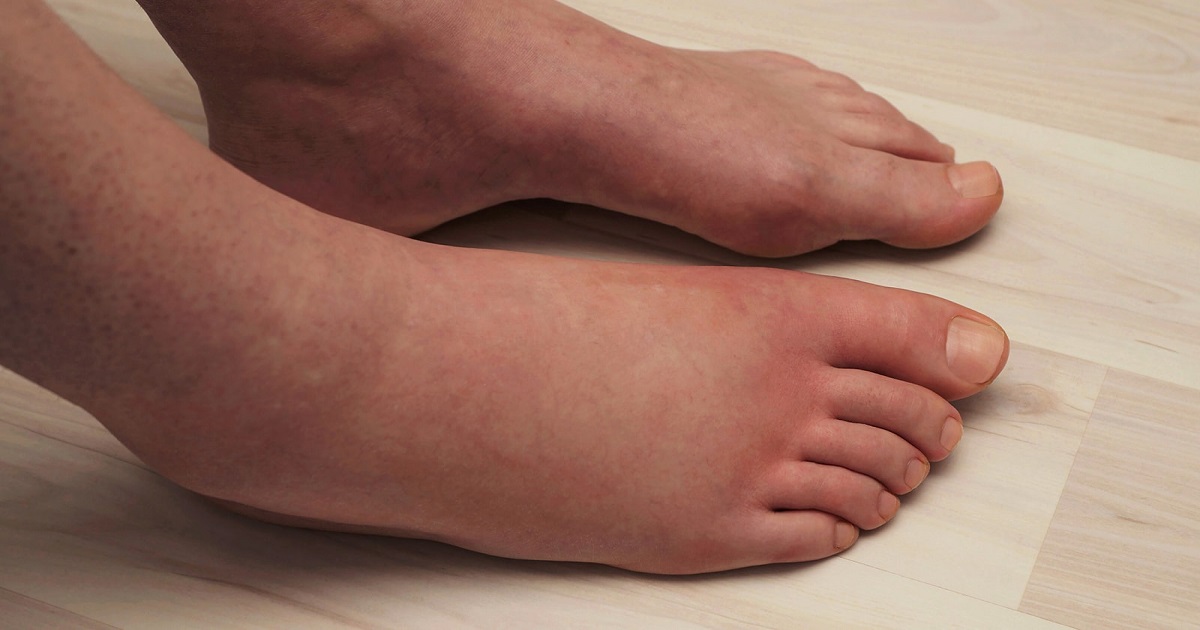
Individuals affected by compartment syndrome commonly experience swelling and tightness in the affected region of the body. Mechanically, compartment syndrome involves the displacement of a fluid or other substance in the tissues inside the fascia that cause it to be unable to hold its volume at a reasonable pressure level. There is a marked increase in the amount of physical matter contained inside the fascia membrane in compartment syndrome patients. The displacement of matter causes the structures inside the fascia to compress against each other, resulting in the surrounding nerves sending this information to the brain. The brain interprets this nerve information and results in the patient feeling a sensation of tightness in the affected area. Swelling occurs when the immune system responds to an infection, foreign body, or cellular damage and injury. There is an increased volume of blood that rushes to the site because the blood vessels expand and allow for this. There is also easier permeability of the vessel walls that causes fluid leakage into the surrounding tissues. Because of these mechanisms that occur inside and around the affected fascia in compartment syndrome, the affected area will appear swollen.
Learn more about complications that can arise due to compartment syndrome now.