The Most Common Types Of Colon Polyps And Polyp Disorders
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
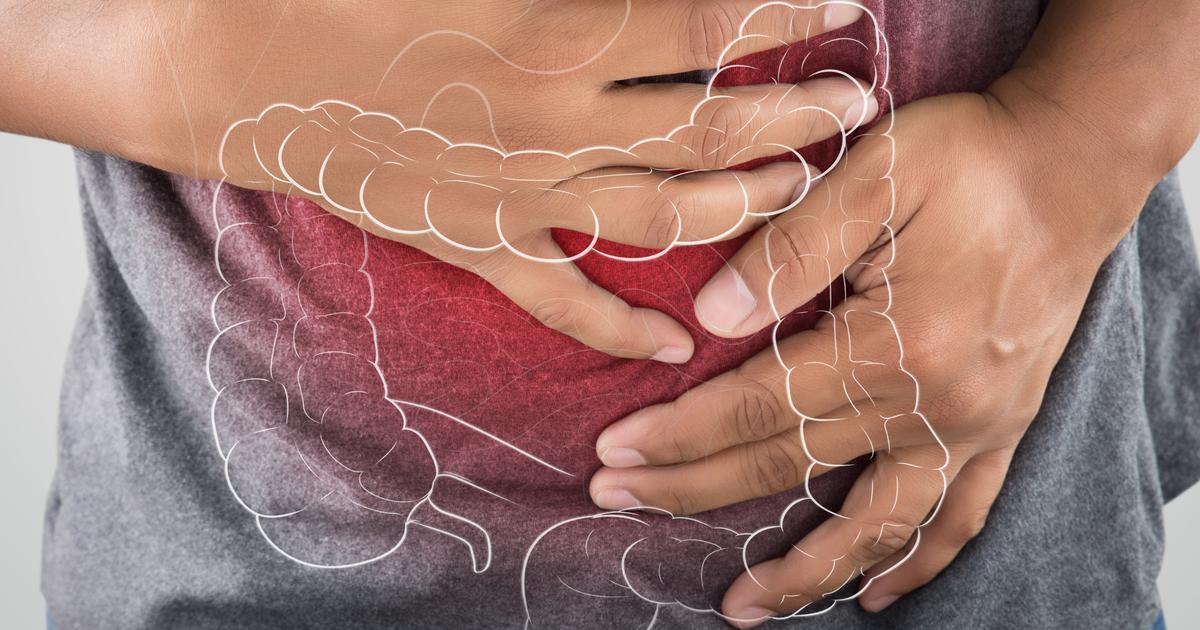
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition that affects the colon and rectum through the development of tissue masses or polyps. This condition can also cause the development of polyps in a patient's upper gastrointestinal tract and duodenum. Familial adenomatous polyposis is caused by a mutation that occurs in an individual's adenomatous polyposis coli gene or APC gene. The majority of patients inherit this mutation from their parents, but around a third experience the mutation spontaneously. When familial adenomatous polyposis is left untreated, an affected individual is expected to develop malignancy of the colon or rectum by the time they reach forty years old. This condition can result in benign skin tumors, benign pigment changes in the retina, anemia, dental abnormalities, desmoids, ampulla polyps, and polyps in the stomach lining. In rare cases, this condition can cause cancers of the adrenal glands, liver, thyroid gland, and central nervous system.
There is no way to cure familial adenomatous polyposis, but there are treatment options an individual can utilize to decrease the chance of developing cancer. Treatment may include the removal of all polyps in the colon, subtotal colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis, total proctocolectomy with a continent ileostomy, or total proctocolectomy with ileoanal anastomosis.
Continue reading to learn about more polyp disorders now.