Medical Consequences Of Childhood Obesity
Fatty Liver Disease
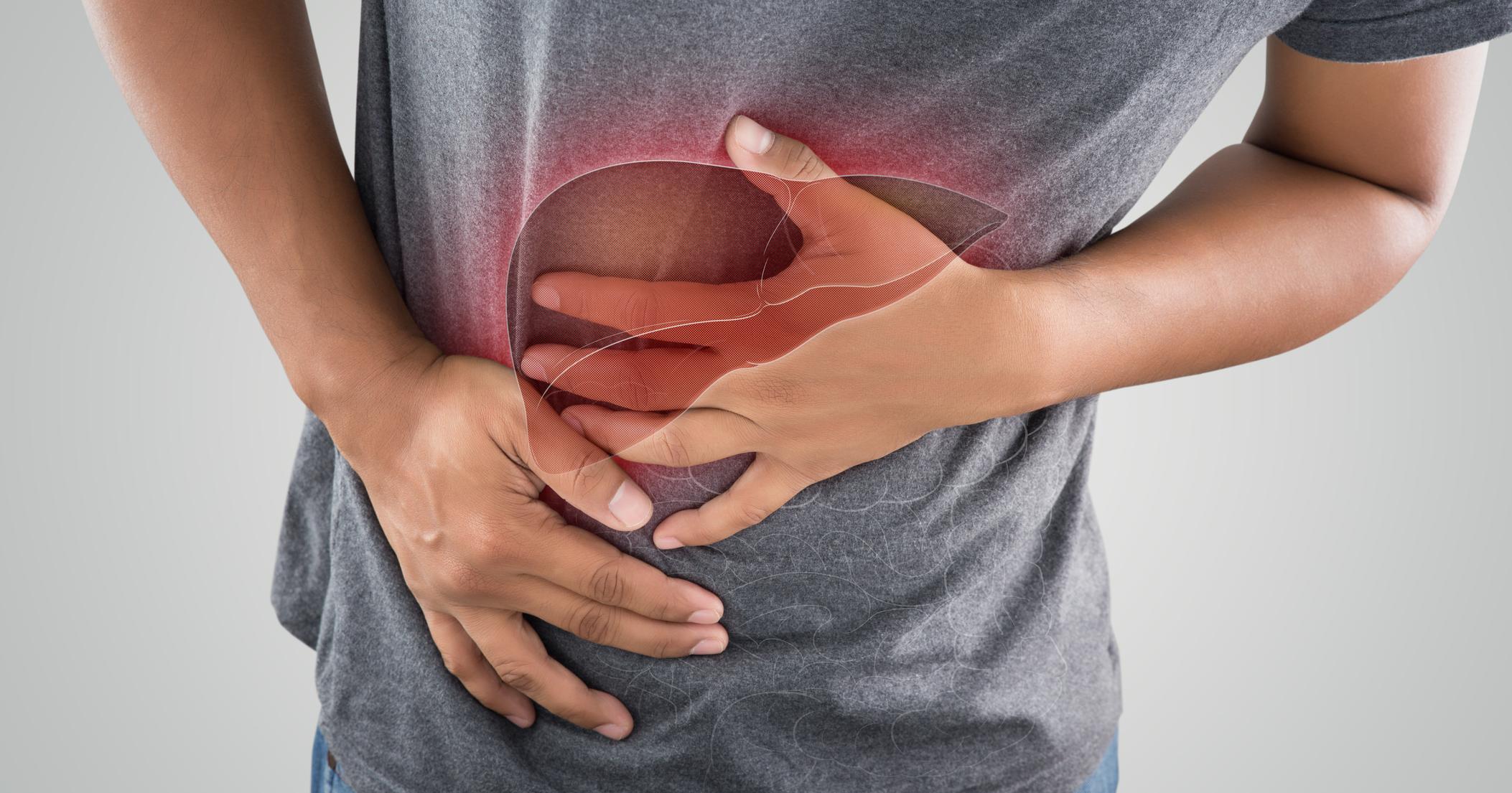
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is linked to obesity and insulin resistance. And with the prevalence of insulin resistance and obesity in children dramatically increasing, the pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disorder is on the rise. This condition is currently the most common chronic liver disease in kids.
This liver disorder is characterized by an uncharacteristic accumulation of fat in this organ. It does not have symptoms and is usually discovered by chance when hepatic steatosis is recognized during abdominal imaging. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is linked to elevations in levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, and aminotransferases. Ultimately, this disorder may eventually result in scarring and liver damage.
Obesity is among the most significant risks to children’s health today. Its prevalence is steadily rising, with the number of obese kids almost tripling over the past twenty-five years. Today, about fifteen percent of children between six and nineteen are obese. The great news, however, is there is something we can do to eradicate this epidemic. Weight loss interventions that work for younger patients are now available, and it is imperative to seek them.
Nevertheless, before you place your child on a diet, or enroll them into a weight loss program, it is best to first talk it over with your doctor. Together, you will formulate a plan of action to help your child and family.