Symptoms Of Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome
Indigestion
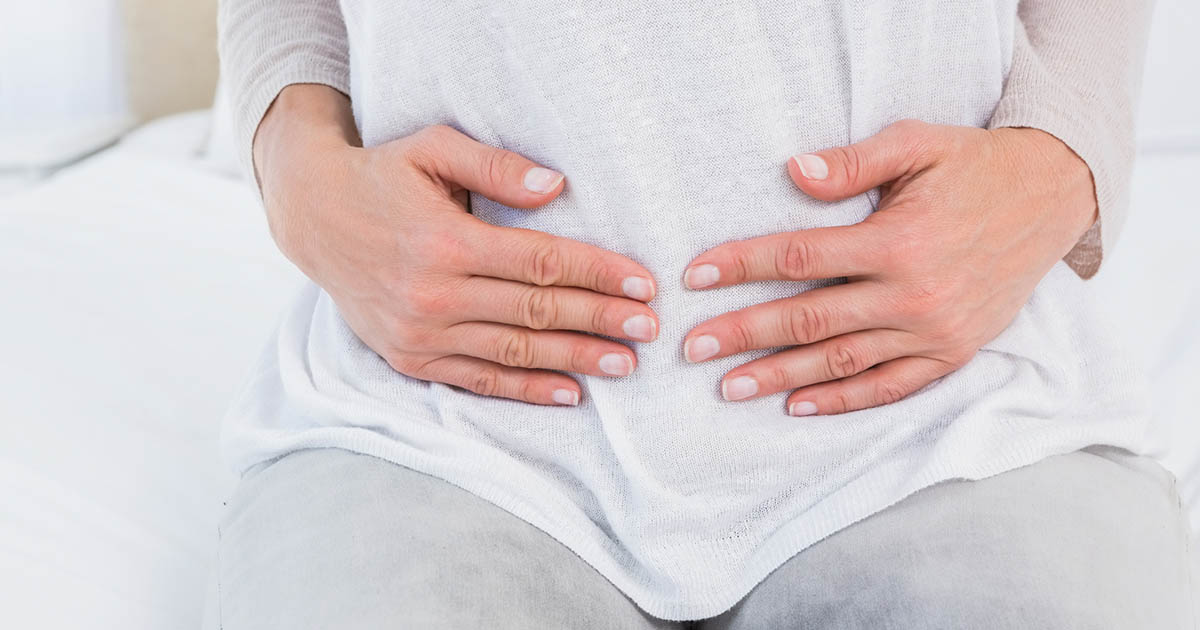
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome affects the lining of certain areas of the stomach. And like all autoimmune disorders, it is characterized by chronic inflammation, something that is never good for bodily tissues. APS can cause the immune system to target part of the gastric mucosa, specifically the parietal cells, resulting in frequent complaints of stomach pain and indigestion.
Complicating this symptom is the tendency for autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome patients to develop chronic candida infections of the mouth and esophagus. Because APS interferes with normal immune function, these patients do not have the same resistance to environmental pathogens, like yeast, that others do. As a result, the infection can take a toll on the esophagus, making reflux or indigestion more likely to occur.
Keep reading to discover even more symptoms of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome.