What Causes Kidney Pain?
Kidney Infection
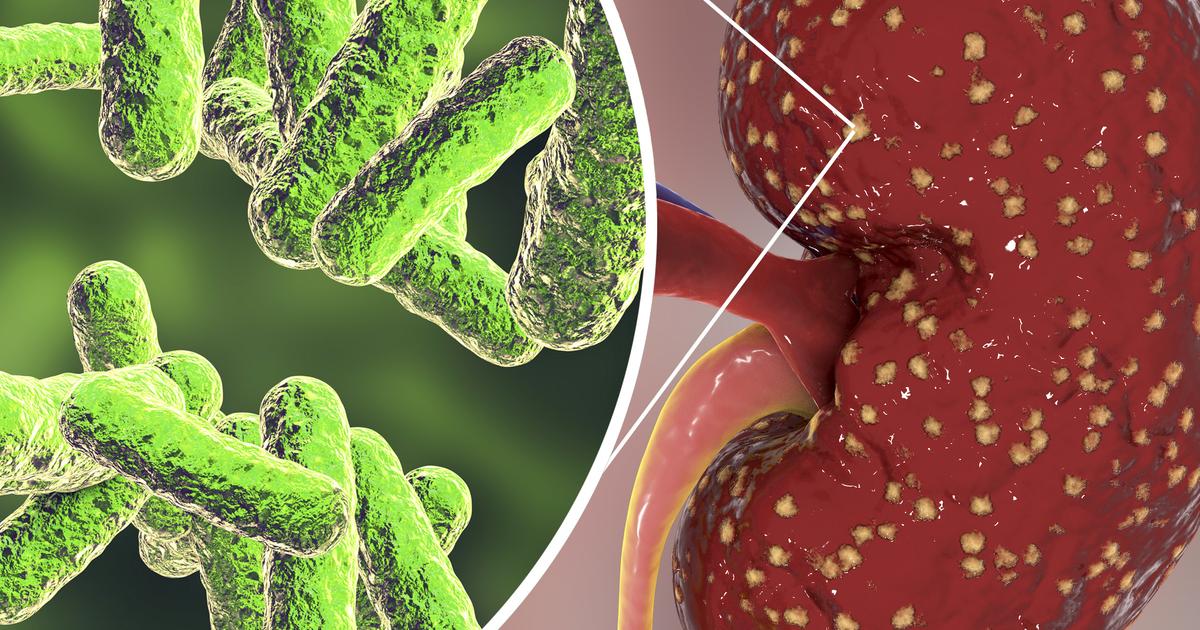
A kidney infection occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract, infect the bladder, move up the ureters, and colonize in the tissues of the kidney. Kidney infections can be caused by numerous factors that allow bacteria to enter the urinary tract and colonize, including female physiology, kidney stones, toilet hygiene, urinary catheter use, enlarged prostate, urethral irritation, and weakened immune system. Symptoms that occur in an individual who has a kidney infection include nausea, vomiting, groin pain, pain with urination, diarrhea, shivering, or kidney pain in the or side.
If a kidney infection is accompanied by a bladder infection, the patient will likely experience bloody urine, burning or stinging during urination, frequent urination, lower abdominal pain, cloudy urine, foul-smelling urine, and an inability to empty the bladder completely. A physician can determine if an individual's kidney pain is caused by a kidney infection through a physical exam, pelvic exam, and urinalysis. Pain from a kidney infection usually resolves within forty-eight hours of beginning treatment with antibiotics.
Learn about a serious kidney disease that can also mean kidney pain now.