Serious Side Effects Of Vasodilators
Fluid Retention
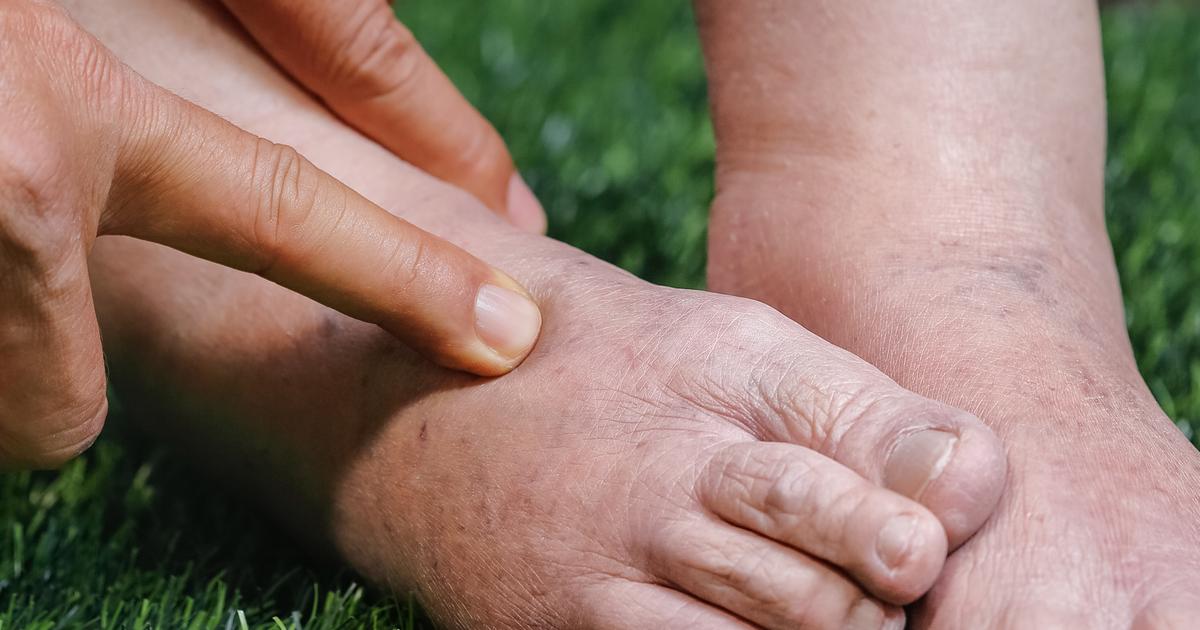
Individuals who take vasodilators may experience fluid retention, which refers to when the body accumulates excessive fluids in the body tissues outside of circulation as a result of some underlying mechanism. Vasodilators are medications that induce the dilation of blood vessels around the body. However, vasodilators do not only act upon the arteries, but they also have this effect on veins. When the veins dilate too much, the valves inside of the veins are unable to do their job as well to push blood against the force of gravity. The result is an excessive pooling of blood in the lower extremities because the blood becomes backed up. Backed up blood in the veins causes the pressure inside of the veins to become higher than the pressure outside of the veins in the surrounding tissues. When the pressure gradient is too high in the veins, they begin to leak fluid into the tissues that surround them as a compensatory measure. In addition, the walls of the veins become more penetrable when their walls are stretched out. This mechanism causes fluid retention in some patients who take vasodilators.
Uncover more side effects of vasodilators now.