Methods Of Treating And Preventing Molluscum Contagiosum
Curettage
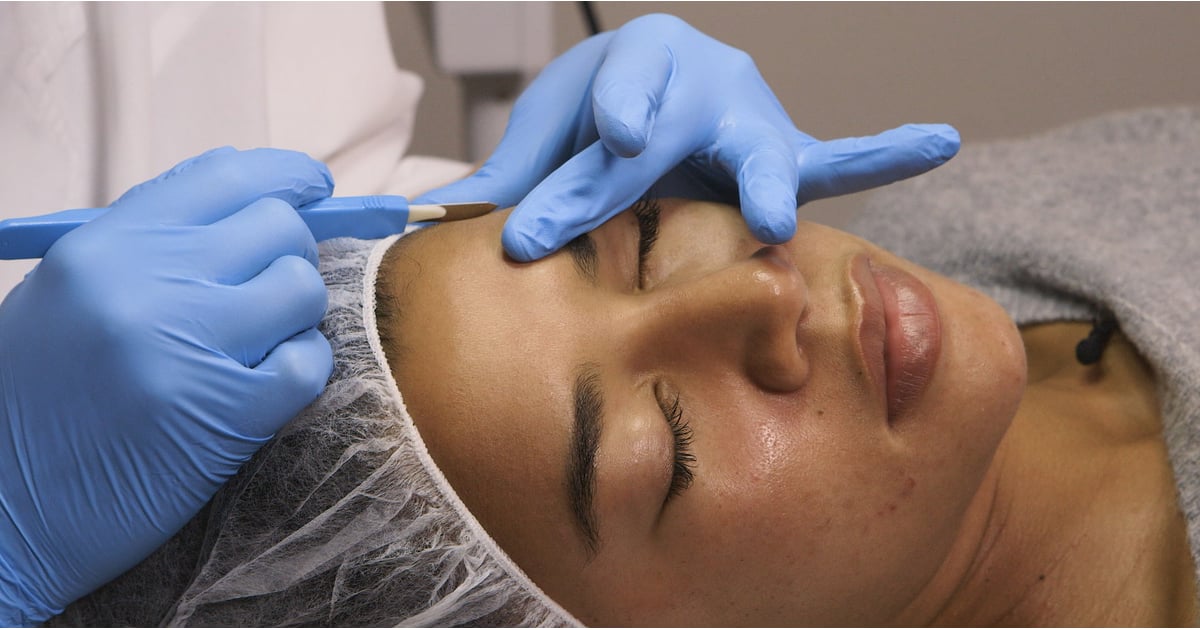
Curettage involves using a device known as a curette to physically remove skin lesions. The curette is shaped like a spoon, and dermatologists use it to pierce the center of each molluscum contagiosum bump. After piercing it, they then scrape away any fluid or other material inside the bump. Local anesthetic is normally used for this procedure, and sutures are not normally needed. Curettage can cause pain, swelling, redness, bleeding, crusting, and scarring at the treatment site. Generally, no recovery time is needed after the procedure, and patients can drive themselves home and resume all normal activities. The dermatologist will provide special aftercare instructions regarding how to clean and bandage the treated area, and patients typically return for a follow-up appointment within a week or two. Depending on the number of bumps involved, patients may need to have the procedure carried out at multiple appointments.