Nasty Skin Conditions That Are NOT Psoriasis
Impetigo
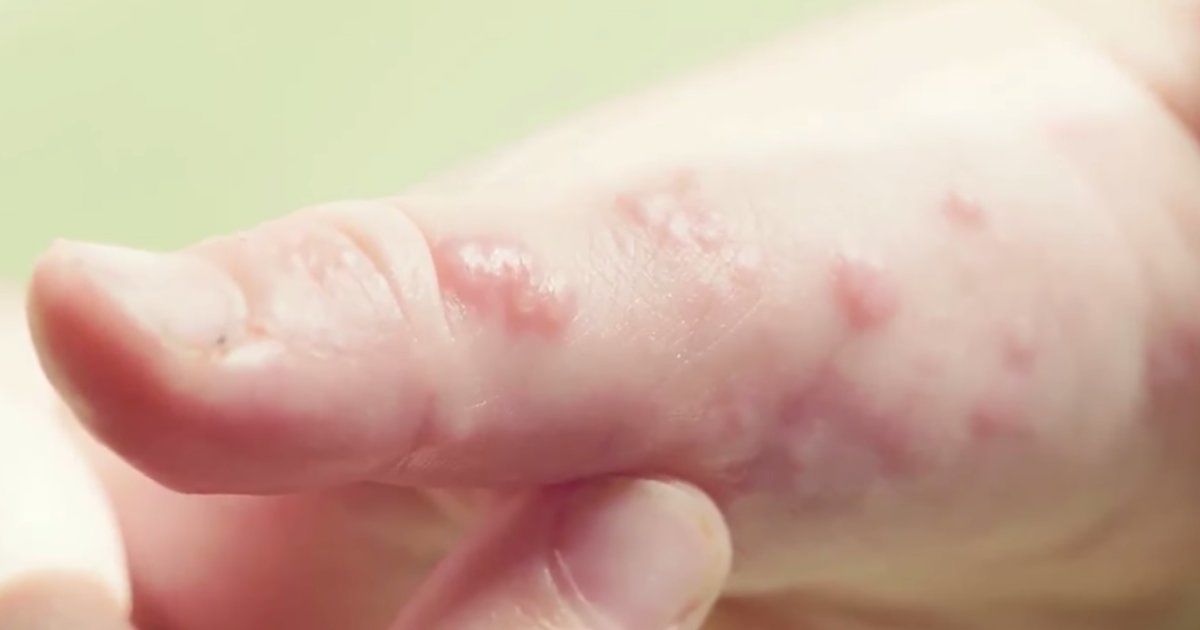
Impetigo is the most common bacterial skin infection in small children between two and five years old who live in Canada, northern Europe, and the northern United States. It is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
There are two main types of impetigo: bullous and nonbullous. The latter is the more common type and affects about seventy percent of patients. In most cases, the patient develops small red blisters around the nose or mouth. The blisters eventually burst, producing pus or fluid, and leave thick, golden-brown crusts behind that soon dry and heal. The blisters generally don’t hurt, but they can be quite itchy. It is essential to make sure the patient doesn’t scratch them, so they don’t spread the infection to others or other parts of their body.
Aureus typically causes the bullous type, which usually affects toddlers or even younger kids. The bacteria produce a toxin that attacks a protein that helps the skin’s layers stay together. The patient develops medium-sized or large blisters on their arms, legs, and around their diaper. The blisters don’t hurt, but they are itchy and red. They eventually burst, leave a yellowish crust, and soon heal. In addition to the blisters, the patient often has swollen glands and a high fever.