Common Side Effects Of Analgesics
Analgesic describes medications specially formulated for alleviating pain. Certain analgesics are available for purchase over-the-counter, while many are only available to buy with a prescription. Some analgesic medications blend two drugs in the analgesic class for enhanced relief. An individual has certain receptors on the cells in their spinal cord, brain, and gastrointestinal tract that help relay pain signals throughout the body. Analgesics work by taking advantage of these receptors and binding to them. This mechanism stops pain signals from reaching the brain. Analgesics are used in individuals who have moderate to severe chronic or acute pain. Analgesics are viable for individuals who cannot utilize nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because they do not produce gastrointestinal bleeding.
Of course, analgesics may produce adverse side effects in some individuals. Get the details on these now.
Upset Stomach
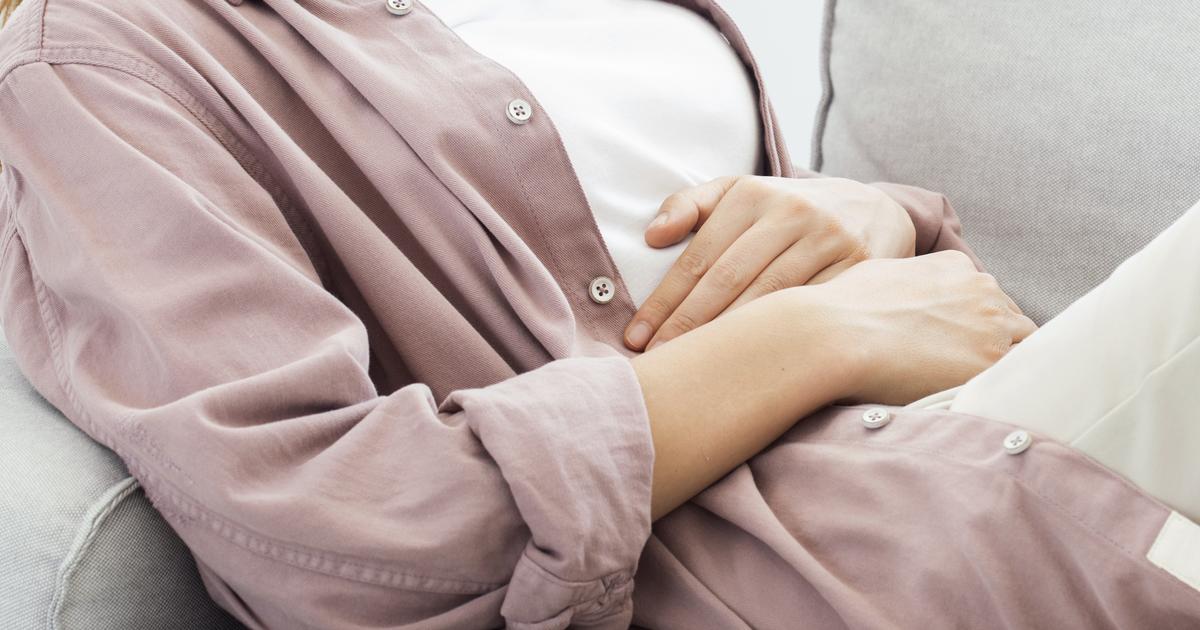

Some individuals who take acetaminophen or opioid-based analgesics may experience an upset stomach and nausea. An upset stomach is the result of the activity of the medication that involves the activation of the chemoreceptor trigger zone and the individual's gastric motility. The dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor zone are critical to the triggering mechanism that causes nausea and stomach upset. A decrease in gastric motility can cause food to back up in an individual's digestive system, allowing it to rot in the digestive organs and cause stomach upset. Some patients experience an increase in the sensitivity of their vestibular system, which manages balance. Increased vestibular sensitivity causes the affected individual to feel nausea and an upset stomach. Nausea and vomiting is a relatively common side effect of analgesics, and more so for those that combine acetaminophen with another medication.
Keep reading to learn more about the side effects of analgesics now.
Dry Mouth

Saliva in the oral cavity serves many different functions, including protecting the teeth from decay and stopping any disease from damaging the gums. Saliva does so by rinsing away corrosive acids, food, and bacteria from the mouth. Opioid-based analgesics have a depressive effect on the individual's nervous system. The part of the nervous system responsible for regulating the activity of an individual's glands is the autonomic nervous system. Opioids reduce the healthy activity of an individual's autonomic system, decreasing the amount of saliva the glands are told to produce. Less saliva in an individual's mouth causes them to experience dry mouth (xerostomia). This side effect may be less apparent in individuals who keep well hydrated, as fluids with a low sugar content can assume some of the functions of saliva.
Uncover more details on the side effects of analgesics now.
Constipation
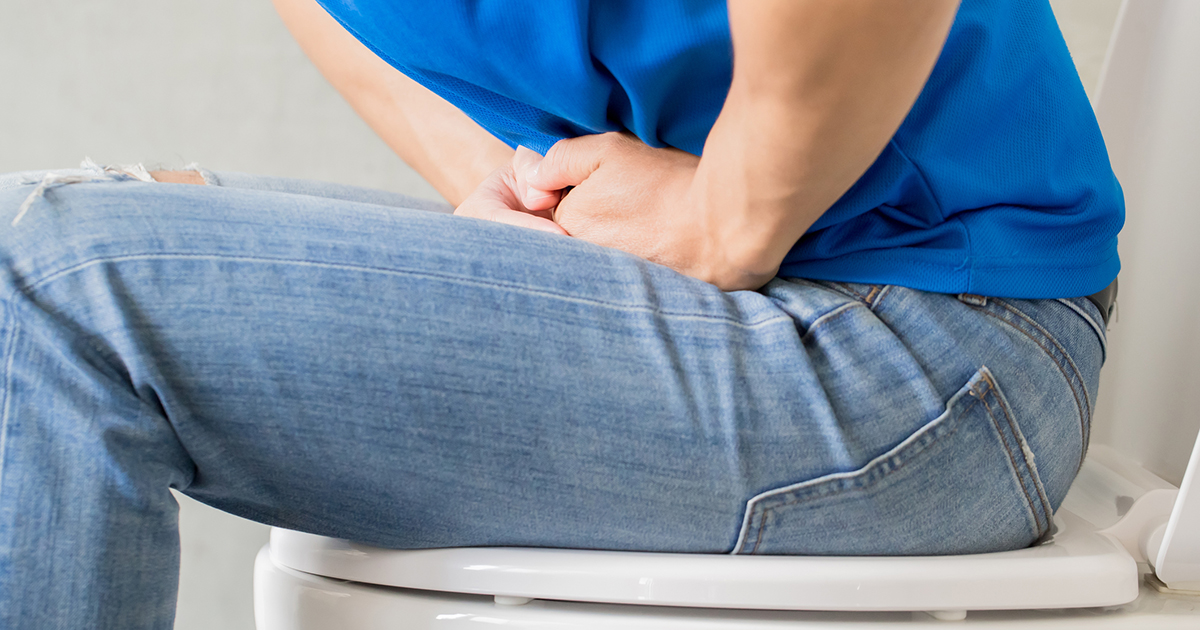

Constipation is one of the most common side effects that occur in individuals who take acetaminophen and opioid-based analgesics. The opioid receptors in an individual's digestive tract are very concentrated. When these receptors are activated by taking this medication, several mechanisms combine to produce constipation. First, the receptors cause healthy gastric emptying to become impaired in an affected individual, increasing the general amount of time food stays in the digestive tract. Next, the activation of these receptors causes a decrease in mucous secretions in the gastrointestinal tract, causing higher resistance against the food that moves through it. Furthermore, the activation of the opioid receptors in the digestive tract causes an increase in the reabsorption of fluid from the food, making stool dry and hard. Most individuals who use analgesics for longer than a couple of weeks typically need to take additional medication to manage this side effect.
Read more about analgesic side effects now.
Fatigue
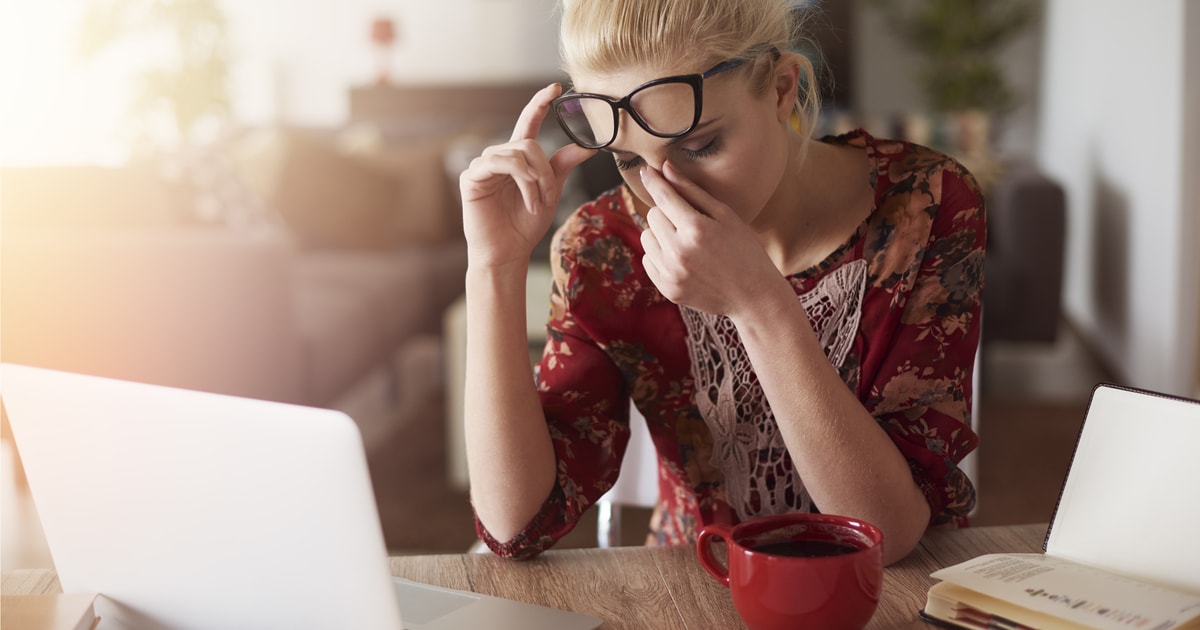

Fatigue describes a state in which an individual has a reduced amount of energy and decreased general efficiency. Fatigue is a relatively common side effect in individuals who take acetaminophen and analgesics that contain opioids. Opioids reduce the amount of pain an individual feels by stopping the pain signals from reaching the brain. However, the medication has to have a suppressive effect on the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems to implicate that mechanism in the body. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for multiple functions the body performs subconsciously. By depressing these functions in the autonomic and central nervous systems, the processes that dictate an individual's alertness and energy are also depressed. Fatigue may be persistent with the use of this type of medication, or it may dissipate as the individual's body adapts to the effects of the medication on their nervous system.
Learn more about side effects linked to analgesics now.
Rash Or Itching
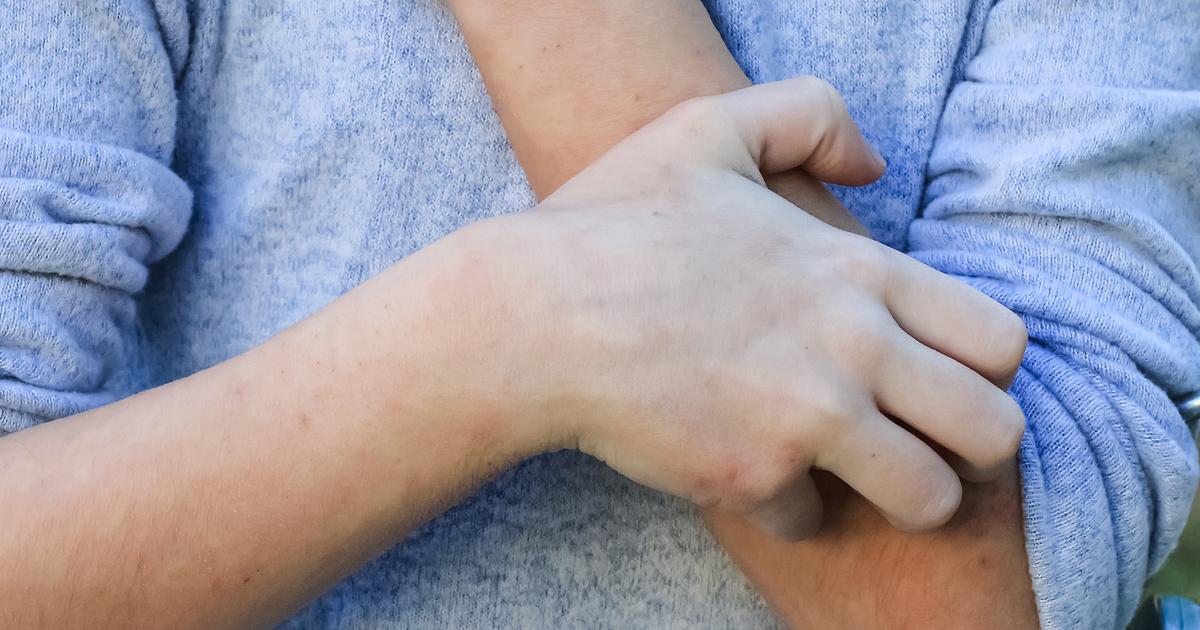
Some individuals who utilize acetaminophen and opioid-based analgesics may experience the development of a rash or itching. The first thought when it comes to itching and a rash with the use of any drug is an allergic reaction. However, this type of allergic reaction tends to be exceedingly rare with opioid-based analgesics. The mechanism more commonly responsible for this adverse side effect is called a pseudoallergy or a hypersensitivity reaction. Psuedo-allergic reactions tend to only occur upon the first use of the drug, where a true allergic reaction requires individuals to have taken it multiple times. The reason this hypersensitivity occurs is because some of the opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord responsible for pain signaling the medication binds itself to can also trigger itching sensations. Similar to other adverse side effects of analgesics, a rash or itching may be persistent or dissipate as the individual's body adjusts to it over numerous regular doses.